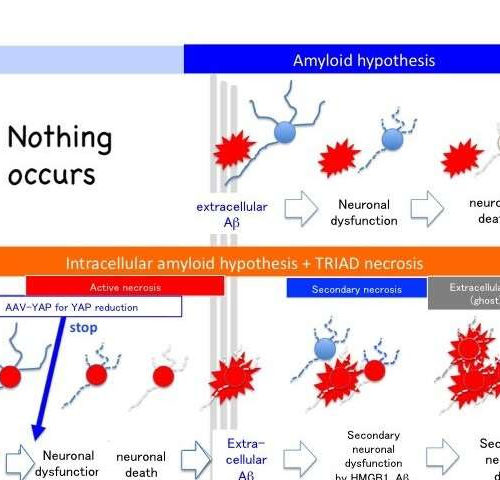
by Tokyo Medical and Dental University Alzheimer’s remains the leading cause of dementia in Western societies, with some estimates suggesting that as many as 24 million people worldwide are living with the disease. Alzheimer’s is characterized by a progressive decline in cognitive ability that eventually affects even basic functions such as walking and swallowing. The...
Category: <span>Neuroscience</span>
New Brazilian study describes neural inflammatory processes in lab-developed human cells
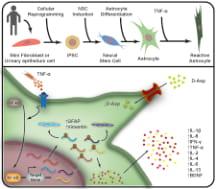
Astrogliosis, an inflammation that occurs in the brain tissue, is common to Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases D’OR INSTITUTE FOR RESEARCH AND EDUCATION Astrocytes are neural cells with many important functions in the nervous system. The inflammation of these cells occurs in brain infections and neurodegenerative disorders, a process called astrogliosis. Aware of this fundamental process...
What are the symptoms of dyslexia by age?
Dyslexia is a condition that interferes with a person’s ability to develop and use language skills. People tend to associate dyslexia with reading problems, but people with this condition can also have a hard time with some math problems, as well as with writing and pronouncing words. Dyslexia does not have anything to do with...
HOW MUCH SLEEP KIDS GET AFFECTS THEIR MENTAL HEALTH
FEBRUARY 4TH, 2020 POSTED BY ALICE SCOTT-WARWICK There’s a link between children’s sleep duration and depression, anxiety, impulsive behavior, and poor cognitive performance, researchers report. In a new paper in Molecular Psychiatry, researchers examine the relationship between sleep duration and brain structure in 11,000 children ages 9-11 from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development dataset. The...
Light therapy holds promise for people with bipolar disorder
by Kerry Blackadar, University of British Columbia But much less is known about the potential benefits of light therapy for people with bipolar disorder, one of the leading causes of disability worldwide. In a meta-analysis recently published in the Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, Dr. Raymond Lam—a professor in the department of psychiatry, director of the...
Tumbleweeds or fibrils: Tau proteins need to choose
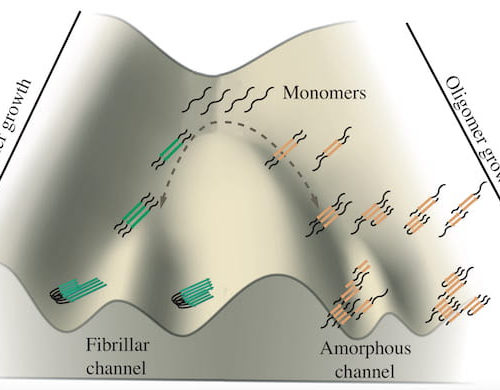
New simulations by Rice University scientists tell a tale of two taus and how they relate to neurological disease. Their work suggests tau proteins take either of two paths to form aggregates suspected of promoting, and perhaps causing, Alzheimer’s and Pick’s (aka frontotemporal dementia) diseases. Precisely why remains a mystery, but figuring it out offers...
Flickering light mobilizes brain chemistry that may fight Alzheimer’s
by Ben Brumfield, Georgia Institute of Technology For over a century, Alzheimer’s disease has confounded all attempts to treat it. But in recent years, perplexing experiments using flickering light have shown promise. Now, researchers have tapped into how the flicker may work. They discovered in the lab that the exposure to light pulsing at 40...
Army develops big data approach to neuroscience
by The Army Research Laboratory A big data approach to neuroscience promises to significantly improve our understanding of the relationship between brain activity and performance. To date, there have been relatively few attempts to use a big-data approach within the emerging field of neurotechnology. In this field, the few attempts at meta-analysis (analysis across multiple...
Researchers provide new insights into the pathogenesis of epilepsy
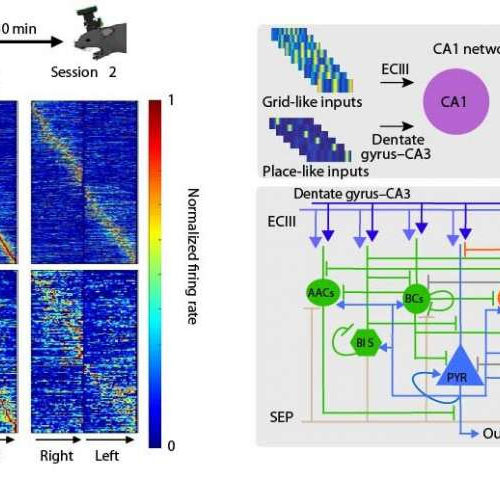
by Foundation For Research and Technology – Hellas, Foundation for Research and Technology – Hellas The laboratories of Drs. Peyman Golshani at the University of California in Los Angeles, Tristan Shuman at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, and Panayiota Poirazi at the Institute of Molecular Biology & Biotechnology (IMBB) at the Foundation for Research...
Neurodevelopment team locates a gene that helps control puberty and human reproduction
by University at Albany Thousands of Americans suffer from the delay or non-appearance of puberty. While the underlying cause is failure in the correct action of the hypothalamic hormone GnRH, the precise genetic causes have not been fully understood. A UAlbany biologist and his research team have now identified a particular gene and its mutation...