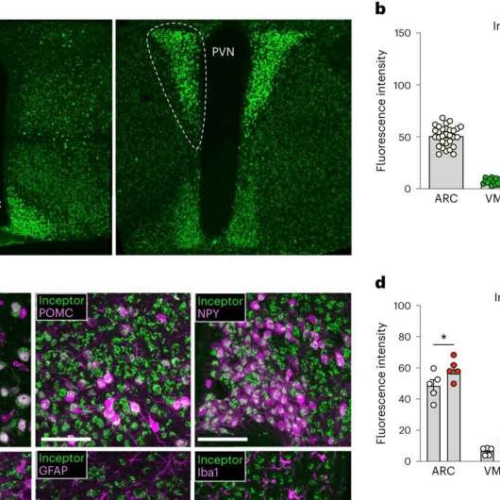
by Verena Schulz, Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres Central inceptor immunoreactivity is restricted to neurons, including those regulating energy and glucose metabolism. Credit: Nature Metabolism (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s42255-024-00991-3Research targeting the insulin-inhibitory receptor, or inceptor, unveils promising avenues for beta cell protection, offering hope for causal diabetes therapy. A novel study in mice with diet-induced obesity...
Category: <span>Diabetes</span>
Once-Weekly Insulin Better Than Daily in Type 2 Diabetes
Drishti Agarwal TOPLINE:Once-weekly insulin icodec shows a higher glycated A1c reduction than once-daily basal insulin analogs in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D), without major safety concerns. METHODOLOGY:A meta-analysis of five phase 3 ONWARDS randomized controlled trials included 3764 patients with T2D.The trials compared the effects of the weekly insulin icodec with those of the...
Researchers uncover potential treatment for cardiovascular complications from type 2 diabetes
by University of Missouri Graphical abstract. Credit: American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology (2023). DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00337.2023New research at the Roy Blunt NextGen Precision Health building has discovered a potential treatment for an underlying cause of cardiovascular disease in people with type 2 diabetes. More than 30 million Americans live with type 2 diabetes. One common...
New Marker of Cardiovascular Risk Discovered in T2D
Anne-Gaëlle Moulun A significant quantity of dysfunctional monocytes appears to indicate poor cardiovascular prognosis in patients with type 2 diabetes, according to a new publication. Nicolas Venteclef, PhD, director of an Inserm institute for diabetes research at Necker Enfants Malades Hospital in Paris, France, led the research. Quantifying InflammationPatients with type 2 diabetes have about...
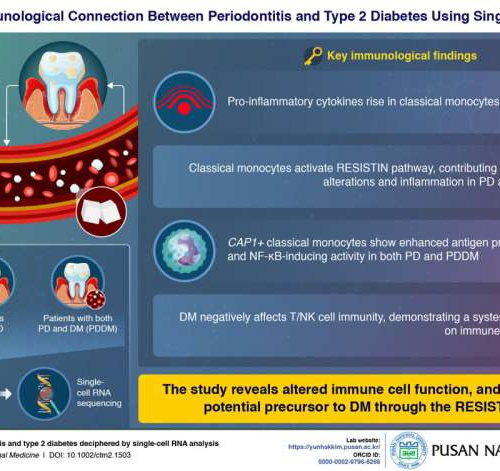
Researchers reveal how diabetes weakens gum defense
by Pusan National University The study associating periodontitis (PD) and diabetes mellitus (DM) using single-cell RNA analysis offers the first immunological explanation, revealing altered immune cell function and suggesting PD as a potential precursor to DM through the RESISTIN pathway. Credit: Yun Hak Kim from Pusan National UniversityPeriodontitis (PD) is a common complication in individuals with...
Gargling away the bad bacteria in type 2 diabetes
Researchers from Osaka University find that gargling with an antiseptic mouthwash can reduce ‘bad’ bacteria in the mouths of people with type 2 diabetes, and may lead to better control of their blood sugarPeer-Reviewed Publication OSAKA UNIVERSITY MECHANISM OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS IMPROVEMENT BY GARGLING WITH MOUTHWASH CREDIT: SAAYA MATAYOSHI Osaka, Japan – More...
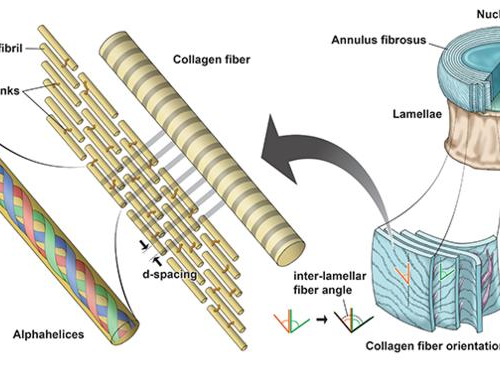
Type 2 diabetes alters the behavior of discs in the vertebral column
In a rat model, the discs became stiffer and changed shape earlier than normalPeer-Reviewed Publication UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN DIEGO THE HIERARCHICAL STRUCTURE OF THE INTERVERTEBRAL DISC (APPROXIMATELY 45–55 MM DIAMETER IN THE HUMAN LUMBAR SPINE AND 2.5–5 MM IN THE RAT COCCYGEAL SPINE) IS COMPOSED OF THE OUTER FIBER-REINFORCED ANNULUS FIBROSUS AND INNER...
Researchers identify new mechanism that could improve the efficiency of diabetes treatments
by University of Barcelona Proposed mechanistic model for the hepatic effects of Gdf15 deficiency on fibrosis, gluconeogenesis and fatty liver via the TGF-β1-SMAD3 pathway. Credit: Metabolism (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155772A study led by the University of Barcelona and the Biomedical Research Networking Center in Diabetes and Associated Metabolic Disorders (CIBERDEM) reveals how a new mechanism could improve...
Overturning Old Myths: New Research Indicates That Insulin Spike After Eating Is Actually a Good Thing
By LUNENFELD-TANENBAUM RESEARCH INSTITUTE Researchers have conducted a study revealing that post-meal insulin surges might indicate good metabolic health, challenging the previously held belief that they are harmful. The study, which focused on long-term cardiometabolic implications in new mothers, found that higher corrected insulin response (CIR) levels are associated with better beta-cell function and a...
Weight loss intervention in people with type 2 diabetes influences cancer-associated proteins
Peer-Reviewed Publication UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL A weight loss intervention in people with type 2 diabetes was found to alter levels of cancer-related proteins, according to the findings of a new University of Bristol-led study. The study, published in eBioMedicine, is the first to show that weight loss in people recently diagnosed with diabetes can change...