A study involving researchers from the University of Liverpool describes how transposable elements are associated with Parkinson’s subtypes and impact disease trajectory. The study, published in Experimental Biology and Medicine, analysed the variation of transposable elements – DNA sequences that can change their position within a genome – and their impact on different trajectories of Parkinson’s disease....
Category: <span>Genetics</span>
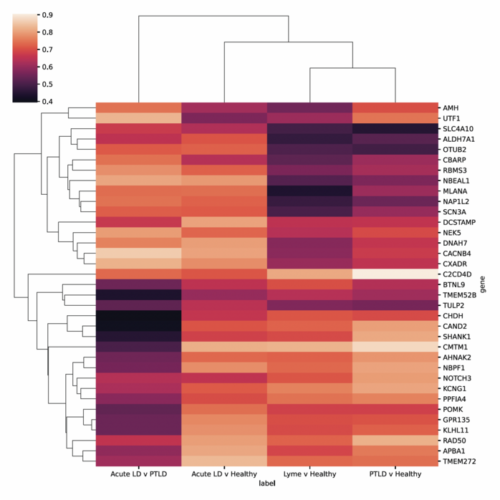
Genes to potentially diagnose long-term Lyme disease identified
THE MOUNT SINAI HOSPITAL / MOUNT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE IMAGE: RESEARCHERS AT ICAHN MOUNT SINAI IN NEW YORK IDENTIFIED 35 GENES THAT COULD BE USED AS BIOMARKERS TO POTENTIALLY DIAGNOSE PATIENTS WITH LONG-TERM LYME DISEASE (LTLD). THE FINDINGS MAY ALSO LEAD TO NEW THERAPEUTIC TARGETS FOR THE HARD-TO-DIAGNOSE DISEASE WITH LIMITED TREATMENT OPTIONS. THE...
Researchers identify a promising new drug target for rare liver cancer
by Rockefeller University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain As a rare and lethal liver cancer that disproportionately harms young adults, fibrolamellar carcinoma is nearly incurable. Surgery can remove the tumor, but no existing therapies are capable of reining in the cancer once it starts to spread throughout the body. Now, a new study demonstrates that fibrolamellar...
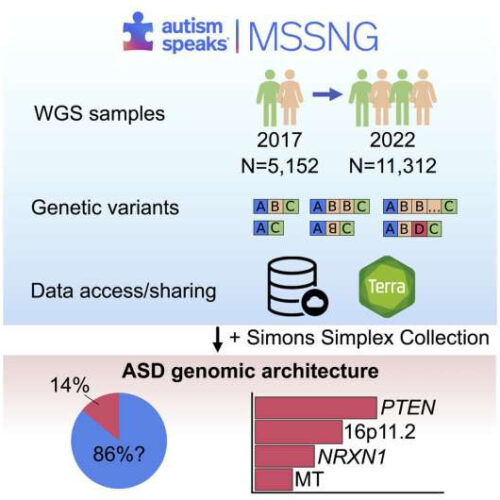
World’s largest autism whole genome sequencing study reveals 134 autism-linked genes
by The Hospital for Sick Children Graphical abstract. Credit: Cell (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.10.009 Researchers from The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) have uncovered new genes and genetic changes associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in the largest autism whole genome sequencing analysis to date, providing better understanding into the ‘genomic architecture’ that underlies this disorder. The study,...
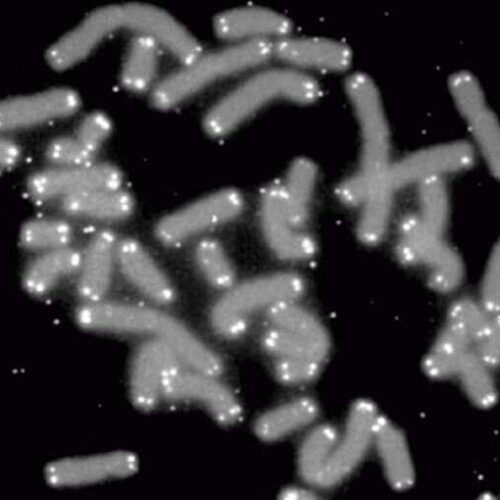
Making melanoma immortal: Scientists discover key genetic step in cancer’s race to live forever
by University of Pittsburgh Human chromosomes (gray) capped by telomeres (white). Credit: PD-NASA; PD-USGOV-NASA Scientists at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine have discovered the missing puzzle piece in the mystery of how melanoma tumors control their mortality. In a paper published in Science this week, Jonathan Alder, Ph.D. and his team describe how they discovered...
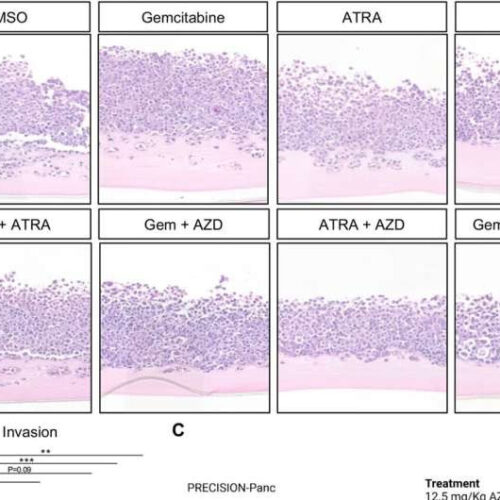
Research identifies new way to halt pancreatic cancer invasion by targeting healthy cells
by Queen Mary, University of London Inhibition of FGFR1 limits invasion in pre-clinical models of PDAC. A Representative H&E images of MIA PaCa-2: PS1 organotypics treated with 100 nM Gemcitabine, 1 μM ATRA, or 1 μM AZD4547 either alone or in combination for 7 days. B Quantification of invasion from A. Images representative of at least 3 biological repeats. Individual colors on graphs indicative...
