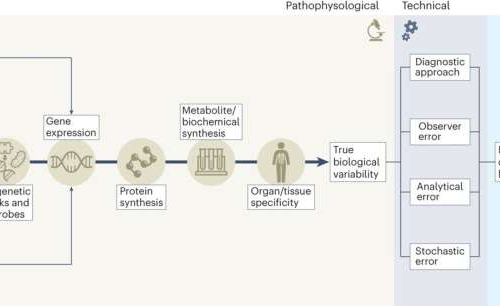
by Erin Digitale, Stanford University Sources of heterogeneity in diabetes. Credit: Nature Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41591-023-02502-5Diabetes can show up in almost anyone: pregnant women, babies, kids, teens, adults both young and old. But the condition’s various forms, all of which affect how the body processes blood sugar, can manifest quite differently in the hundreds of millions...
Category: <span>Diabetes</span>
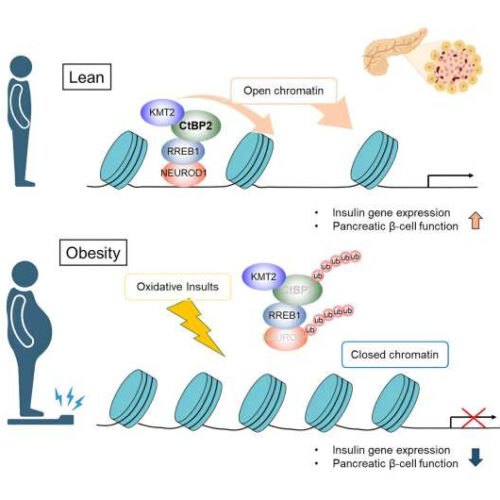
Unraveling the mechanism behind obesity-induced pancreatic β-cell dysfunction
by University of Tsukuba Credit: Cell Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112914 Obesity not only increases the risk of metabolic syndrome-related diseases, such as diabetes, fatty liver, and atherosclerosis, but also remarkably impacts seemingly unrelated conditions, such as cancer, psychiatric disorders, and immune function. To understand this wide range of diseases and develop therapeutic approaches for the...
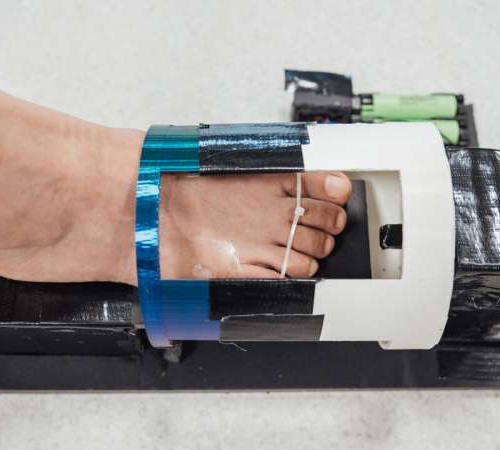
Scientists develop innovative magnetic gel that heals diabetic wounds three times faster
by National University of Singapore A bandage pre-loaded with magnetic hydrogel is placed on the wound and an external device is used to accelerate the wound healing process. Credit: National University of SingaporeDiabetic patients whose natural wound-healing capabilities are compromised often develop chronic wounds that are slow to heal. Such non-healing wounds could cause serious infections...
Eating red meat twice a week may increase type 2 diabetes risk, study finds
Experts claim latest research from Harvard University adds a greater level of certainty about the link Andrew Gregory Health editor The chances of a person developing type 2 diabetes can increase even if they eat red meat just two times a week instead of an alternative option, researchers have said. Replacing red meat with plant-based protein...
Erectile dysfunction linked to undiagnosed prediabetes, type 2 diabetes in young men
by Bridjes O’Neil, Saint Louis University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainErectile dysfunction (ED) is more common in older individuals with long-term Type 2 diabetes. However, emerging research at Saint Louis University School of Medicine has found that ED indicates undiagnosed prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in young men under 40. Although the prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes declined...
Scientists reveal mechanistic link between zinc levels and diabetes
by eLife Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainResearchers have identified a mechanistic link between zinc levels in humans and the risk of type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease. The research, published today as a Reviewed Preprint in eLife, is described by editors as a fundamental study that substantially advances our understanding of the role of zinc...
Hookworms successfully prevent type 2 diabetes in human trial
By Bronwyn Thompson The microscopic larvae the trial participants were innoculated with James Cook University For many, the idea of having a few dozen hookworms set up shop in your gut sounds more like a Survivor challenge than a beneficial health therapy, but scientists see a bright future in this human worm farm for treating many chronic conditions. In...
Scientists Reveal Best Dieting Strategy for Losing Weight With Type 2 Diabetes
TOPICS: Diabetes Nutrition Weight Loss By AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR NUTRITION AUGUST 16, 2023 Time-restricted eating between noon and 8 p.m. led to more weight loss in type 2 diabetes patients compared to calorie counting, with both methods improving blood sugar levels. Professional consultation is recommended before adopting this approach due to medication concerns. Study suggests that time-restricted...
New Guidelines on Diabetes-Related Laboratory Testing
Miriam E. Tucker July 25, 2023 New guidelines from the American Association of Clinical Chemistry (AACC) and American Diabetes Association (ADA) address laboratory measures in the diagnosis and management of diabetes. The document, entitled, “Guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus,”is primarily aimed at both laboratory professionals and clinicians...
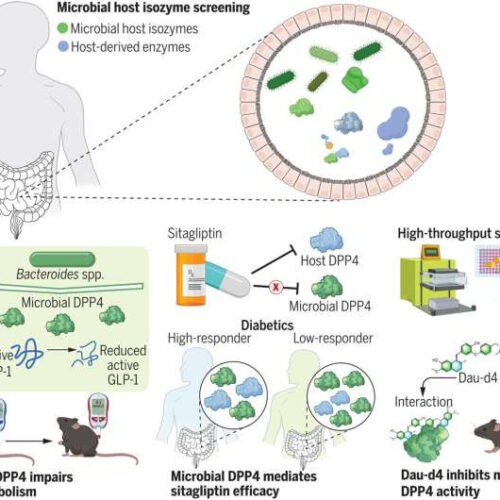
Synergistic effect of a traditional Chinese medicinal compound on existing diabetes drug found
by Justin Jackson, Medical Xpress Discovery and inhibition of a gut microbial–host isozyme to regulate host metabolism. Differences in the gut microbiota may explain why some individuals respond to antidiabetic DPP4 inhibitors but others do not. An activity-based enzyme activity screening system identified gut microbial DPP4 isozymes that can decrease active GLP-1 but cannot be...