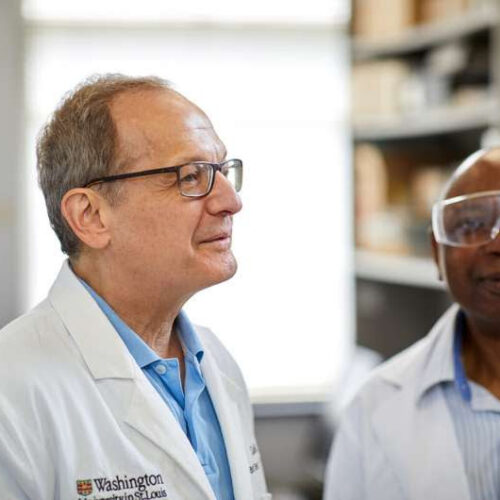
by Washington University School of Medicine Senior investigator Samuel Klein, MD, (left), in the laboratory with Adewole Okunade, PhD. Klein’s team found that NMN improved the ability of insulin to increase glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Credit: Matt Miller A natural compound previously demonstrated to counteract aspects of aging and improve metabolic health in mice has...
Category: <span>Diabetes</span>
New research reveals why some of us are hungry all the time
by King’s College London Credit: CC0 Public Domain New research shows that people who experience big dips in blood sugar levels, several hours after eating, end up feeling hungrier and consuming hundreds more calories during the day than others. A study published today in Nature Metabolism, from PREDICT, the largest ongoing nutritional research program in the world that looks at responses...
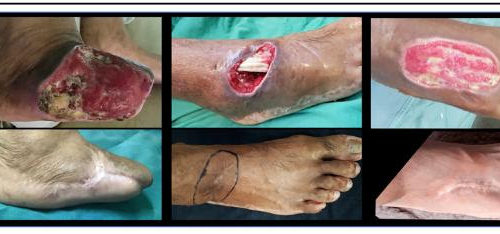
Stem cell therapy research could help patients with non-healing diabetic foot ulcers
ALPHAMED PRESS IMAGE: EXAMPLES OF COMPLETE CLOSURE (100%). CREDIT: ALPHAMED PRESS Durham, NC – According to the results of a phase 1 clinical trial just published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine, a new stem cell therapy shows promise of making diabetes-related amputations a thing of the past. The trial involved injecting diabetes patients suffering from non-healing...
Team identifies new approach to tackling heart disease in people with Type 2 diabetes
by Gillian Rutherford, University of Alberta Pharmacy researcher John Ussher led new research identifying a protein that could be key to developing treatments to prevent a type of heart failure that is common but often hidden in people with Type 2 diabetes. Credit: Julia Brown Photography A University of Alberta laboratory has uncovered a new approach to preventing...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers develop materials for oral delivery of insulin medication
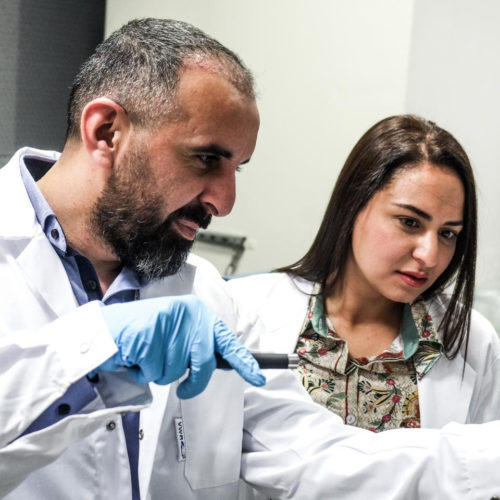
NEW YORK UNIVERSITY IMAGE: NYUAD’S RESEARCH SCIENTIST FARAH BENYETTOU AND PROGRAM HEAD OF CHEMISTRY ALI TRABOLSI CREDIT: NYU ABU DHABI A revolutionary technology developed within the Trabolsi Research Group at NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) could dramatically improve the well-being of diabetic patients through a simple and straightforward way: an insulin oral delivery system that could replace traditional subcutaneous injections...
Fasting acts as diet catalyst in those with metabolic syndrome
by Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine Credit: CC0 Public Domain One in four Germans suffers from metabolic syndrome. Several of four diseases of affluence occur at the same time in this ‘deadly quartet’: obesity, high blood pressure, lipid metabolism disorder and diabetes mellitus. Each of these is a risk factor for severe cardiovascular conditions, such...
Weekly insulin helps patients with type 2 diabetes achieve similar blood sugar control to daily insulin
THE ENDOCRINE SOCIETY WASHINGTON–A new once-weekly basal insulin injection demonstrated similar efficacy and safety and a lower rate of low blood sugar episodes compared with a daily basal insulin, according to a phase 2 clinical trial. The study results, which will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting, compared an investigational drug...
Eating before 8:30 a.m. could reduce risk factors for type 2 diabetes
by The Endocrine Society Credit: CC0 Public Domain People who start eating before 8:30 a.m. had lower blood sugar levels and less insulin resistance, which could reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, according to a study presented virtually at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting. “We found people who started eating earlier in...
Two new diabetes drugs may work better for Asian people
by University of Glasgow Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Two relatively new but increasingly used diabetes drugs (with one of these classes also now approved for used in heart failure in people with or without diabetes) are possibly more effective in people with an Asian background than in people with a White background, according to new research....
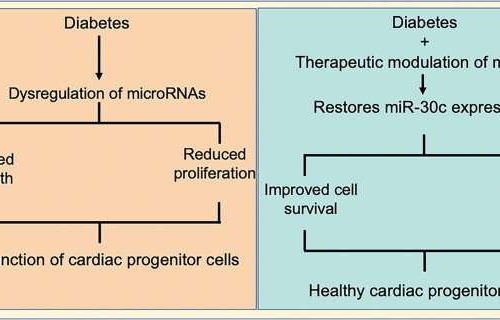
Discovery for treatment of heart disease in type-2 diabetics
by University of Otago Graphical abstract. Credit: Diabetologia (2021). University of Otago researchers have discovered one of the reasons why more than 50 percent of people with type 2 diabetes die from heart disease. And perhaps more significantly, they have found how to treat it. Associate Professor Rajesh Katare, of the Department of Physiology, says it...