A 45-minute hospital procedure could enable those with type 2 diabetes to stop using insulin. A small hot water-filled balloon is put down the throat to heat up the lining of the duodenum – the upper part of the small intestine – so some of its surface cells are burned away and replaced. These cells...
Category: <span>Diabetes</span>
Study reveals the role of our ‘second brain’ in diabetes
Researchers have uncovered new clues to the mystery of how the gut’s nervous system affects glucose metabolism in the rest of the body. Their findings could lead to new treatments for type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes causes the body’s cells to become less sensitive to signals from insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating levels of...
Targeting our second brain to fight diabetes
UNIVERSITÉ CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN IMAGE: PATRICE CANI (UCLOUVAIN) AND CLAUDE KNAUF (INSERM) HAVE DISCOVERED A ‘JAMMER’ THAT BLOCKS COMMUNICATION BETWEEN THE GUT AND THE BRAIN, THUS PREVENTING PROPER REGULATION OF SUGAR AND CAUSING INSULIN RESISTANCE. Since 2004, Claude Knauf (INSERM) and Patrice Cani (UCLouvain) have been collaborating on molecular and cellular mechanisms in order to...
Remote control of blood sugar: Electromagnetic fields treat diabetes in animal models
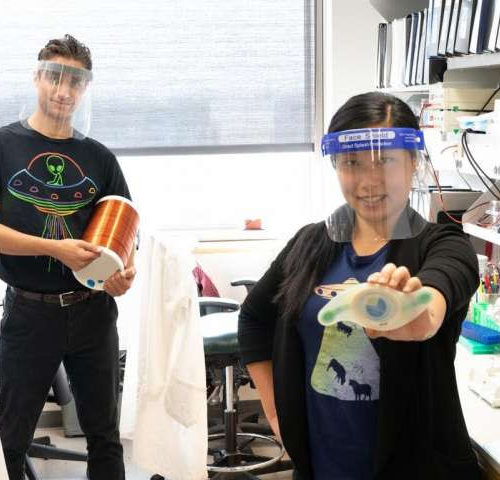
by Jennifer Brown, University of Iowa Calvin Carter and Sunny Huang (pictured in their lab at the University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine) may have discovered a safe new way to manage blood sugar non-invasively using electromagnetic fields (EMFs). Their findings, published in Cell Metabolism, show that exposing diabetic mice to a combination of static...
Newer Type 2 diabetes medications have heart and kidney disease benefits, too
AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION DALLAS, Sept. 28, 2020 — Two newer groups of medications prescribed primarily for Type 2 diabetes treatment (SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists) could significantly reduce risks associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and heart disease. Based on analyses of the clinical trials through March 2020, a group of leading experts in diabetes, heart...
Diabetes drug boosts survival in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19 pneumonia
BOSTON CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL BOSTON – Sitagliptin, a drug to lower blood sugar in type 2 diabetes, also improves survival in diabetic patients hospitalized with COVID-19, suggests a multicenter observational study in Italy. Patients given sitagliptin in addition to insulin had a mortality rate of 18 percent as compared with 37 percent in matched patients receiving...
Diabetes dramatically reduces the kidney’s ability clean itself
by Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University Drs. Zheng Dong and Zhengwei Ma, MCG research associate and the study’s first author. Credit: Kim Ratliff, Augusta University photographer The kidneys often become bulky and dysfunctional in diabetes, and now scientists have found that one path to this damage dramatically reduces the kidney’s ability to clean up after itself....
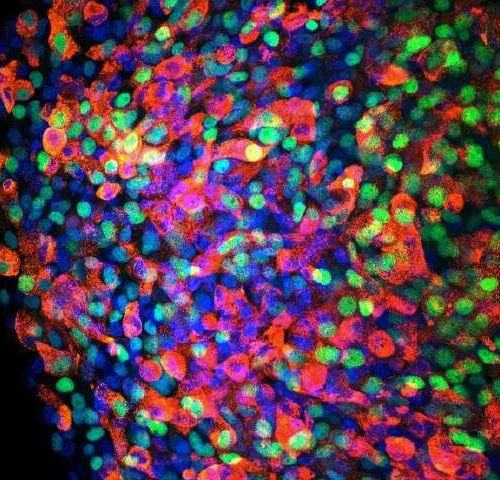
Type 1 diabetes from a beta cell’s perspective
by Eva Frederick, Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Confocal micrograph from immunofluorescence staining of human pluripotent stem cells differentiated beta-like cells in 3D organoid culture with an anti-C-peptide antibody (red) and an anti-PDX1 antibody (green). DAPI was used to stain nuclei. Credit: Haiting Ma/Whitehead Institute Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that occurs when T-cells in...
AI-basedc device will help monitoring blood sugar without painful finger pricks
Would you like to stab your finger several times per day every day just to survive? Probably not and yet millions of people with diabetes live like that. Finger pricks are necessary to measure blood glucose levels, but they are also painful or at least uncomfortable. Now scientists found a better way – they designed...
New risk factors for type 2 diabetes uncovered
A new ‘global atlas’ study characterizes insomnia as a novel risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. In total, the researchers identified 19 risk factors and dismissed 21 suggestive risk factors based on insufficient scientific evidence. New research indicates insomnia is a possible risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Globally, around 463 million adults lived with diabetes...