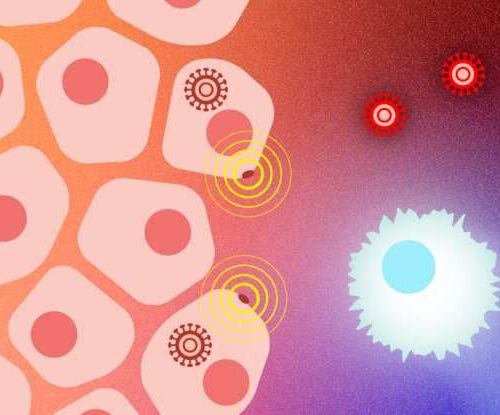
by Allessandra Dicorato, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard Credit: Susanna Hamilton, Broad Communications Peptides encoded by unexplored regions of the SARS-CoV-2 genome provoke strong immune responses compared to other known peptides. Current COVID-19 vaccines are effective at preventing severe disease, including infection caused by known variants of concern. But new variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus...
Category: <span>Peptides</span>
New drugs to fight COVID-19 developed
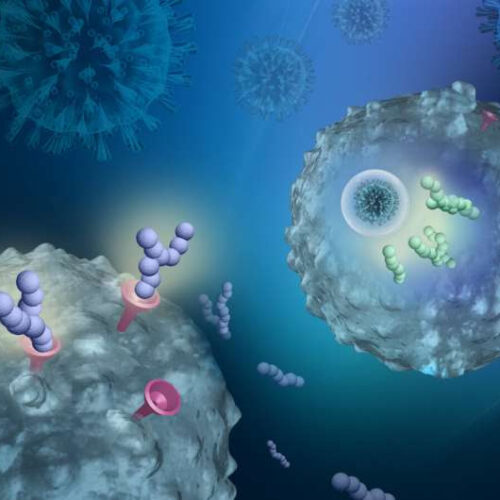
by QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute The illustration depicts two peptide drugs to target SARS-CoV-2. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein uses the ACE2 receptor (pink funnel) to bind to and invade cells. With the first peptide drug (purple balls), the virus latches onto the cloaking peptides (purple balls, which protect ACE2), which they mistake for ACE2 receptor on...
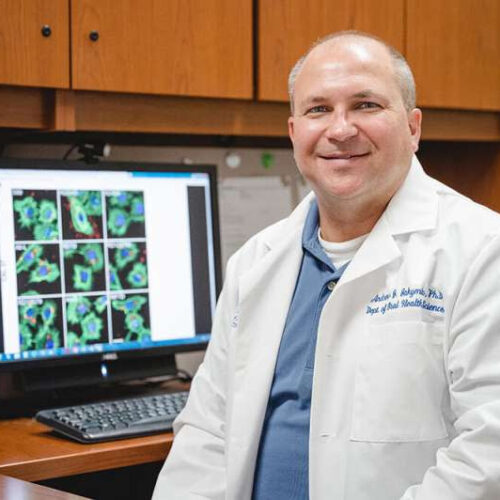
Chemical changes to peptide siRNA-carrier enhance gene silencing for future cancer drugs
by Caroline Wallace, Medical University of South Carolina Dr. Andrew Jakymiw and his team found a peptide carrier with heightened potential to deliver a cancer therapeutic for oral cancer. Credit: Marquel Coaxum MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researchers are exploring the use of peptide carriers for the delivery of small RNA drugs as a novel treatment for cancer. The...
Pirfenidone reduces scar tissue in patients with heart failure
by American College of Cardiology Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction who took the antifibrotic drug pirfenidone saw a significant reduction in a marker of heart muscles carring compared with patients who received a placebo, based on findings from an early-phase trial presented at the American College of Cardiology’s 70th...
