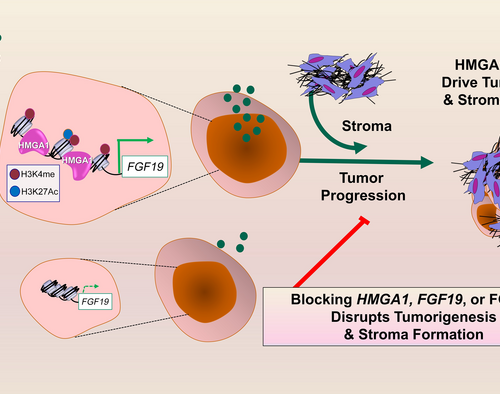
JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE IMAGE: THE HIGH MOBILITY GROUP A1 (HMGA1) PROTEIN FUNCTIONS AS A “MOLECULAR SWITCH” THAT “FLIPS ON” EXPRESSION AND SECRETION OF A CRITICAL GROWTH FACTOR, CALLED FGF19, IN PANCREATIC CANCER. TOGETHER WITH HMGA1, FGF19 PROMOTES TUMOR PROGRESSION AND FORMATION OF A DENSE WALL-LIKE STRUCTURE CALLED THE “STROMA”, WHICH PREVENTS THERAPY FROM REACHING TUMOR...
Category: <span>Cancer</span>
Drug combination restores ability of leading treatment to signal for death of blood cancer cells
by NYU Langone Health Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Despite the promise of new medications that promote cancer cell death in people with acute myeloid leukemia, leukemic cells often adopt features that let them evade the drugs’ effects within a year. Now, new research using human tissue samples and mouse models has found that resistance of leukemia cells to a widely...
Study suggests that maintaining normal vitamin D levels may benefit patients with advanced skin cancer
by Wiley Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain New research indicates that for patients with advanced skin cancer, it may be important to maintain normal vitamin D levels when receiving immunotherapy medications called immune checkpoint inhibitors. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society. Vitamin D has many effects on the body,...
Appropriate use criteria for lymphoscintigraphy in sentinel node mapping and lymphedema/lipedema
by Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) and 10 other professional societies have issued new appropriate use criteria (AUC) for lymphoscintigraphy in sentinel node mapping and lymphedema/lipedema. The criteria, summarized in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (JNM), include a list of relevant clinical...
Antibiotics after breast cancer linked to poorer survival, study finds
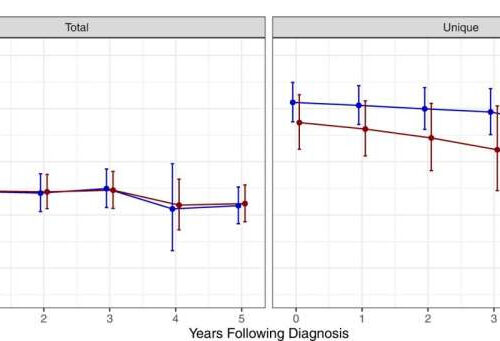
by Krista Conger, Stanford University Medical Center Landmarking analysis to evaluate the impact of antimicrobial exposure on survival over time on N = 772 independent patients. Data were presented as the hazard ratios ± 95% confidence intervals that reflect the risk of ongoing antimicrobial exposure at yearly intervals post-diagnosis and are plotted for the cumulative exposure definitions of total and...
Ultralow Dose of Nivolumab Offers Huge Cost Savings
M. Alexander Otto, PA, MMS January 18, 2023 A randomized clinical trial from India raises the possibility of huge cost savings by using much lower doses of immunotherapy. The researchers used just 6% of the recommended dose of nivolumab instead of the full dose in their treatment of patients with advanced head and neck cancer, and the addition of...
Tiny DNA circles are key drivers of cancer
Tiny circles of DNA harbor cancer-associated oncogenes and immunomodulatory genes promoting cancer development. They arise during transformation from pre-cancer to cancer, say Stanford Medicine-led team. Tiny circles of DNA that defy the accepted laws of genetics are key drivers of cancer formation, according to an international study led by researchers at Stanford Medicine. The circles called extrachromosomal...