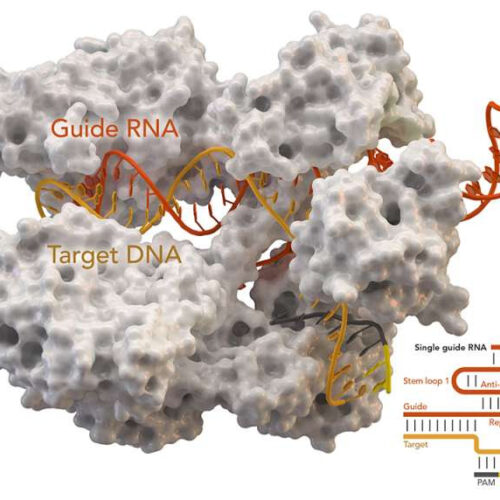
First use of CRISPR to substitute genes to treat patients with cancer
by University of California, Los Angeles CRISPR-associated protein Cas9 (white) from Staphylococcus aureus based on Protein Database ID 5AXW. Credit: Thomas Splettstoesser (Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 4.0) For the first time, scientists have used CRISPR technology to insert genes that allow immune cells to focus their attack on cancer cells, potentially leaving normal cells unharmed and increasing...
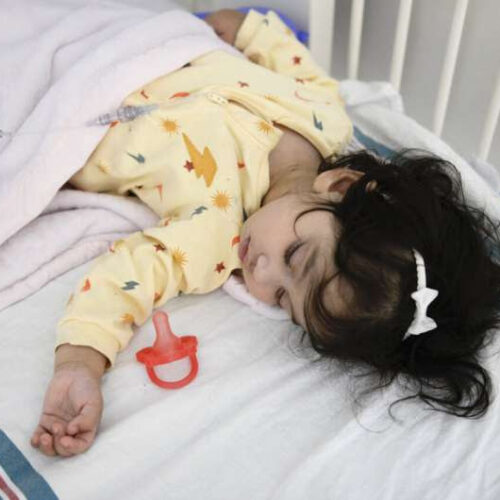
Rare, deadly genetic disease successfully treated in utero for first time
by University of California, San Francisco Patient Ayla Bashir. Credit: University of California, San Francisco Using a protocol developed at UC San Francisco, physicians have successfully treated a fetus with a devastating genetic disorder for the first time, and the child is now thriving as a toddler, a case study in the New England Journal of...
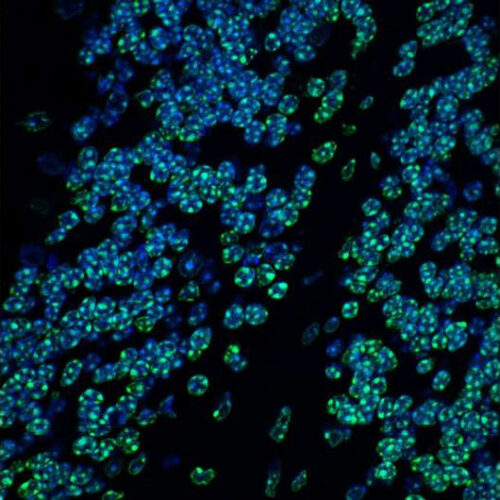
HUSH gene-silencing complex contributes to normal brain development and function
by IMBA- Institute of Molecular Biotechnology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences Magnification of the mouse cerebellum, the brain region that plays an important role in motor control. Nuclear DNA is shown in blue. In green is the tri-methylation of lysine 9 on histone H3 (H3K9me3), an indicator of silenced heterochromatin. Credit: ©Hagelkruys/IMBA The gene-silencing...
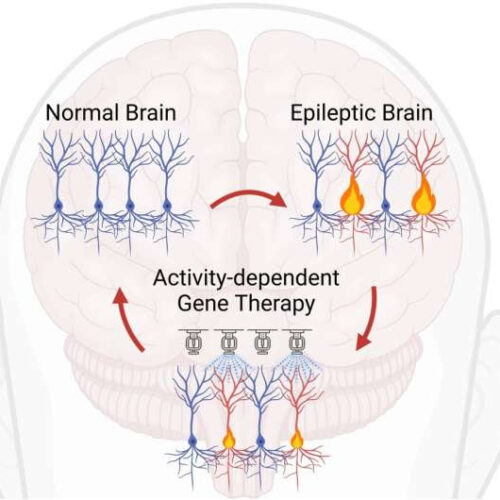
Gene therapy targeting overactive brain cells could treat neurological disorders
by University College London Schematic of the Activity-dependent Gene Therapy. Credit: Gabriele Lignani A new treatment for neurological and psychiatric diseases, that works by reducing the excitability of overactive brain cells, has been developed by UCL researchers. Many brain diseases, such as epilepsy, are caused by excessive activity of a small number of brain cells. These...