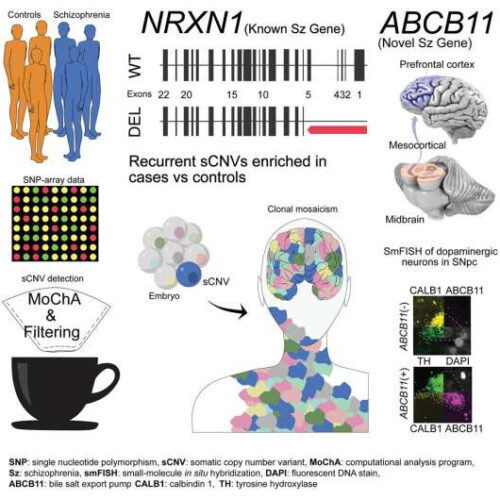
by Cell Press Schizophrenia-associated somatic copy number variants from 12,834 cases reveal recurrent NRXN1 and ABCB11 disruptions. Credit: Cell Genomics / Maury et al. As a psychiatric disorder with onset in adulthood, schizophrenia is thought to be triggered by some combination of environmental factors and genetics, although the exact cause is still not fully understood. In...
Category: <span>Genetics</span>
Dissecting the genetic factors involved in systemic lupus erythematosus development
by University of Tsukuba Credit: Saiful52/Shutterstock Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a typical autoimmune rheumatic disease. This multifactorial condition results from a combination of multiple genetic and acquired factors. Human leukocyte antigen (HLA), which is responsible for individual differences in immune response, is one of the major genetic factors associated with SLE development. However, its contribution...
Genetic discovery could help prevent irreversible blindness in people with glaucoma
by QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute Credit: CC0 Public Domain International research led by QIMR Berghofer has found hundreds of new genes linked to a person’s risk of developing glaucoma, including key genetic targets that could, for the first time, pave the way for treatments that prevent the retinal damage that causes blindness. The findings, from the largest-ever global...
Base editing shows potential superiority for curing sickle cell disease
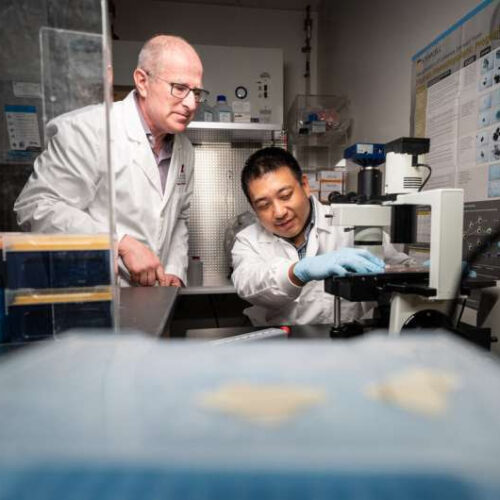
by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital (L to R) Co-corresponding author Mitchell Weiss, M.D., Ph.D., St. Jude Department of Hematology chair and co-corresponding author Jonathan Yen, Ph.D., St. Jude Therapeutic Genome Engineering director at a microscope in the lab. Gene therapy that alters hemoglobin genes may be an answer to curing sickle cell disease (SCD) and...
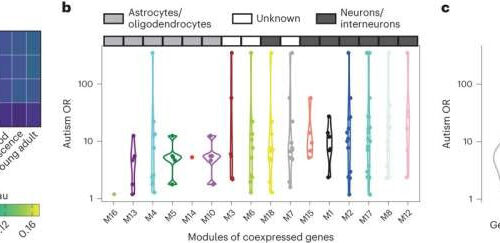
Autism-related genes in non-autistic individuals show a long-term socioeconomic influence
by Justin Jackson, Medical Xpress Relationship between gene expression profile and autism odds ratio (OR). a, Correlation between autism OR and gene expression in distinct brain regions and developmental periods for 130 genes for which at least one variant was identified among individuals with autism. Cortical regions were grouped as follows: posterior inferior parietal cortex,...
New study reveals a potential big leap for gene therapy
AARHUS UNIVERSITY IMAGE: A NEW STUDY LED BY PROFESSOR YONGLUN LUO FROM THE DEPARTMENT OG BIOMEDICINE AT AARHUS UNIVERSITY SHOWS THAT ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) MAY HOLD THE KEY TO A SHARPER AND MORE PRECISE DNA SCISSOR. THIS DISCOVERY MAY BE A BREAK THROUGH FOR MORE EFFICIENT GENE THERAPY. CREDIT: LINE RØNN, HEALTH AARHUS UNIVERSITY Artificial...
Breakthrough Hair Loss Treatment May Have Been Discovered Using MicroRNA
SScientists may have discovered a breakthrough treatment that could help reverse hair loss by using microRNA. herkisi/Getty Images Scientists have discovered that a type of microRNA may help treat hair loss. This microRNA could aid hair regrowth by softening hair follicles, which naturally become stiffer as we age and contribute to hair loss. According to...
FDA Approves First Gene Therapy for Treatment of Certain Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
June 22, 2023 Today, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Elevidys, the first gene therapy for the treatment of pediatric patients 4 through 5 years of age with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) with a confirmed mutation in the DMD gene who do not have a pre-existing medical reason preventing treatment with this therapy. “Today’s approval addresses...
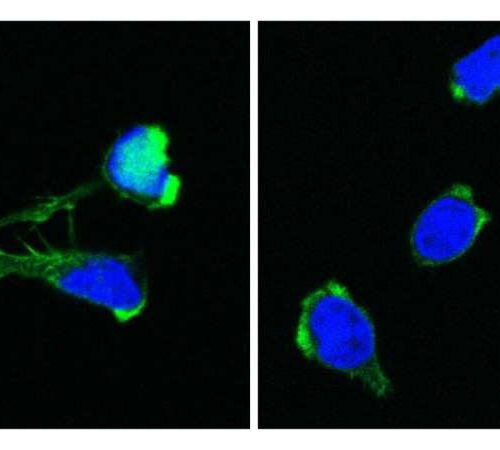
Newly discovered genetic defect disrupts blood formation and immune system
by St. Anna Children’s Cancer Research Institute Healthy T cells (left) and DOCK11-deficient T-cells (right) with visible nucleus (blue) and aktin-cytoskeleton (green). Credit: St. Anna Children’s Cancer Research Institute In the quest to find the origin of the puzzling symptoms in four children, researchers from St. Anna Children’s Cancer Research Institute, the CeMM Research Center...
Low oxygen levels restore balance and coordination in a mouse model of a movement disorder
by Allessandra DiCorato, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard Friedreich’s ataxia is a rare, inherited disease that causes progressive nervous system damage, impairing balance and coordination and leaving patients unable to walk by early adulthood. Now, researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have found that treatment with continuous hypoxia—low-oxygen conditions comparable to levels...