by Bill Snyder, Vanderbilt University Medical Center Timeline and process overview. Credit: Nature Medicine (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-02796-zAn analysis of genomic data from nearly 250,000 participants in the National Institutes of Health’s All of Us Research Program has identified more than 275 million previously unreported genetic variations, nearly 4 million of which have potential health consequences.The data,...
Category: <span>Genetics</span>
Researchers are using RNA in a new approach to fight HIV
You know mRNA, now meet siRNAPeer-Reviewed Publication UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO Society learned about the value of mRNA during the COVID-19 pandemic when we saw scientists and medical professionals harness its power to deliver a vaccine for the virus within a year. Now, University of Waterloo pharmacy associate professor Emmanuel Ho has developed a novel nanomedicine...
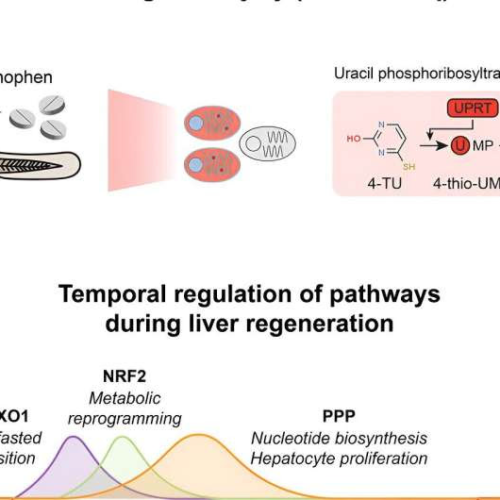
One step closer to reversing liver failure: Study shows how liver is triggered to regrow when damaged
by Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Credit: Developmental Cell (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.01.024Researchers at Peter Mac have made a key discovery in liver regeneration that may have important implications for liver cancer. Joint research by Associate Professor Andrew Cox and Professor Mark Dawson, published Feb. 15 in Developmental Cell, has identified how the liver is triggered to regrow...
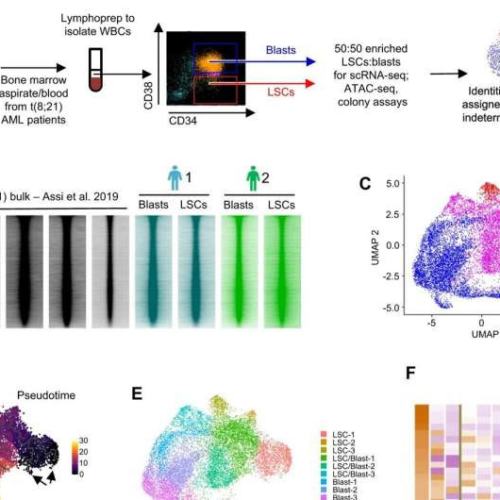
Why leukemic stem cells not harmed by chemotherapy begin to grow and produce AML cells after treatment
by University of Birmingham AML-subtype specific gene expression and chromatin accessibility is established in LSCs. Credit: Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45691-4The mystery of why myeloid leukemia starts to grow again after chemotherapy has killed the bulk of malignant cells, and how growth may be blocked by repurposed drugs, has potentially been solved through new research. The...
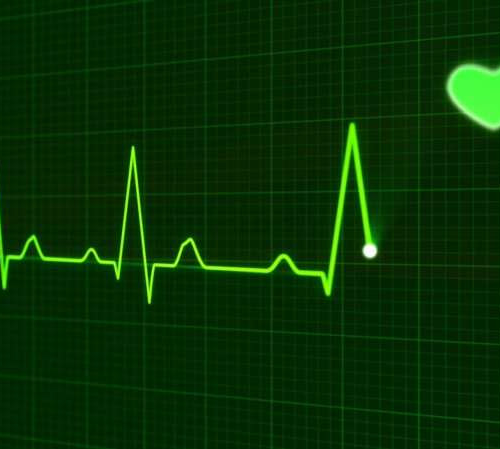
Not too late to repair: Gene therapy improves advanced heart failure in animal model
by Ana María Rodríguez, Baylor College of Medicine Credit: CC0 Public DomainHeart failure remains the leading cause of mortality in the U.S. During a heart attack blood stops flowing into the heart. Without oxygen, part of the heart muscle dies. The heart muscle does not regenerate; instead, it replaces dead tissue with a scar made of...
