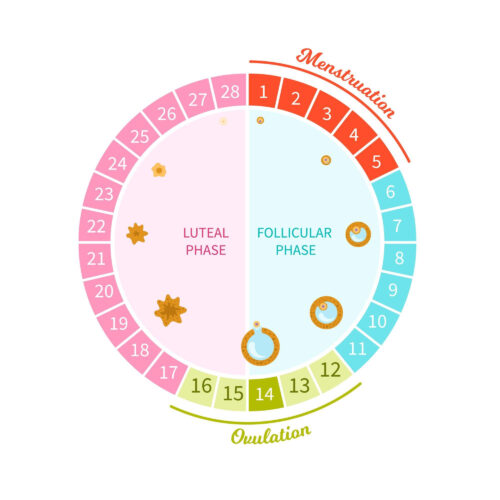
By Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta, Ph.D.Reviewed by Aimee Molineux Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a type of endocrine disorder characterized by an abnormal menstrual cycle and the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries. The condition is developed due to excessive production of male sex hormones (androgens) by the ovaries. Image Credit: pathdoc/Shutterstock Despite not having...
Category: <span>Metabolic</span>
Anti-tumor drug promotes Anti-tumor drug in mice
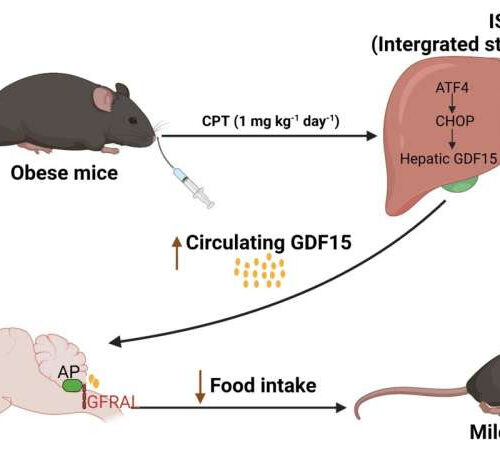
by Public Library of Science Proposed model for the anti-obesity effects of Camptothecin in obese mice. Created with biorender.com. Credit: Jun Feng Lu (CC BY 4.0, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) An anti-tumor drug promotes weight loss in mice at low doses by activating a natural hunger-suppressing pathway, according to a new study publishing February 24th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by...
TRAINING’ YOUR FAT MAY WARD OFF DISEASES AS YOU AGE
How well does your fat function? It isn’t a question that one gets asked very often. Nonetheless, research in recent years suggests that the function of our fat tissue, or adipose tissue, is central to why our bodies decay with age, and strongly linked to human diseases like diabetes 2, cancer, and obesity often develop...
Promising new drug target to treat diabetes and other metabolic diseases
By Rich Haridy February 14, 2022 A newly discovered compound heightens the expression of a protein that helps regulate insulin secretion from the pancreas Depositphotos A new preclinical study has demonstrated how an experimental drug can treat type 2 diabetes by increasing the expression of a recently discovered protein found to influence insulin signaling in...
‘Energy crisis’ in fat cells behind inflammation associated with obesity
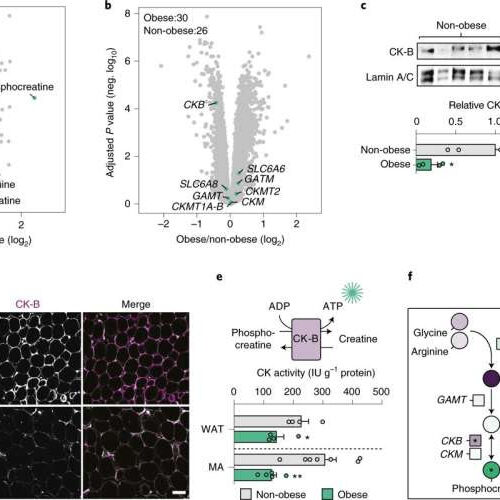
by Karolinska Institutet Fig. 1: Obesity is associated with altered phosphocreatine/creatine metabolism in human WAT. a, Polar metabolites in subcutaneous WAT of obese (n = 13) and non-obese (NO, n = 13) subjects (cohort 1) highlighting metabolites in the phosphocreatine/creatine pathway (green dots). Data are represented in a volcano plot with fold changes (log2) and adjusted P values (negative...
Researchers identify new method for stimulating signaling to improve metabolic health and possibly treat obesity
by Greg Glasgow, CU Anschutz Medical Campus Credit: CC0 Public Domain Following up on a 2018 study that identified an epigenetic modifier known as histone deacetylase 11 (HDAC11) as a potential therapeutic target for treating obesity and diabetes, researchers from the University of Colorado School of Medicine have published new research that finds HDAC11 regulates...
Can we harness intestinal cells to treat endocrine disorders?
by Nancy Fliesler, Children’s Hospital Boston Using a newly developed protocol, Daniel Zeve, MD, and David Breault, MD, have been able to derive human enteroendocrine cells from human intestinal stem cells via intestinal organoids. Credit: Daniel Zeve, Boston Children’s Enteroendocrine cells punch above their weight. Constituting just about 1 percent of intestinal cells, they produce,...
Do COVID-19 vaccinations increase the length of the menstrual cycle?
Interview conducted by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Feb 4, 2022 Thought LeadersProfessor Alison EdelmanProfessor of Obstetrics and GynecologyOregon Health & Science University School of Medicine In this interview, we speak to Professor Alison Edelman about her latest research that investigated the effects COVID-19 vaccinations have on the menstrual cycle. Please can you introduce yourself and tell...
Optimizing indoor light conditions to mimic the natural light-dark cycle could help mitigate adverse metabolic effects
by Diabetologia Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain A new study published in Diabetologia finds that the timing of exposure to bright light can have a significant influence on postprandial (post-meal) glucose metabolism, thermoregulation, and energy expenditure during sleep in overweight, insulin-resistant adults. The research was conducted by Jan-Frieder Harmsen, Patrick Schrauwen, and colleagues at the Department of Nutrition...
New tech could reverse diseases, including IBS and diabetes, using intestinal cells
A newly developed technology platform has the potential to treat diseases like diabetes, IBS, and obesity by using enteroendocrine (EE) cells found in human intestinal cells, according to a recent study. Although enteroendocrine cells make up only about 1% of intestinal cells, they produce around fifteen different hormones that play a role in regulating digestion...