(A) Schematic illustration of the LMO7 molecule. (B) Representative histological images showing fluorescence expression in the left SI of a mouse. (C) Illustration of the timeline of events within a single day of imaging. (D) Schematic of the experimental setup used to image bioluminescence in the mouse. Credit: NeuroImage (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2024.120882 University of Rochester researchers have...
Category: <span>parkinsons</span>
Direct Brain A-Dopamine Infusion Promising for Parkinson’s Disease
PHILADELPHIA — Continuous intracerebroventricular administration of an anaerobic dopamine formulation (A-dopamine) appears safe in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) and may avoid complications associated with levodopa, results from a first in-human trial suggest. A-dopamine induced a dose-dependent improvement in motor symptoms in refractory patients with severe levodopa complications and had a “really great” safety profile, said study investigator...
Innovative technology may enable early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease
News Release 16-Sep-2024 Breakthrough from Tel Aviv University: Peer-Reviewed PublicationTel-Aviv University image: Research team (Left to right) Prof. Uri Ashery and PhD candidate Ofir Sade. Credit: Tel Aviv University The researchers: “Our technology will enable the detection of initial signs of Parkinson’s at the cellular level up to 20 years before the first motor symptoms...
Erasing ‘bad memories’ to improve long term Parkinson’s disease treatment – Parkinson’s
by Katherine Gaither, University of Alabama at Birmingham Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Common treatments for Parkinson’s disease can address short-term symptoms, but can also cause extensive problems for patients in the long run. Namely, treatments can cause dyskinesia, a form of uncontrollable movements and postures. In a recent study published in The Journal of Neuroscience,...
Another 3 common pesticides are now linked to Parkinson’s disease risk
Three more pesticides commonly used in the United States have now been linked to heightened Parkinson’s risk. Image credit: Abstract Aerial Art/Getty Images.Parkinson’s disease prevalence is growing fast, and similar to some other neurological conditions, its causes are unclear.The potential impact of chemicals that are toxic to neurons in the part of the brain affected...
Mutation provides insights into mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease
by Olivia Dimmer, Northwestern University sites in iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons. (A and B). Credit: Journal of Cell Biology (2024). DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202304042A mutated protein expressed in lysosomes may contribute to Parkinson’s disease, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study published in the Journal of Cell Biology. Parkinson’s disease is the second-most common neurodegenerative disorder in the...
A newly discovered receptor appears to protect against Parkinson’s disease—but only in females
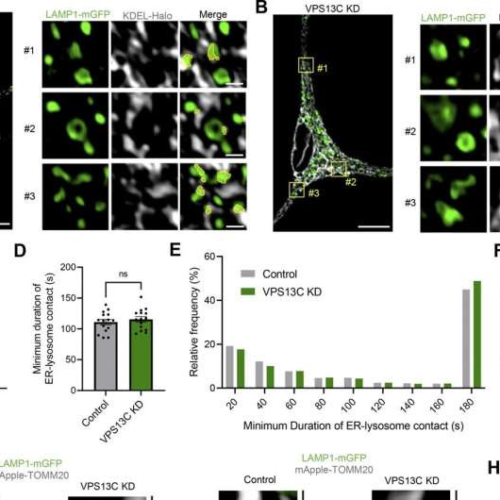
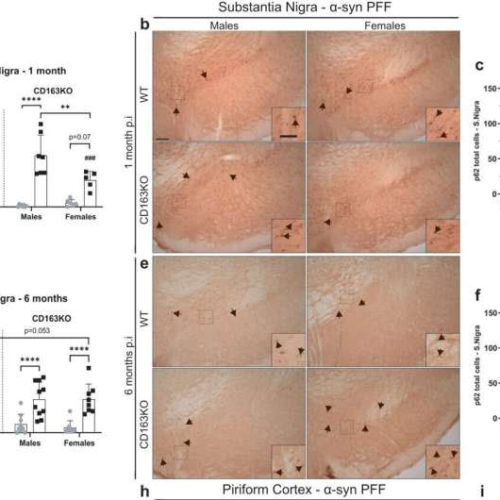
by Marina Romero-Ramos, Aarhus University Differential expression of p62/SQSTM1 autophagy marker in the substantia nigra, piriform cortex and amygdala after α-syn PFF injection. Bar graphs with individual points illustrate the total number of p62+ cells in the SN at a 1 and d 6 months p.i. b Representative images of p62/SQSTM1 immunostaining in α-syn PFF animals...
Targeting the mRNA of ‘undruggable’ proteins in the fight against Parkinson’s disease
by Justin Jackson , Medical Xpress Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainResearchers at the Scripps Research Institute, Florida, have developed a new method to counteract α-synuclein protein levels by targeting the mRNA that forms them. The strategy unlocks many research doors with potential therapeutic approaches for addressing neurodegenerative diseases. In a paper, “Decreasing the intrinsically disordered protein α-synuclein...
Research reveals how a malfunctioning mechanism can lead to Parkinson’s disease
by Ruhr-Universitaet-Bochum NEMO is associated with pathological protein aggregates. Credit: Nature Communications (2023). DOI:10.1038/s41467-023-44033-0 Researchers have identified a mechanism that promotes the breakdown of harmful protein deposits. If it malfunctions, it can lead to Parkinson’s disease. NEMO, a protein that is primarily associated with signaling processes in the immune system, prevents the deposition of protein aggregates...
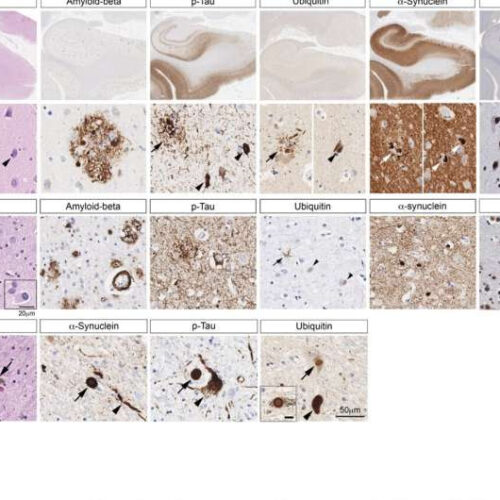
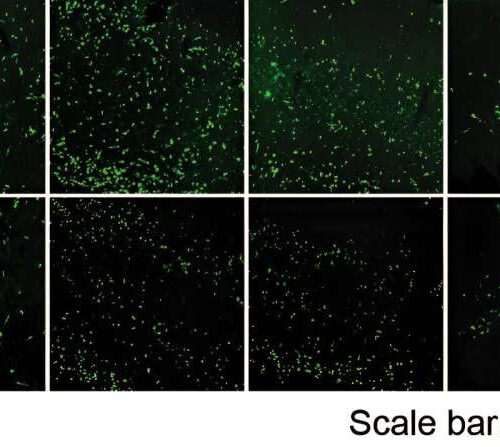
New findings about key pathological protein in Parkinson’s disease open paths to novel therapies
by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Second row shows how rapamycin dampens alpha-synuclein protein production in a magnified area of a mouse brain. Credit: Mohammed Khan and Ted Dawson, Johns Hopkins Medicine A so-called pathological protein long associated with Parkinson’s disease has been found in a new study to trigger cells to increase protein synthesis,...