by British Medical Journal Reasonably good evidence suggests that most diets result in similar modest weight loss and improvements in cardiovascular risk factors over a period of six months, compared with a usual diet, finds a study published by The BMJ today. Weight reduction at the 12 month follow-up diminished, and improvements in cardiovascular risk...
Category: <span>Nutrition & Dietics</span>
The Danger of Fast Carbs
Processed carbohydrates have become a staple of the American diet, and the consequences are wreaking havoc on our bodies. I stood in the supermarket a couple of years ago examining the Nutrition Facts label on a box of breakfast cereal and realized that it did not tell me all I needed to know about what...
Too much salt weakens the immune system
by University of Bonn A high-salt diet is not only bad for blood pressure, but also for the immune system. This is the conclusion of a current study under the leadership of the University Hospital Bonn. Mice fed a high-salt diet were found to suffer from much more severe bacterial infections. Human volunteers who consumed...
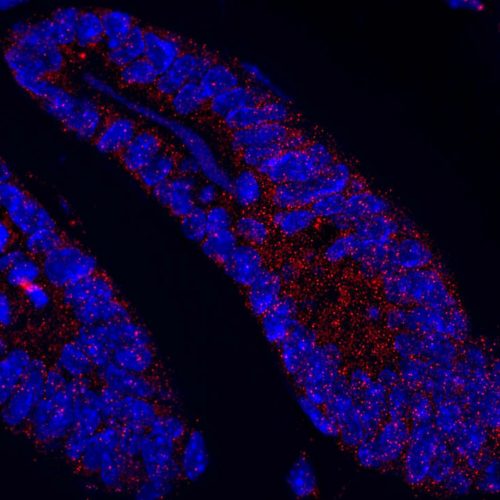
Loss of protein disturbs intestinal homeostasis and can drive cancer
UNIVERSITY OF ZURICH Colorectal carcinoma (CRC), the most common form of intestinal cancer, is the second leading cause of cancer related death worldwide. While some patients have a genetic predisposition to the disease, the majority of cases are sporadic and largely influenced by the ever-increasing “Western lifestyle”, which includes obesity, poor diet and physical inactivity.
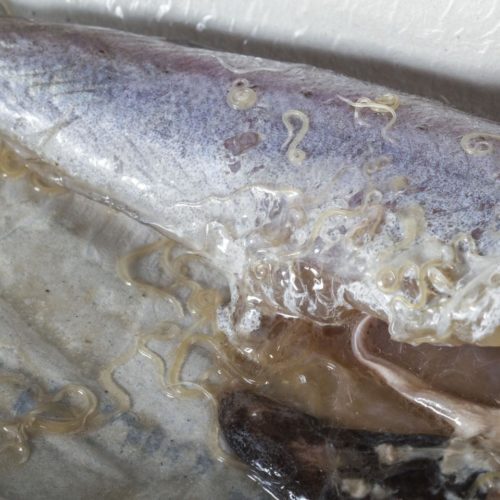
‘Sushi parasites’ have increased 283-fold in past 40 years
UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON The next time you eat sashimi, nigiri or other forms of raw fish, consider doing a quick check for worms. A new study led by the University of Washington finds dramatic increases in the abundance of a worm that can be transmitted to humans who eat raw or undercooked seafood. Its 283-fold...
Diet has an impact on the multiple sclerosis disease course
Neurology RUHR-UNIVERSITY BOCHUM The short-chain fatty acid propionic acid influences the intestine-mediated immune regulation in people with multiple sclerosis (MS). This has been shown by a team from the Department of Neurology of Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) at St. Josef-Hospital in an international study headed by Professor Aiden Haghikia. The application of propionic acid in addition...
Study shows low carb diet may prevent, reverse age-related effects within the brain
by Stony Brook University A study using neuroimaging led by Stony Brook University professor and lead author Lilianne R. Mujica-Parodi, Ph.D., and published in PNAS, reveals that neurobiological changes associated with aging can be seen at a much younger age than would be expected, in the late 40s. However, the study also suggests that this...
Guidance issued for food intake in inflammatory bowel disease
(HealthDay)—In an article from the International Organization for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, published online Feb. 14 in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, recommendations are presented regarding specific food consumption for patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Arie Levine, M.D., from the Wolfson Medical Center at Tel Aviv University in Israel, and colleagues reviewed the...
Eating meat: links to chronic disease might be related to amino acids – new findings
by Laura Brown, The Conversation Plant-based diets have been popular in the media recently, but research shows that going vegetarian or vegan isn’t only good for the environment, but for our health, too. Meat-rich diets are linked to a range of health problems, from heart disease and strokes to type two diabetesand some cancers. People...
People who eat a big breakfast may burn twice as many calories
Study finds eating more at breakfast instead of dinner could prevent obesity THE ENDOCRINE SOCIETY WASHINGTON–Eating a big breakfast rather than a large dinner may prevent obesity and high blood sugar, according to new research published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. Our body expends energy when we digest food for...