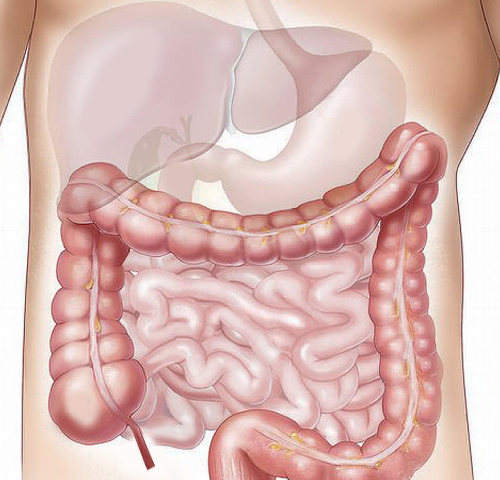
by Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania After one consumes food or a beverage containing fructose, the gastrointestinal system, or gut, helps to shield the liver from damage by breaking down the sugar before it reaches the liver, according to a new multi-center study led by researchers in the Perelman School of...
Category: <span>Nutrition & Dietics</span>
Oat and rye bran fibres alter gut microbiota, reducing weight gain and hepatic inflammation
In a newly published experimental study, the consumption of dietary fibre from oat and rye brans supported the growth of beneficial gut microbiota, which in turn ameliorated cholesterol metabolism, enhanced gut barrier function and reduced hepatic inflammation. In addition, diets enriched with oat or rye bran were shown to attenuate weight gain. The effects of...
Raw milk may do more harm than good
Not properly stored, it’s a source of antibiotic-resistant microbes UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – DAVIS Raw or unpasteurized cows’ milk from U.S. retail stores can hold a huge amount of antimicrobial-resistant genes if left at room temperature, according to a new study from researchers at the University of California, Davis. The study also found bacteria that...
Daily coffee may lower risk for developing arrhythmia
Regular coffee consumption is associated with a significantly lower risk for arrhythmias, according to a study presented recently as part of the Heart Rhythm Society online meeting: HRS 2020 Science. Eun-Jeong Kim, M.D., from the University of California in San Francisco, and colleagues investigated the association between habitual caffeine consumption and the risk for arrhythmia...
Study reveals plant compound beats sugar cravings
by Massey University With millions of people around the world still confined to their homes due to COVID-19 lockdown restrictions, many have reported over-indulging in home-baking, snacks and sugary treats, potentially leading to increases in body weight. But researchers at Massey University may have found a solution by investigating a plant compound that showed a...
Transgenic rice containing anti-hypertensive peptides lowers blood pressure in hypertensive rats
Reviewed by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. In the future, taking your blood pressure medication could be as simple as eating a spoonful of rice. This “treatment” could also have fewer side effects than current blood pressure medicines. As a first step, researchers reporting in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistryhave made transgenic rice that contains...
Premature epigenomic aging acts like a ‘sleeper cell’ that is awakened by Western-style diet
by Baylor College of Medicine The epigenome is sometimes referred to as the “software” or “operating system” of the genome. It comprises small chemical modifications to DNA and the proteins that make up our chromosomes, and controls the activity of all the genes within the genome. During early life, as our organs develop, the epigenome...
Why an apple a day could keep multiple sclerosis away: Compound that gives the fruit’s skin its sheen could help reverse devastating damage caused by the disease
Chemical found in apple peel could transform multiple sclerosis treatment Compound could be turned into the first drug that reverses disease’s damage Testing on mice, paralysed animals given ursolic acid were able to walk again A chemical in apple peel could transform the treatment of multiple sclerosis, research reveals. The compound that gives apple skin...
Sugar breaks down neural circuits that may cause us to overeat
By Nick Lavars June 09, 2020 It is well known that consuming food and drink high in sugar is not great for us, but scientists are continuing to unravel the intricacies of how the sweet stuff drives negative health outcomes. The latest finding comes from researchers at the University of Michigan, who through studies in...
Female athletes at risk for nutritional deficiencies
Lack of proper nutrition education may affect female athletes’ performance and long-term health, says Rutgers researcher RUTGERS UNIVERSITY Two decades of research among female athletes over the age of 13 years shows that a lack of nutrition knowledge about what they need to eat to stay healthy and compete may contribute to poor performance, low...