Investigational drug may improve stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma patients
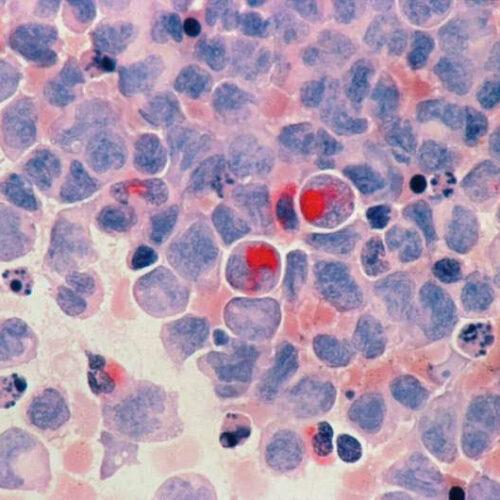
WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE IMAGE: SHOWN ARE MULTIPLE MYELOMA CELLS FROM A PATIENT. AN INTERNATIONAL PHASE 3 CLINICAL TRIAL LED BY WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE IN ST. LOUIS HAS SHOWN THAT THE INVESTIGATIONAL DRUG MOTIXAFORTIDE — WHEN COMBINED WITH THE STANDARD THERAPY FOR MOBILIZING STEM CELLS — SIGNIFICANTLY INCREASED THE NUMBER OF STEM...
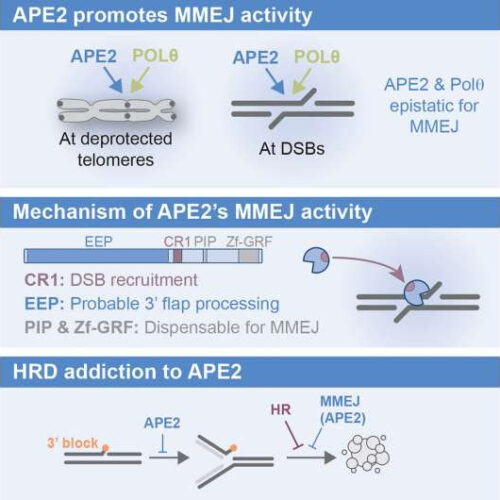
Researchers identify promising new target for drug-resistant breast and ovarian cancers
by Lisa Marshall, University of Colorado at Boulder Graphical abstract. Credit: Molecular Cell (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.03.017 CU Boulder researchers have discovered a protein’s crucial role in helping breast and ovarian tumors survive and thrive and have found that suppressing that protein kills cancer cells without harming healthy ones. The findings, published Tuesday, April 12, in the journal Molecular...
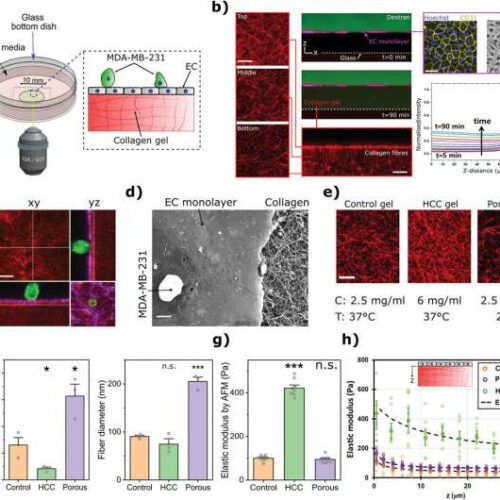
How cancer cells muscle their way into other organs
by University College London 3D Extravasation assay for probing mechanics of cancer cells, endothelium, and the underlying ECM. a) Schematic representation of the extravasation assay. b) Quantification of the permeability of the HUVECs monolayer (magenta) formed on top of a thin collagen substrate. The permeability was calculated by measuring the changes of 70 kDa dextran (green) intensity...