COMPUSCRIPT LTD Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this article the authors Zhong, Cuiyu; Zhang, Lei; Huang, Jiandong; Huang, Songyin; Yao, Yandan from Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China; Guangzhou Regenerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory, Guangzhou, China and Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Guangdong, China review antimicrobial peptides with anticancer properties. There is...
Category: <span>Peptides</span>
Data on OneSkin’s Peptide 14, a Topical Serotherapeutic, in Human Skin Models and Skin Biopsies
You might recall that OneSkin recently launched a cosmetic product claimed to reduce levels of senescent cells in aged skin, as measured by the usual markers for cellular senescence, such as p16 expression and senescence-associated β-galactosidase. Removal of senescent cells is more or less literal rejuvenation, given that the accumulation of such cells drives chronic...
Peptide is a key mediator in the regulation of compulsive alcohol drinking
by Boston University School of Medicine Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have identified that a peptide, pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating mediator is involved with compulsive consumption of alcohol. In addition, they have discovered that this protein acts in an area of the brain called the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis, or BNST, a region...
New method shows great potential for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
UPPSALA UNIVERSITY IMAGE: IN ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE, A PROTEIN (PEPTIDE) FORMS CLUMPS IN THE BRAIN AND CAUSES SUFFERERS TO LOSE THEIR MEMORY. IN A RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLE, A RESEARCH GROUP AT UPPSALA UNIVERSITY DESCRIBED. In Alzheimer’s disease, a protein (peptide) forms clumps in the brain and causes sufferers to lose their memory. In a recently published...
Beetroot peptide as potential drug candidate for treating diseases
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VIENNA In a recent study, a research group led by Christian Gruber at MedUni Vienna’s Institute of Pharmacology isolated a peptide (small protein molecule) from beetroot. The peptide is able to inhibit a particular enzyme that is responsible for the breakdown of messenger molecules in the body. Due to its particularly stable molecular structure...
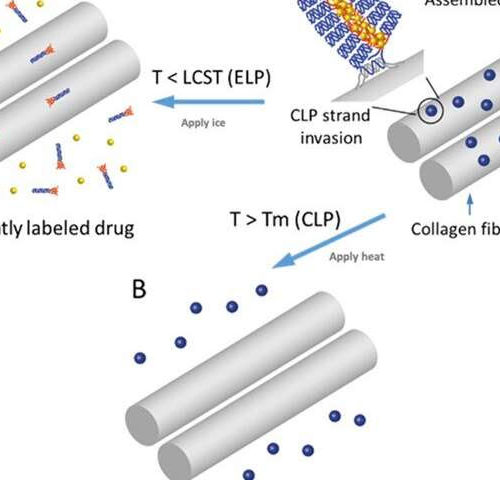
Researchers advance drug delivery systems to treat connective tissue disorders
by Karen B. Roberts, University of Delaware University of Delaware Professor Kristi Kiick is leading collaborative research to create new drug delivery systems with the potential to improve treatment for diseases that affect connective tissues, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, which is an autoimmune disease. The UD researchers have devised tiny cargo-carrying systems many times smaller than a human...
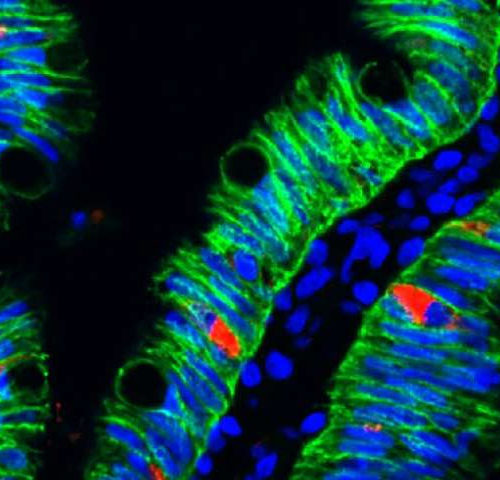
Scientists identify hormone that might help treat malabsorption
by Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center A human intestinal organoid with enteroendocrine cells (red) embedded within the intestinal cells of the HIO (green). Scientists at Cincinnati Children’s used human intestinal organoids grown from stem cells to discover how our bodies control the absorption of nutrients from the food we eat. They further found that one hormone...
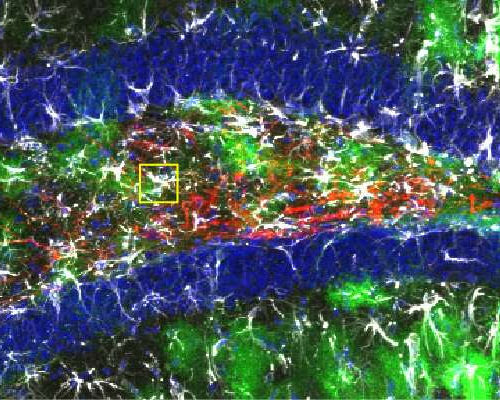
Lack of key neuropeptide induces neuroinflammation to impair neural stem cells and limit new neuron production
by Mark Derewicz, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine The dentate gyrus houses neural stem cells in a thin zone near the blue-labeled granule cells. Cholecystokinin interneurons (red) extend elaborate processes and release neuropeptide onto astrocytes (green) to induce neurogenesis in brain of adult mouse. Credit: University of North Carolina at Chapel...
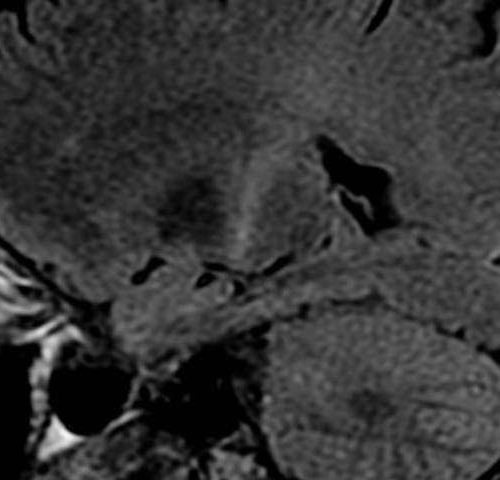
Protein study may be key to treating fibrotic diseases
by Bill Snyder, Vanderbilt University An MRI with increased signal in the posterior part of the internal capsule which can be tracked to the motor cortex consistent with the diagnosis of ALS. Credit: Frank Gaillard/Wikipedia A protein linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a progressive neurological disease that causes muscle weakness, may be a key...
Phosphoprotein biomarkers to guide cancer therapy are identified
by University of Alabama at Birmingham Precision medicine in cancer treatment uses genetic changes in the cancer cells to select the best therapies for individual patients. Now researchers led by James Bibb, Ph.D., professor of surgery at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, suggest using a broader lens of post-translational modification analysis to identify new...