by Scott Lafee, University of California – San Diego Credit: CC0 Public Domain Writing in the July 12, 2021, online issue of Nature Communications, researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine describe a new approach that uses machine learning to hunt for disease targets and then predicts whether a drug is likely...
Category: <span>Artificial Intelligence</span>
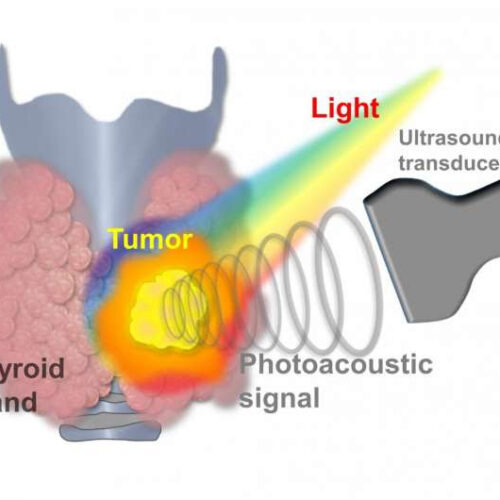
Thyroid cancer now diagnosed with AI photoacoustic/ultrasound imaging
by Pohang University of Science & Technology A schematic diagram of acquiring the photoacoustic signal generated when laser light is irradiated to a malignant thyroid nodule with an ultrasonic sensor. Credit: POSTECH A lump in the thyroid gland is called a thyroid nodule, and 5-10% of all thyroid nodules are diagnosed as thyroid cancer. Thyroid...
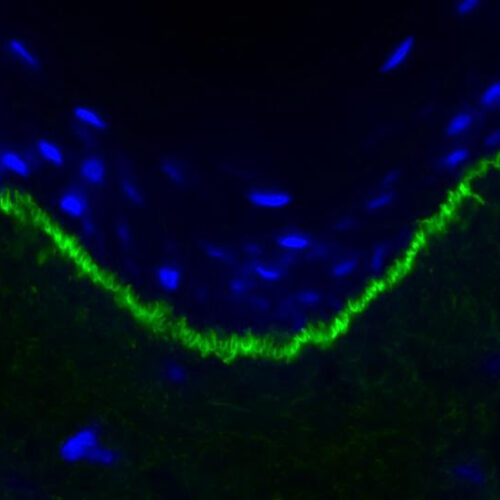
Artificial intelligence provides faster diagnosis for debilitating blistering disease
UNIVERSITY OF GRONINGEN IMAGE: THIS PICTURE OF A MICROSCOPIC SLIDE SHOWS THE U-SHAPED PATTERN (IN GREEN) VISIBLE IN THE SKIN BIOPSY OF AN EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA ACQUISITA PATIENT. CREDIT: UMCG/UNIVERSITY OF GRONINGEN Scientists at the University of Groningen have trained an Artificial Intelligence system to recognize a specific pattern in skin biopsies of patients with the...
Artificial intelligence predicts brain age from EEG signals recorded during sleep studies
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF SLEEP MEDICINE DARIEN, IL – A study shows that a deep neural network model can accurately predict the brain age of healthy patients based on electroencephalogram data recorded during an overnight sleep study, and EEG-predicted brain age indices display unique characteristics within populations with different diseases. The study found that the model...
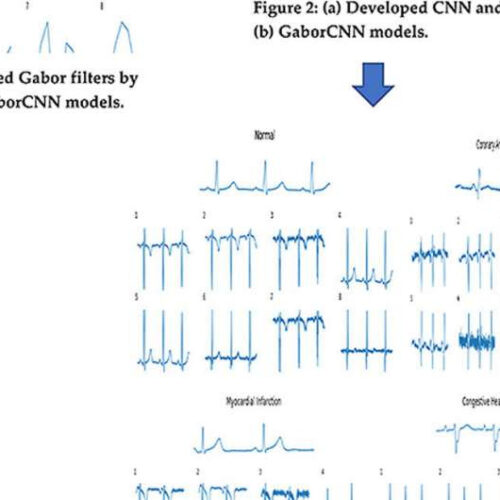
New artificial intelligence tool could speed up diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases
by Nanyang Technological University An abstract of how Gabor-CNN was used to train the diagnostic tool to recognize patterns in patients’ ECGs by inputting examples of ECG signals that reflect cardiovascular diseases. Credit: NTU Singapore A team of researchers from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Ngee Ann Polytechnic, Singapore (NP), and the National Heart Centre...
AI outperforms humans in creating cancer treatments, but do doctors trust it?
by University Health Network Credit: CC0 Public Domain The impact of deploying Artificial Intelligence (AI) for radiation cancer therapy in a real-world clinical setting has been tested by Princess Margaret researchers in a unique study involving physicians and their patients. A team of researchers directly compared physician evaluations of radiation treatments generated by an AI machine learning (ML) algorithm to conventional radiation...
The robot smiled back
COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE IMAGE: The Robot Smiles Back: Eva mimics human facial expressions in real-time from a living stream camera. The entire system is learned without human labels. Eva learns two essential capabilities: 1) anticipating what itself would look like if it were making an observed facial expression, known as...
New AI technology protects privacy
TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF MUNICH (TUM) IMAGE: PD DR. RICKMER BRAREN (L.) UND PROF. DANIEL RUECKERT (R.) EXPLORING DIAGNOSTIC POSSIBILITIES USING ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR MEDICAL IMAGE DATA. CREDIT: ANDREAS HEDDERGOTT / TUM Digital medicine is opening up entirely new possibilities. For example, it can detect tumors at an early stage. But the effectiveness of new AI...
Artificial Intelligence is making cancer vaccines closer to reality
Imagine if you could get vaccinated for cancer. You would just get a shot or a couple of shots and your immune system would learn how to recognize and kill cancer. This sci-fi-sounding idea is not that far from reality. Especially now that scientists at the University of Waterloo have employed machine learning to identify...
Trial demonstrates early AI-guided detection of heart disease in routine practice
by Mayo Clinic Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Heart disease can take a number of forms, but some types of heart disease, such as asymptomatic low ejection fraction, can be hard to recognize, especially in the early stages when treatment would be most effective. The ECG AI-Guided Screening for Low Ejection Fraction, or EAGLE, trial set out to...