by Norwegian University of Life Sciences (NMBU) Sabina Leanti La Rosa. Credit: Norwegian University of Life Sciences (NMBU) Have you heard about the food additive E415? It is also known as xanthan gum. Most likely, you eat it several times a week. Xanthan gum is used in everyday foods such as baked goods, ice cream...
Category: <span>Nutrition & Dietics</span>
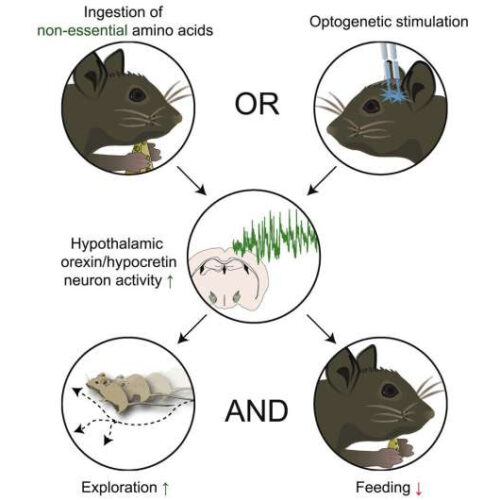
Ubiquitous nutrients suppress appetite and promote movement
by Fabio Bergamin, ETH Zurich Graphical abstract. Credit: Current Biology (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.02.067 In experiments on mice, researchers at ETH Zurich show that non-essential amino acids act as appetite suppressants and promote the urge to move. Their research is published in Current Biology and provides insight into the neural mechanism that controls this behavior. Proteins can suppress appetite, so...
Hold the salt: Study reveals how reducing sodium intake can help patients with heart failure
by University of Alberta Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain For the past century people with weak hearts have been told to lower their salt intake, but until now there has been little scientific evidence behind the recommendation. The largest randomized clinical trial to look at sodium reduction and heart failure reported results simultaneously in The Lancet and at the American College...
How food and diet impact the treatment of disease
by The City University of New York Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Today, the Center for Food As Medicine (famcenter.org) and the Hunter College NYC Food Policy Center (nycfoodpolicy.org) released its groundbreaking, 335 page (with more than 2500 citations), first ever, academic narrative review and report of the food as medicine movement, titled “Food As Medicine:...
Nordic diet may improve cholesterol, blood sugar, even without weight loss
New research explores the health benefits of the so-called Nordic diet. Morten Falch Sortland/Getty Images Researchers investigated the health effects of a healthy Nordic diet (HND) using metabolic analysis. They found that the diet positively affects glucose metabolism, cholesterol, and cardiometabolic risk. They conclude that metabolic analysis is an effective way to assess dietary outcomes....
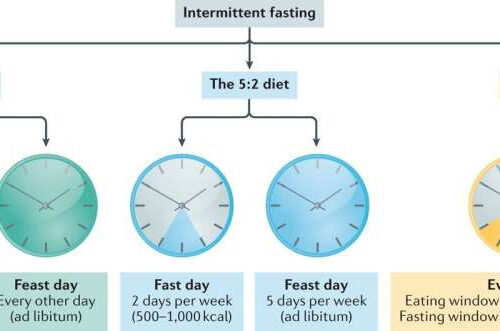
Research team provides guidelines, recommendations for intermittent fasting
by University of Illinois at Chicago Credit: Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41574-022-00638-x A University of Illinois Chicago team has summarized research on intermittent fasting to provide insights into its effects on the body and to provide advice for incorporating these diets in everyday life. They have also presented recommendations for future research into these popular diet...
Trial Testing Cocoa Flavanol Supplement Shows Promise for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk
Large-scale randomized trial found signs of preventive cardiovascular effects for cocoa flavanols, including a 27 percent reduction in the secondary endpoint of cardiovascular death. There was a 10 percent reduction in total cardiovascular events, the trial’s primary outcome, that was not statistically significant. The first large-scale trial to test the long-term effects of a cocoa flavanol supplement...
The Green Mediterranean diet modifies the bacterial population in our gut, with specific bacteria mediating weight loss and cardiac risk reduction
BEN-GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV BEER-SHEVA, Israel, March 10, 2022 – The green Mediterranean diet (MED) has a striking effect on the microbial population of the human gut (i.e., the “gut microbiome”). In a large-scale clinical interventional trial- the DIRECT PLUS – the gut microbiome of green MED dieters was enriched with bacteria that are...
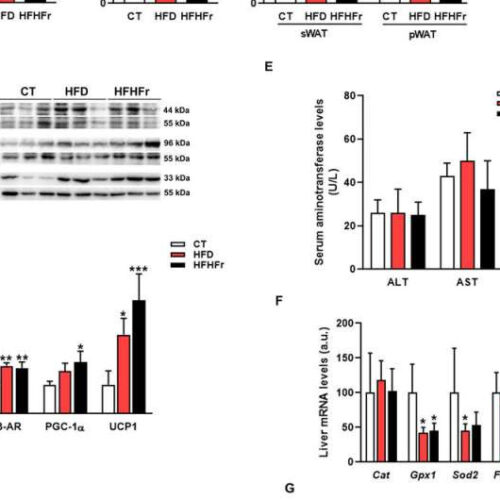
A new study relates liquid fructose intake to fatty liver disease
by University of Barcelona Effect of HFD and HFHFr on caloric intake, body weight, thermogenic markers in BAT, and inflammatory markers in liver: A) Bar plots showing the AUC of caloric intake for the full length of the study (3 months) corresponding to the three experimental groups studied: Control (CT), high fat diet (HFD), and...
MS: Keto diet may improve fatigue, mood, and quality of life
A recent study suggests that the keto diet might help some people with MS. martin-dm/Getty Images A preliminary study has found that participants with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS) who followed a ketogenic diet for 6 months experienced improvements in fatigue, mood, and the quality of life. The study also demonstrated improvements in walking distance, disability,...