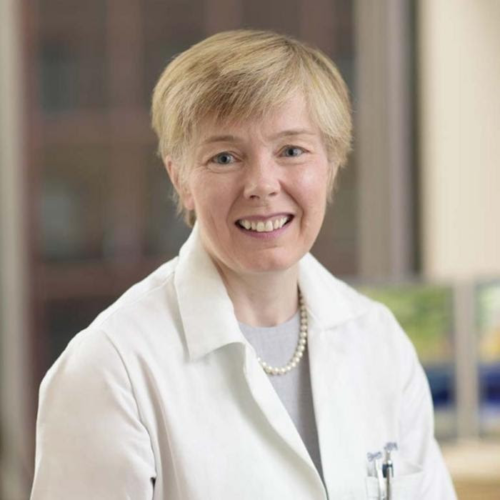
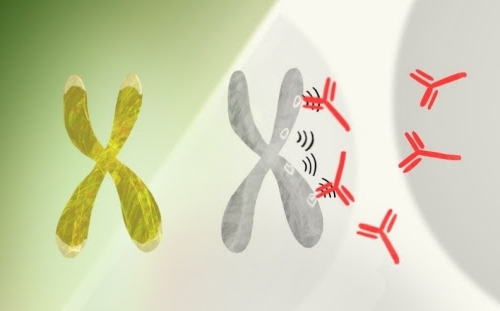
Research throws light on the mystery of why women are much more prone to autoimmune disorders: A molecule made by one X chromosome in every female cell can generate antibodies to a woman’s own tissues. By Bruce Goldman X chromosomes and autoimmunityIn every cell in a woman’s body, one X chromosome is disabled to ensure...
Category: <span>Immunology</span>
Newest COVID shots are 54% effective in preventing symptoms, CDC finds
by Mike Stobbe A Moderna Spikevax COVID-19 vaccine is seen at a drugstore in Cypress, Texas, Sept. 20, 2023. On Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said the updated COVID-19 vaccine was 54% effective at preventing symptomatic infection in adults. The shot became available last year as a replacement vaccine...
Immune cells lose ‘killer instinct’ in cancerous tumors – but functionality can be re-awakened
First study tracking how NK cells respond to the tumour microenvironment in real time discovered that stimulating the IL-15 pathway prevented the rapid loss of function and improved tumor controlPeer-Reviewed Publication UNIVERSITY OF BIRMINGHAM Some immune cells in our bodies see their ‘killer instinct’ restricted after entering solid tumours, according to new research. In a...
Vaccine targeting KRAS in pancreatic and colorectal cancer shows promise
Peer-Reviewed Publication MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENTER MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENTER MEDICAL ONCOLOGIST EILEEN O’REILLY HELPED LEAD A CLINICAL TRIAL INVESTIGATING A READY-MADE VACCINE AS A TREATMENT FOR PANCREATIC AND COLORECTAL CANCERS WITH CERTAIN KRAS MUTATIONS.CREDIT: MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING A new vaccine shows encouraging early results as a potential off-the-shelf treatment for certain patients...
UMass Chan advances research into long COVID, myalgic encephalomyelitis
By Sarah Willey The study discovered similarities in immune system dysfunction as a potential biomarker among people living with long COVID and myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome.A study led by UMass Chan Medical School viral immunologists Liisa Selin, MD, PhD, and Anna Gil, PhD, discovered similarities in immune system dysfunction as a potential biomarker among people living...
