Zarrin Hossain January 05, 2022 Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is associated with a number of risk factors and now new research, published in Diabetes Care, suggests that increased levels of liver fat and a smaller pancreas volume may also add to a greater risk of developing T2D. Head of Research Communications at Diabetes UK, Dr. Lucy Chambers, commented that this breakthrough...
Category: <span>Diabetes</span>
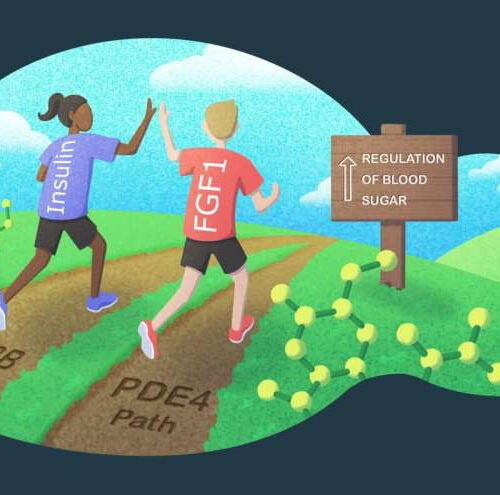
Researchers find a new route for regulating blood sugar levels independent of insulin
by Salk Institute Insulin and FGF1 both regulate blood sugar levels using independent pathways. Credit: Salk Institute The discovery of insulin 100 years ago opened a door that would lead to life and hope for millions of people with diabetes. Ever since then, insulin, produced in the pancreas, has been considered the primary means of...
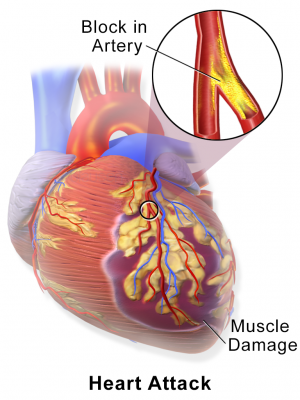
New study could inform treatment and prevent heart attack in diabetic patients
by Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute Myocardial Infarction or Heart Attack. Credit: Blausen Medical Communications/Wikipedia/CC-A 3.0 A new study by researchers at the Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute and Monash University could help inform treatment and prevent serious events like a heart attack or death in diabetic patients at high risk of serious cardiovascular events....
AAN issues guideline for treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy
by American Academy of Neurology Diabetic neuropathy refers to nerve damage due to diabetes and it may lead to pain and numbness, most often in the hands and feet. To help neurologists and other doctors determine the best treatment for people with diabetic neuropathy, the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) has issued a guideline on...
New Type 2 Diabetes Treatment Shows Promise in First Human Study
Mitchel L. Zoler, Ph.D., for Medscape November 18, 2021 Key Takeaways Patients with type 2 diabetes who received daily treatment with sodium phenylbutyrate for 2 weeks had significant improvements in peripheral insulin sensitivity and glucose oxidation. The treatment appeared safe, with no reported adverse events. Why This Matters The results show, for the first time in humans, that treatment with an...
Research takes early step towards drug to treat common diabetes complication hypoglycaemia
by University of Exeter Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain New research has taken an important step towards the goal for a treatment for the common diabetes complication hypoglycaemia, or low blood sugar. In all forms of diabetes, blood sugars become too high as the body is either unable to produce insulin, or cannot make enough of it,...
A potential protector against a mild heart attack’s aftereffects on metabolism
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study in mice shows transplanted brown fat can reduce type 2 diabetes risk factors after a heart attack, an encouraging finding for scientists who hope to apply the so-called “good” fat’s beneficial properties to drugs that can help prevent health problems. In the study, transplanting brown fat...
Black Beans Help Fix Insulin Resistance and Gut Bacteria Balance
Adding cooked black beans to a high-fat diet improved sensitivity to insulin and other measures often related to diabetes and restored gut bacteria balance in obese mice, according to a USDA Agricultural Research Service study. As little as the mouse-size equivalent of a single serving a day of black beans—about a half cup for a...
In Type 2 Diabetes, Arterial Stiffening Causes Increased Structural Damage to the Brain
Researchers here mine patient data in order to demonstrate that type 2 diabetes combines with the age-related stiffening of blood vessels to produce greater structural damage in the brain, leading to a more rapid cognitive decline. This correlation between stiffening and damage was not observed in non-diabetic patients. This is an interesting result, as a reasonable view of the...
Newly identified hormone may be a critical driver of type 1 and type 2 diabetes
by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain A newly discovered hormone named fabkin helps regulate metabolism and may play an important role in the development of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, according to research led by the Sabri Ülker Center for Metabolic Research at Harvard T.H. Chan School of...