by University of East Anglia Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain The severity of a diarrheal disease could be down to the bacteria in your gut, according to new research from the University of East Anglia. Cryptosporidiosis is responsible for over 100,000 deaths annually, predominantly in children under five. It also affects animals, and a new study published...
Category: <span>Microbiology</span>
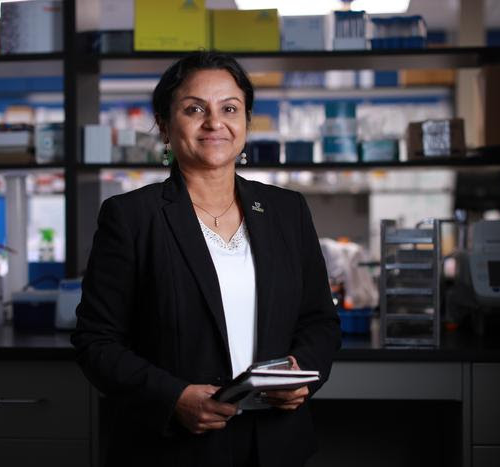
A new connection between the gut microbiota and prostate inflammation in aging men
by Impact Journals LLC Microscopic image of the expression of the cytoplasmic immunohistochemical reaction to IL-6. Credit: Aging (2023). DOI: 10.18632/aging.205091 A new research paper titled “Tissue immunoexpression of IL-6 and IL-18 in aging men with BPH and MetS and their relationship with lipid parameters and gut microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids” has been published...
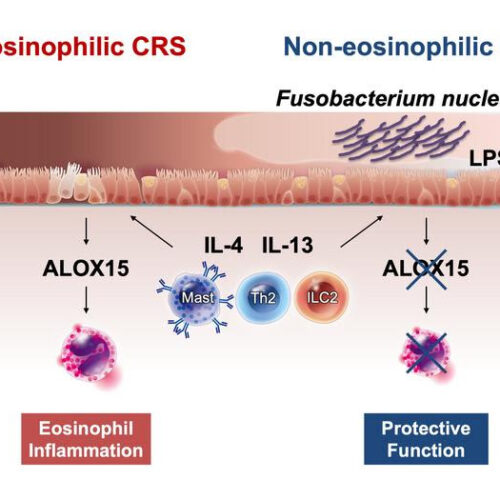
Nasal microorganism to the rescue? Study confirms protective role of bacterium in chronic rhinosinusitis
Scientists investigate how microbes in the nasal mucosa may influence the pathophysiology of chronic sinusitis Peer-Reviewed Publication UNIVERSITY OF FUKUI EXPERIMENTS CONDUCTED IN A RECENT STUDY BY RESEARCHERS FROM JAPAN SUGGEST THAT THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDES (LPS) PRODUCED BY THE BACTERIAL SPECIES F. NUCLEATUM SUPPRESSES THE EXPRESSION OF ALOX15 AND PREVENTS EXCESSIVE INFILTRATION OF EOSINOPHILS, WHICH CAUSES...
Different antibiotics’ effects on gut microbes may impact hypertensive organ damage
by American Society of Nephrology Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain New research in rodents indicates that altering gut microbes may affect the development of organ damage associated with hypertension. The findings will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023, November 1–5. For the study, scientists used narrow-spectrum antibiotics to specifically deplete Gram-negative or Gram-positive bacteria in rats...
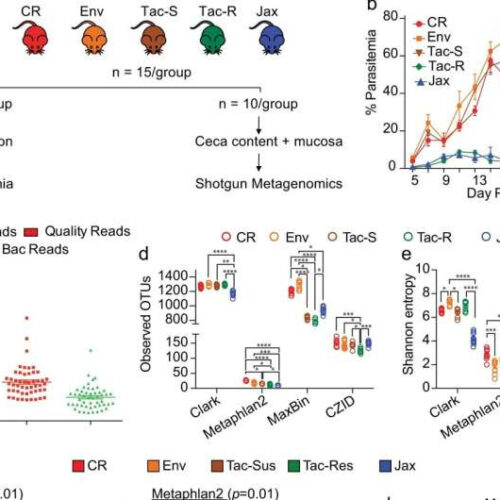
Study links specific gut bacteria to increased risk of severe malaria
by Indiana University Shotgun metagenomics revealed distinct gut microbiota composition and genetic potential within and between the hyperparasitemia resistant and susceptible mice. a C57BL/6 mice were acquired from four different vendors (N = 15/group): Charles River Laboratories (CR), Envigo (Env), Taconic Biosciences (Tac), and Jackson Laboratory (Jax). Mice from Taconic Biosciences were obtained from two different facilities with...
