by American Physiological Society Credit: CC0 Public Domain New research identifies the importance of the protein adropin in preventing stiffness in the arteries of people with obesity and type 2 diabetes. The study is published ahead of print in the American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. Arterial stiffness is a condition associated with aging and...
Category: <span>Diabetes</span>
Simple, inexpensive surgical procedure for diabetic foot ulcers greatly reduces healing time, amputation rates
by Diabetologia Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Performing proactive surgery to adjust the mechanics of the foot, appears to be effective to treat diabetic foot ulcers, a common and debilitating complication of diabetes, withoutthe potential complications and at significantly lower cost compared to conservative management. The preliminary study, being presented at the annual meeting of the...
Scientists hail ‘incredible’ results of pill which works TWICE as quickly at lowering blood sugar and helping people lose weight
By JOHN ELY SENIOR HEALTH REPORTER FOR MAILONLINE PUBLISHED: 18:00 EDT, 14 September 2022 | UPDATED: 18:03 EDT, 14 September 2022 Millions of diabetics could see life-changing results from an ‘incredible’ new drug, researchers suggested today. Tirzepatide works by mimicking hormones that help both control blood sugar and suppress appetite, helping people shed pounds. It was already...
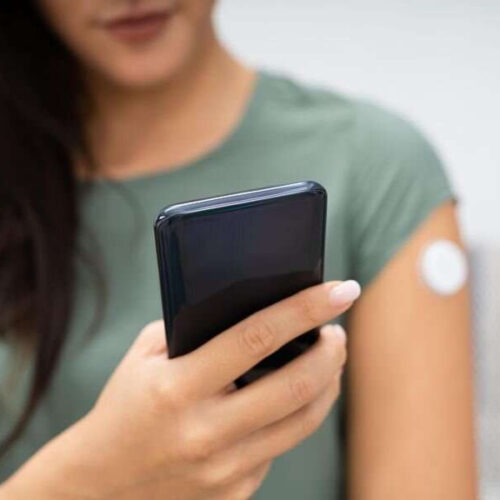
Automated insulin delivery ups time in target glucose range in type 1 diabetes
Among patients with type 1 diabetes, percentage of time in the target glucose range is increased with the use of an open-source automated insulin delivery (AID) system, according to a study published in the Sept. 8 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine. Mercedes J. Burnside, M.B., Ch.B., from the University of Otago in New...
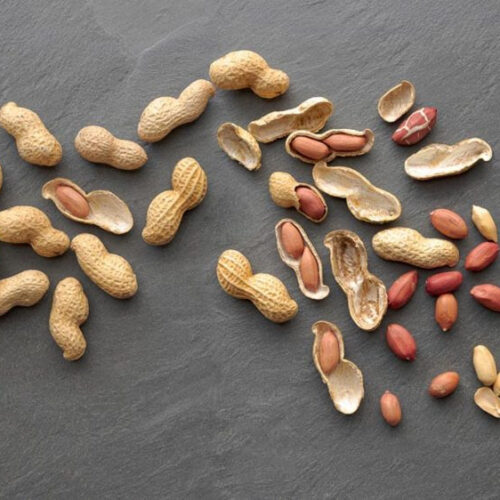
Eating Peanuts May Help With Weight Loss, Blood Pressure, and Glucose
BY QUINN PHILLIPS | SEPTEMBER 9, 2022 Regular consumption of peanuts before meals may help support metabolic health — in the areas of body weight, blood pressure, and blood glucose — according to a new study published in the journal Nutrients. Peanuts aren’t widely thought of as a health food, but there is evidence that they may be compatible with...
Recommended blood sugar levels to avoid diabetes-related damage
LINKÖPING UNIVERSITY IMAGE: HANS ARNQVIST, PROFESSOR EMERITUS AT LINKÖPING UNIVERSITY. CREDIT: THOR BALKHED/LINKÖPING UNIVERSITY The levels of long-term blood sugar, HbA1c, can be used to accurately determine the risk of a person with type 1 diabetes developing eye- and kidney complications. A study from Linköping University, Sweden, has shown that this level should be lower than...
Study shows game-changing obesity drug more than halves risk of type 2 diabetes
DIABETOLOGIA The risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) is more than halved by weekly injections of new obesity drug semaglutide, according to new research being presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Stockholm, Sweden (19-23 Sept). Semaglutide was recently approved in the US as an obesity...
New AI Tech Could Detect Type 2 Diabetes Without a Blood Test
Julie Stewart September 07, 2022 Imagine that instead of a patient visiting their doctor for blood tests, they could rely on a noninvasive at-home test to predict their risk of diabetes, a disease that affects nearly 15% of US adults (23% of whom are undiagnosed), according to the CDC. This technology could become a reality thanks...
Individuals with type 2 diabetes respond differently to exercise
by Karolinska Institutet Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Regular exercise helps prevent and delay the development of type 2 diabetes and its complications. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet, together with a team of international scientists, have discovered that activation of the immune system in skeletal muscle during exercise may underlie the difference in how individuals with type...
Better blood sugar control in teens may limit diabetes-related brain damage
by Nemours Children’s Health System Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Tight control of blood sugar in teens with Type 1 diabetes may help reduce the disease’s damaging effects on the brain, effects which have been shown even in younger children, according to a study published online today in Nature Communications. The findings indicate that better glucose control can...