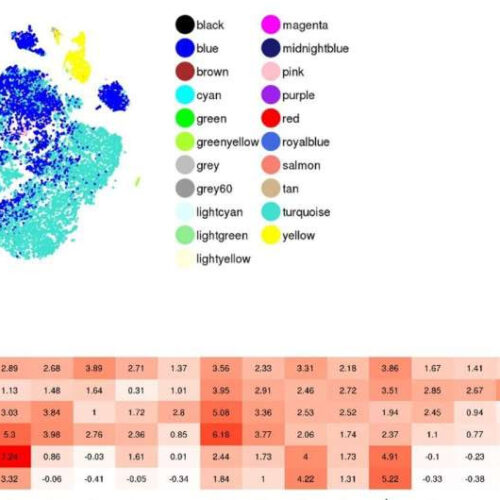
by Kyoto University Detailed analysis focusing on non-endocrine cells and validation of identified markers for detecting non-endocrine subpopulations. (a) Newly classified cell populations by reference component analysis (RCA) on the t-SNE projection. (b) A heatmap of tissues and cell lines with high similarity (reference component score > 2.5) to non-endocrine cells (brown, green, red and magenta). See...
Category: <span>Diabetes</span>
Scientists uncover key cellular mechanism that shows saturated fat can worsen diabetes
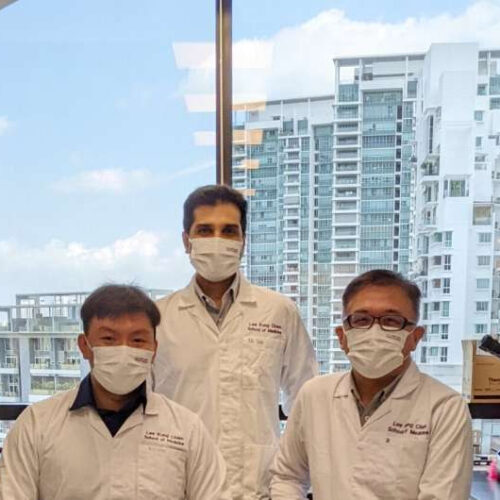
by Nanyang Technological University Scientists at NTU LKCMedicine have mapped a novel cellular pathway that shows that saturated fat contributes to the development of diabetes and can worsen the disease, underscoring its role in metabolic diseases. Credit: NTU LKCMedicine Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore’s (NTU Singapore) Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine (LKCMedicine) have...
Diabetes researchers find gut microbiota regulate pancreatic growth, exocrine function, and gut hormones
BOSTON COLLEGE Chestnut Hill, Mass. (4/13/2022) – Gut microbes can regulate the exocrine and endocrine functions of the pancreas and hormone production of the gastrointestinal tract, findings that may help develop potential treatments for diabetes and other diseases, a team of researchers from Boston College, Joslin Diabetes Center, and Maastricht University, Netherlands, report in the...
New study reveals that healthy plant-based diets are associated with a lower risk of developing diabetes
by Diabetologia Credit: CC0 Public Domain New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes [EASD]) finds that the consumption of healthy plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, coffee, and legumes, is associated with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes (T2D) in generally healthy people and support their...
Insomnia could increase people’s risk of type 2 diabetes, study finds
New research has found that people who have difficulty getting to sleep or staying asleep had higher blood sugar levels than people who rarely had sleep issues. The University of Bristol-led findings suggests insomnia could increase people’s risk of type 2 diabetes and that lifestyle or pharmacological treatments that improve insomnia could help to prevent or treat...
Long-term follow-up reduces risk of type 2 diabetes
by Steinar Brandslet, Norwegian University of Science and Technology 189 people were recruited for the start of the study, and 70 percent completed the five year programme. Many participants experienced very good results. Credit: Shutterstock, NTB Type 2 diabetes is an inherited disease, but habits can affect the risk of getting it. Obesity due to...
C-Path receives qualification opinion from EMA on Type 1 Diabetes Biomarker Initiative
CRITICAL PATH INSTITUTE (C-PATH) IMAGE: THE T1D CONSORTIUM IS WORKING TO QUALIFY ISLET AUTOIMMUNITY ANTIBODIES AS PROGNOSTIC BIOMARKERS TO BE USED IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF THERAPIES FOR THE TREATMENT, AND ULTIMATELY THE PREVENTION, OF TYPE 1 DIABETES. CREDIT: COURTESY OF C-PATH TUCSON, Ariz., April 5, 2022 — Critical Path Institute’s (C-Path) Type 1 Diabetes Consortium (T1DC) today...
Black people with diabetes disproportionately affected by diabetic ketoacidosis during COVID
THE ENDOCRINE SOCIETY WASHINGTON—Black people with diabetes were more likely to develop cases of a life-threatening complication called diabetic ketoacidosis during the pandemic, even in people without COVID-19, according to a new study from the TID Exchange published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. People with diabetes are more likely to get...
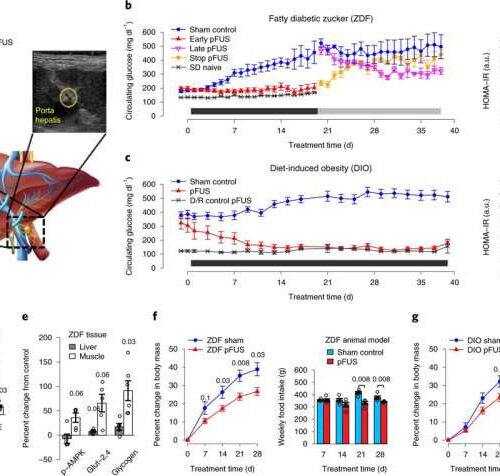
Treating diabetes without drugs? Novel non-pharmacologic treatments are on the horizon
by Jane E. Dee, Yale University Daily ultrasound stimulation of the liver–brain neural pathway prevents or reverses the onset of hyperglycaemia in multiple animal models of T2D. Credit: Nature Biomedical Engineering (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41551-022-00870-w A multi-institutional team including Yale School of Medicine (YSM) has demonstrated the ability to use ultrasound to stimulate specific neurometabolic pathways in the...
Gene map may identify heart disease risk for people with type 2 diabetes
by American Heart Association Credit: CC0 Public Domain A risk score based on a gene map predicted the likelihood of high blood pressure leading to heart problems or stroke in people with Type 2 diabetes, according to a study published today in the American Heart Association’s peer-reviewed journal Hypertension. This tool may be especially useful in...