Fungus in the gut linked to severe COVID-19
By Rich Haridy October 24, 2023 High levels of antibodies targeting Candida albicans, a common gut fungus, were linked to the most severe cases of COVID DepositphotosOver the last few years one of the persistent mysteries of SARS-CoV-2 infections has been the seeming randomness in how severe COVID-19 can be from person to person. Beyond those...
Study shows engineered gut bacteria can treat hypertension
The finding from scientists at The University of Toledo opens new doors in the pursuit of harnessing our body’s own microbiome to regulate blood pressure Peer-Reviewed Publication UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO DR. BINA JOE, A DISTINGUISHED UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR AND CHAIR OF THE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY IN THE UTOLEDO COLLEGE OF MEDICINE AND LIFE SCIENCES,...
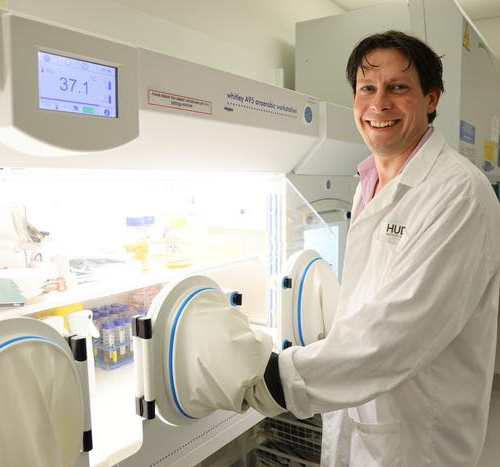
Deep dive into the gut unlocks new disease treatments
Understanding the relationships within the microbiome opens the door to a new world of medical opportunities for conditions from Inflammatory Bowel Disease to infections, autoimmune diseases and cancers.Peer-Reviewed Publication HUDSON INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL RESEARCH CREDIT: HUDSON INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL RESEARCH The more diverse species in your gut, the better it is for your health. Now...
New Algorithm Cleans Microbiome Data With Unprecedented Efficiency
None of us are born with a fully functioning immune system and microbiome, and the first few months of life are crucial for establishing strong lifelong defenses. Better understanding how germs influence the development of human immunology would reap innumerable benefits, but for years, scientists haven’t been able to answer the most basic question: where does inoculation...
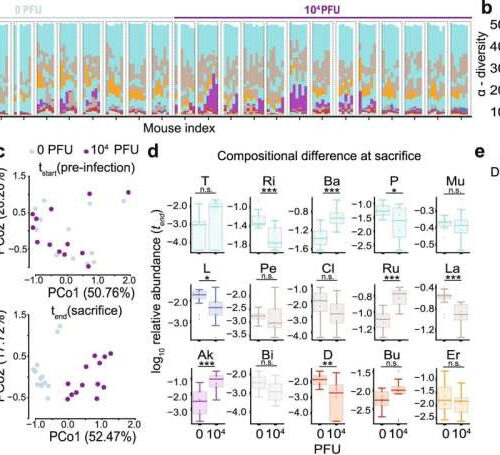
COVID-19 virus increases risk for other infections by disrupting normal mix of gut bacteria
by NYU Langone Health SARS-CoV-2 infection causes gut microbiome alterations in mice. K18-hACE2 mice were infected intranasally with 0 or 104 PFU of SARS-CoV-2. Fecal samples for microbiome analyses were collected daily from day 0 (before infection) until sacrifice; mice were sacrificed on days 5–7. Results show pooled data from three independent experiments with n = 3–5 mice...