by Adam Pope, University of Alabama at Birmingham The study, led by Barbara Gower, Ph.D., is the first randomized clinical trial of a hypothesis that reducing fat stored around organs, through diet alone, can rescue beta-cell function. Credit: University of Alabama at Birmingham A clinical trial now enrolling at the University of Alabama at Birmingham is...
Category: <span>Diabetes</span>
Common osteoporosis drug may reduce risk of type 2 diabetes
DIABETOLOGIA New research being presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), held online this year, suggests that the widely used osteoporosis drug alendronate reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes. It has been known for decades that patients with diabetes have a higher risk of fractures – suggesting a...
Researchers identify potential cause and treatment for obesity and insulin resistance
by Monash University Credit: Shutterstock Monash University researchers have shown for the first time that mesenteric (gut) lymphatic dysfunction is a potential cause of and therapeutic target for obesity and insulin resistance. The groundbreaking study, published in Nature Metabolism, identified a profoundly damaging cycle in which a high fat diet promotes dysfunction of the mesenteric lymphatics, that in turn leads to...
What to know about Omnipod
Diabetes is a chronic health condition affecting blood glucose levels. In some cases, it requires constant management in the form of monitoring blood glucose levels and administering insulin. Technologies such as the Omnipod system may facilitate this management and improve care in people living with diabetes. Relying on insulin therapy for the management of diabetes can be stressful. Worry...
Differences in cellular signaling offer clues to insulin resistance
by Max Bingham, Harvard Medical School Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain In what could be a starting point for new therapeutics to tackle insulin resistance, a major driver of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome present in 20–30 percent of the general U.S. population, researchers recently found that insulin resistance in the general population seems likely to be caused...
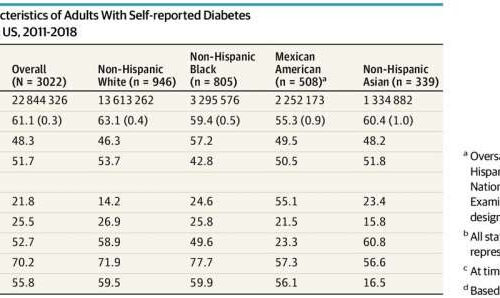
Black and Mexican American adults develop diabetes at a younger age
by Kristin Samuelson, Northwestern University Credit: DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.4945 Certain racial and ethnic minorities develop type 2 diabetes at a younger age than white Americans, meaning current diabetes screening and prevention practices for them may be inadequate and inequitable, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study. American adults are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at an average age of 50...
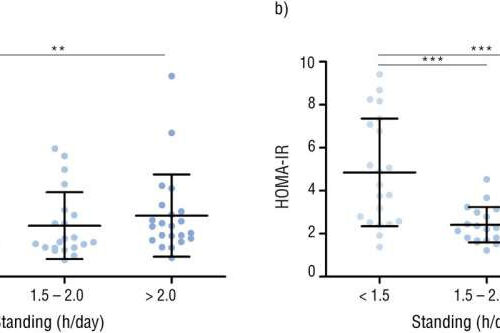
Association between standing and insulin sensitivity
by University of Turku Fig. 1. Dose-response association between standing time and insulin sensitivity. Insulin sensitivity presented as a) M-value and b) HOMA-IR stratified by tertiles of accelerometer-measured standing time (h/day; means [SD]) in sedentary adults with metabolic syndrome (n = 64). HOMA-IR = homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance. ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001. Credit: DOI: 10.1016/j.jsams.2021.08.009 Insulin is a key hormone...
Why do people with diabetes develop severe COVID-19?
by Kelly Malcom, University of Michigan Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians have noted that certain patients are at especially high risk of developing severe illness or dying from coronavirus infection. Type 2 diabetes—a condition affecting more than 10 percent of the U.S. population— is one of the main risk factors for severe...
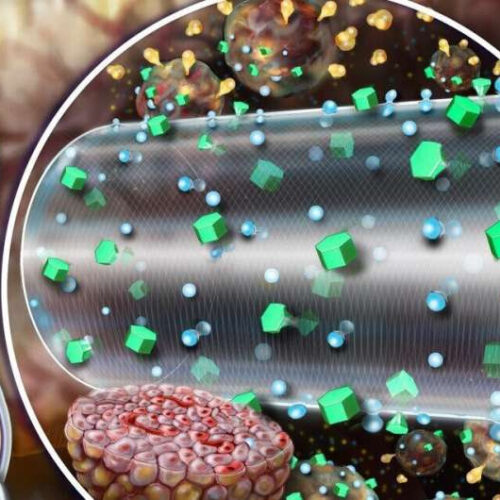
Building a better bioartificial pancreas
by Brigham and Women’s Hospital A convection-enhanced encapsulation device as pictured enhances nutrient transport leading to improved survival and improved glucose responsive insulin secretion of the transplanted beta cells. Credit: Randal McKenzie More than 40 million people worldwide are affected with type 1 diabetes (T1D) mellitus, an autoimmune disease in which insulin producing β-cells in the...
International experts outline diabetes remission diagnosis criteria
People with type 2 diabetes should be considered in remission after sustaining normal blood sugar levels for three months or more, according to a new consensus statement from the Endocrine Society, the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Diabetes UK and the American Diabetes Association, and co-published in Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, Diabetologia, Diabetic Medicine and Diabetes...