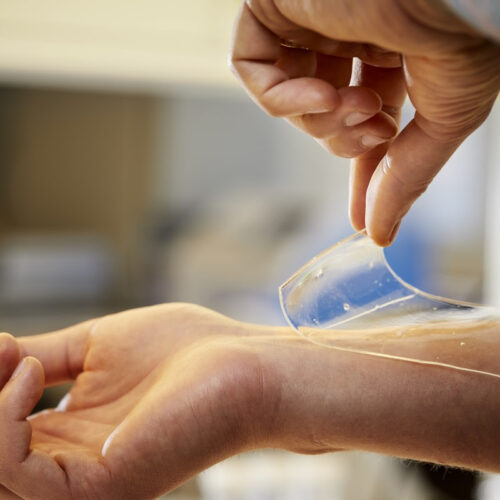
Hydrogel wound dressing uses immune system proteins to kill bacteria
By Ben Coxworth May 11, 2021 The technology is currently being commercialized by Chalmers spinoff company Amferia Anna-Lena Lundqvist It’s no secret that the more we use antibiotics, the greater the chances that bacteria will develop a resistance to them. A new antibacterial wound dressing is designed to get around that problem, by using proteins...
Treatment for Alzheimer’s disease found effective in preventing inflammation in orthopedic implants
Dental and orthopedic implants are widely used around the world. Common causes for implant failure are the immune response against oral bacteria and titanium particles shed by the implant. These and other phenomena can generate an inflammatory response, activating the osteoclasts (bone resorbing cells), and ultimately leading to osteolysis (destruction of bone tissue) around the...
A hairpin to fight cancer
WILEY The inhibition of pathological protein-protein interactions is a promising approach for treating a large number of diseases, including many forms of cancer. A team of researchers has now developed a bicyclic peptide that binds to beta-catenin–a protein associated with certain types of tumor. The secret of their success is the cyclic nature and the...
Artificial Intelligence is making cancer vaccines closer to reality
Imagine if you could get vaccinated for cancer. You would just get a shot or a couple of shots and your immune system would learn how to recognize and kill cancer. This sci-fi-sounding idea is not that far from reality. Especially now that scientists at the University of Waterloo have employed machine learning to identify...
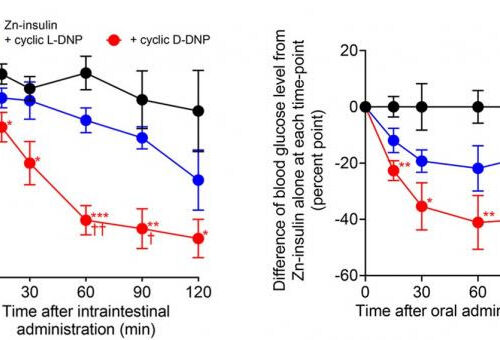
Toward painless oral insulin administration
KUMAMOTO UNIVERSITY IMAGE: LEFT: BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS CONTINUED TO DECREASE FROM 15 TO 60 MINUTES AFTER ADMINISTRATION. THIS DECREASE IN BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS PERSISTED UNTIL AT LEAST 120 MINUTES AFTER ADMINISTRATION. RIGHT: A DECREASE IN BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS WAS OBSERVED 15 MINUTES AFTER ORAL ADMINISTRATION, AND THE HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT PERSISTED UNTIL 120 MINUTES AFTER ADMINISTRATION....
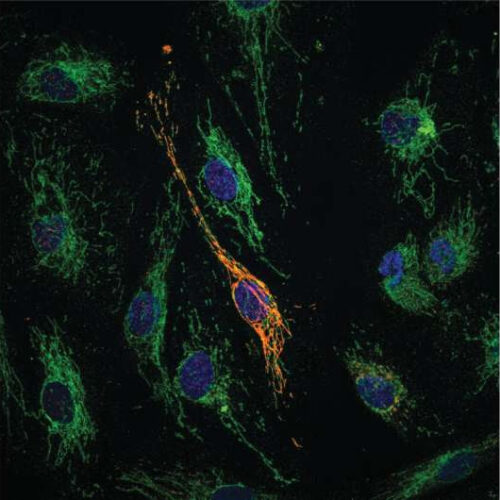
Newly-discovered molecule provides dual protection against vascular inflammation
by Federico Graciano, Duke-NUS Medical School Microscope imagining showing colocalisation of MOCCI (red) with a mitochondrial protein (green). Credit: Duke-NUS Medical School A multidisciplinary team of researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School and the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) in Singapore has discovered a new mitochondrial peptide called MOCCI that plays an important role in regulating inflammation of blood...