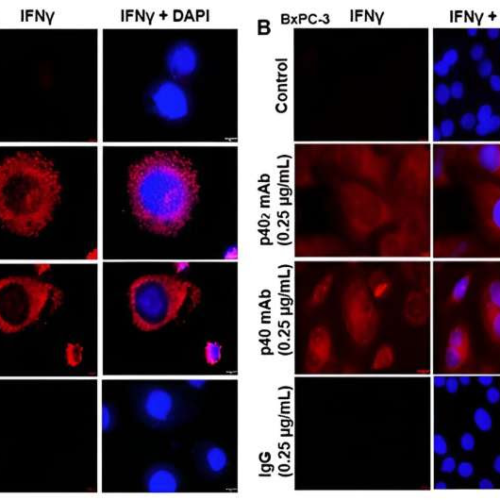
New potential immunotherapies for pancreatic cancer
by Rush University Medical Center Neutralization of p402 and p40 increases levels of IFN-γ in pancreatic cancer cells. Immunohistochemical analysis at 60× magnification of PANC-1 (A) and BxPC-3 cells (B) treated with p40 homodimer or p40 monomer were labeled with IFN-γ (red). DAPI was used to stain the nuclei. Cells positive for IFN-γ were counted and...
Genetically Modified Pluripotent Stem Cells May Evade Immunological Rejection After Transplantation
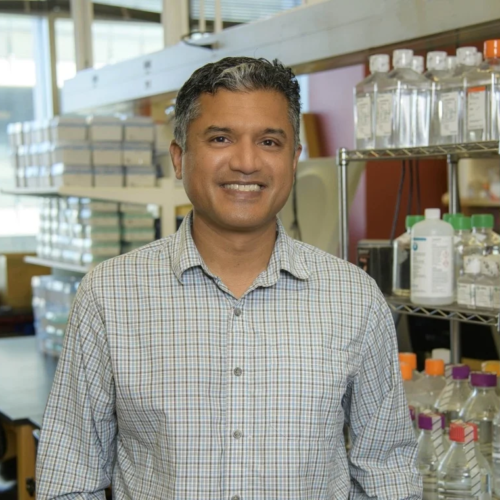
Researchers say the genetically engineered stem cells also could pave the way for new regenerative medicine treatments for diseases such as Type 1 diabetes. Deepta Bhattacharya, who is on the University of Arizona Health Sciences Center for Advanced Molecular and Immunological Therapies advisory council, is a professor of immunobiology in the UArizona College of Medicine...
The US eliminated measles in 2000: Why is it back now?
by Angela Roberts, The Baltimore Sun Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public DomainThe Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is urging health care providers to be “on alert” for patients with symptoms of measles—a virus declared eliminated in the U.S. in 2000—after nearly two dozen cases have been reported across the country in the past month. Between Dec....
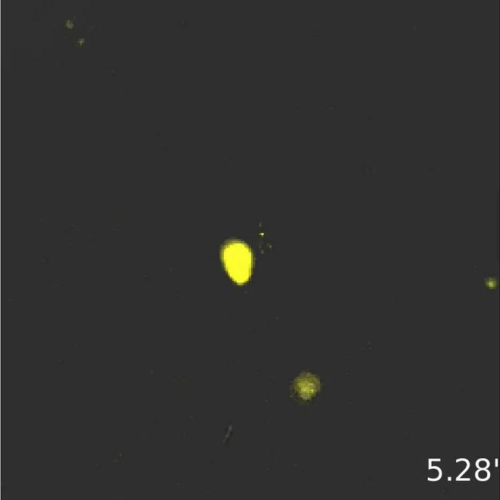
When and how immune cells decide to form pathogen memories
During infection, reversible switch permits flexible formation of memory T cells, long-lived blood cells that can remember pathogen encounters and respond upon reinfection.Peer-Reviewed Publication UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON SCHOOL OF MEDICINE/UW MEDICINE THIS MOVIE SHOWS A SINGLE NAIVE CD8 T CELL. A TYPE OF WHITE BLOOD CELL INVOLVED IN IMMUNITY ACTIVATING IN RESPONSE TO STIMULATION THROUGH...
Molecule can quickly, and briefly, boost white blood cell counts
Peer-Reviewed Publication YALE UNIVERSITY New Haven, Conn. — Treatment with a molecule known as A485 can quickly and temporarily increase levels of white blood cells, a critical part of the body’s immune system, an effect that is difficult to deliver with currently available pharmaceuticals, a new Yale study finds. In an experiment, the researchers found...