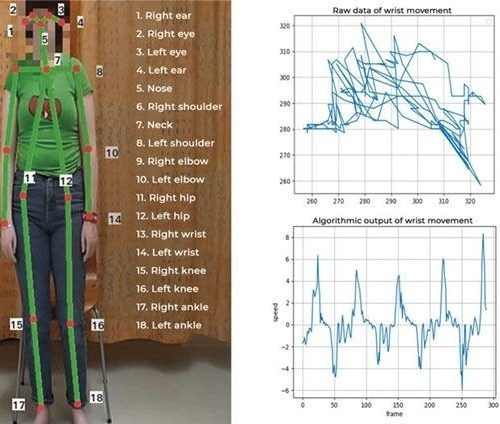
Fast, reliable and automatic assessment of the severity of myoclonic jerks from video footage is now possible, thanks to an algorithm using deep convolutional neural network architecture and pretrained models that identify and track key points in the human body. Published in Seizure, the study is a joint effort by the Epilepsy Centre at Kuopio...
Category: <span>Neuroscience</span>
Differences between deep neural networks and human perception
Stimuli that sound or look like gibberish to humans are indistinguishable from naturalistic stimuli to deep networks. When your mother calls your name, you know it’s her voice — no matter the volume, even over a poor cell phone connection. And when you see her face, you know it’s hers — if she is far...
Scientists identify new biochemical ‘warning sign’ of early-stage depression
High levels of anthranilic acid in blood are indicative of an increased risk of developing major depressive disorder, new study from Japan says FUJITA HEALTH UNIVERSITY Chronic pain, or inflammation, is believed to be one of the major factors in the onset of major depressive disorder. Therefore, to better understand what happens physiologically during depression,...
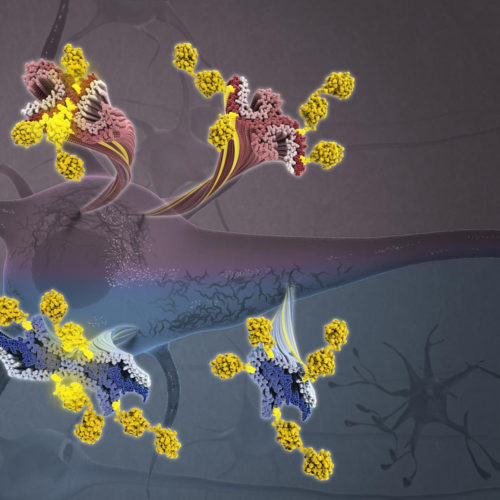
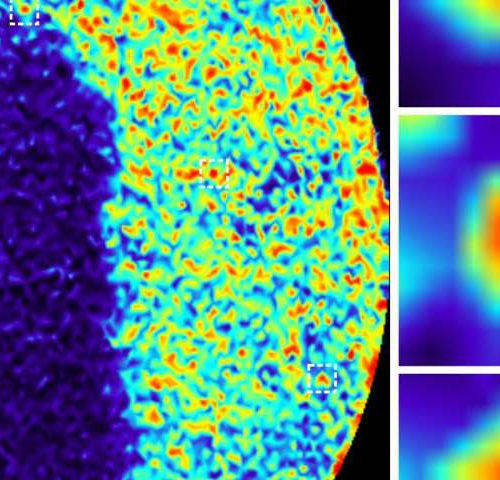
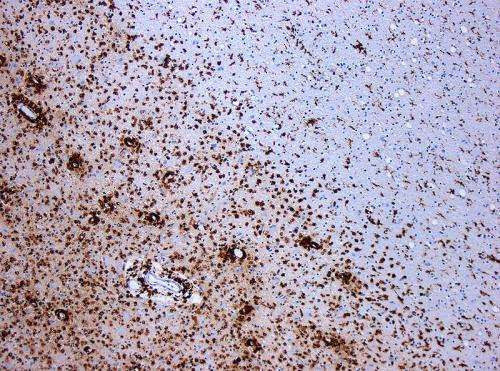
Toxic protein, linked to Alzheimer’s and neurodegenerative diseases, exposed in new detail
Columbia-led team harnesses two powerful technologies to identify promising targets for diagnosing and treating neurodegenerative diseases THE ZUCKERMAN INSTITUTE AT COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY NEW YORK — The protein tau has long been implicated in Alzheimer’s and a host of other debilitating brain diseases. But scientists have struggled to understand exactly how tau converts from its normal,...
Study in mice: Brain cells long thought of as passive play key role in memory
by Mark Dallas, The Conversation Microglia are resident immune cells in your brain that act as first responders, always on the lookout for trouble. Accounting for about 10% of our brain cells, they were historically thought of as passive bystanders in the brain until injury or infection kicked them into action. These cells were first...
Virtual reality programs support the treatment of children with acquired brain injury
by Estonian Research Council The use of virtual environments is a new and fast-developing field in pediatric neurorehabilitation. The first longitudinal study in Estonia on the cognitive and social rehabilitation of children with acquired brain injury was completed at the University of Tartu, confirming the efficiency of using computer-based programs and virtual reality for improving...
Brain training does not improve early number skills, say researchers
by Emma Griffiths, University of Sheffield Psychologists at the University of Sheffield have identified that core thinking skills are crucial in developing early number skills, and why children might differ widely in their early maths ability. Research from the University of Sheffield, funded by the Nuffield Foundation, investigated why children differ so much in their...
Hard times are coming: Brain tissue stiffness is crucial for neurogenesis
by Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres In mammalian adult brains, neural stem cells are only present in few specific regions, so-called niches. Only these niches are capable of generating new neurons. For the first time, researchers have defined the proteome of these niches, the entire set of expressed proteins, and compared it to other...
Researchers find synchronization of memory cells critical for learning and forming memories
by University of New Hampshire The phrase “Pavlov’s dogs” has long evoked images of bells, food and salivating dogs. Even though this tried-and-true model of repetitive patterns mimics a variety of learning processes, what happens on a cellular level in the brain isn’t clear. Researchers at the University of New Hampshire took a closer look...
New discovery provides hope for improved multiple sclerosis therapies
by Trinity College Dublin Scientists from Trinity College Dublin have made an important discovery that could lead to more effective treatments for people living with multiple sclerosis (MS) and other autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis. Their work highlights the significant potential of drugs targeting a specific immune molecule (IL-17) implicated in MS. Demyelination...