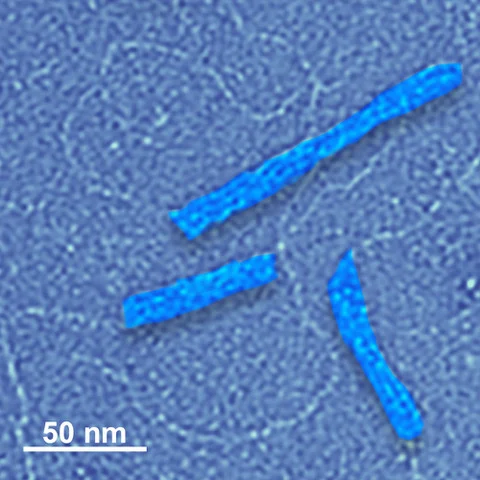
Building a DNA Nanoparticle to be Both Carrier and Medicine
Scientists have been making nanoparticles out of DNA strands for two decades, manipulating the bonds that maintain DNA’s double-helical shape to sculpt self-assembling structures that could someday have jaw-dropping medical applications.Four DNA nanostructures, two butted up against each other, highlighted in this electron microscope image. The structures are a little longer than 50 nanometers. A...
Scientists gain new insights into how small intestine works
by Ernie Mundell It was the ancient Greeks who first divided the 20-foot length of the small intestine into three parts: The duodenum, the jejunum and the ileum. However, the organ may finally be ready for an update: U.S. researchers say the small intestine is actually comprised of five distinct segments, each being responsible for...
Alterations in the blood immune system found to increase cancer risk
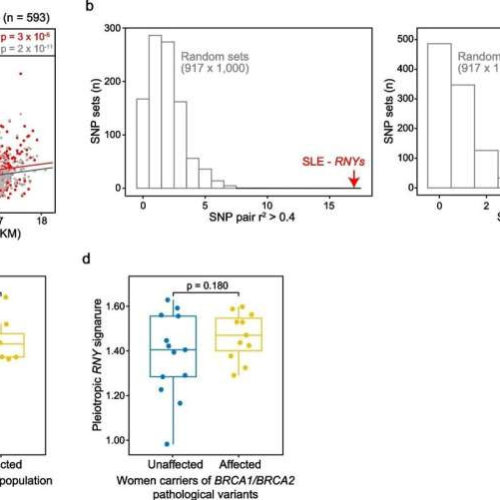
by Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute Pleiotropic RNYs are linked to SLE risk and plasma RNYs are relatively abundant preceding breast cancer diagnosis. a Scatter plot of the correlation of the levels of expression between RO60 and the pleiotropic or non-pleiotropic RNY signatures in TCGA normal tissue. The PCCs and p values are indicated....
New study identifies gene believed to be responsible for ALS and dementia
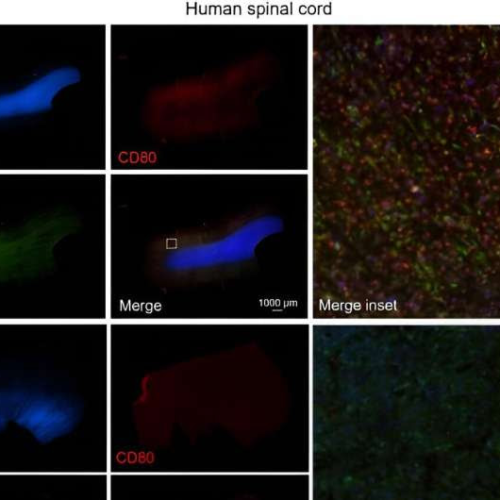
by Case Western Reserve University Representative human spinal cord tissue imaged at 4X objective for DAPI (blue), CD80 (red), and Iba1 (green) from an C9ORF72 ALS case and a non-ALS control. Scale bars represent 1000 µm or 100 µm as indicated. Credit: Science Translational Medicine (2024). DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adg7895Researchers at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine...
Gene editing precisely repairs immune cells
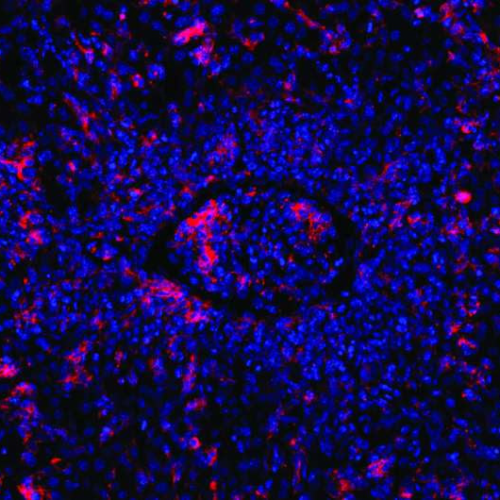
by Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine Mutated T cells are unable to kill B cells (red) induced by the Epstein-Barr virus. This causes other immune cells to flow into the area of infection, thereby blocking a blood vessel (center). Credit: Elijah D. Lowenstein and Xun Li, K. Rajewsky Lab, Max Delbrück CenterSome hereditary genetic defects...