By Paul McClure Researchers have discovered a protein associated with antiviral defense can exacerbate COPDDepositphotos A new study has found that TLR7, a protein that normally triggers our immune system to defend against certain viruses, plays a pivotal role in exacerbating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or COPD. The unexpected discovery may lead to new therapeutic approaches...
Category: <span>Proteomics</span>
Novel Bacterial Protein can Prolong Cell Longevity by Acting Directly on Mitochondria
Nov 10 2023São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) Researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil, partnering with colleagues in Australia, have identified a novel bacterial protein that can keep human cells healthy even when the cells have a heavy bacterial burden. The discovery could lead to new treatments for a wide array of...
FDA approves first treatment for congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
by Lori Solomon The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved Takeda Pharmaceuticals Adzynma, the first recombinant protein product indicated for prophylactic or on-demand enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) in adult and pediatric patients with congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (cTTP). Adzynma is a purified recombinant form of the ADAMTS13 enzyme that enhances the low levels of...
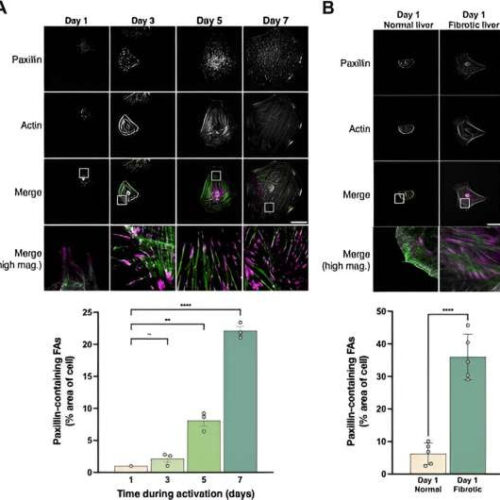
From soft tissue to stiff leather: Understanding the role of paxillin in liver fibrosis
by Medical University of South Carolina Paxillin localization during HSC activation. (A) HSCs were isolated, grown on glass coverslips for 7 days, and fixed. Paxillin was labeled at the specified time points as described in the Materials and Methods. DAPI was used to label nuclei. The boxes in row 3 of the panel illustrate magnified area in...
Rab32 and Rab38 Crucial for Bone Resorption and Pigmentation of Skin, Hair
Reviewed by Lily Ramsey, LLMOct 26 2023 Bone is maintained via delicate balance between formation and resorption, and its imbalance leads to bone related diseases like osteoporosis rheumatism and periodontitis. In studies published in scientific journals J Biol Chem and Cell Struct Funct, researchers led by Osaka University revealed proteins named Rab32 and Rab38 play...
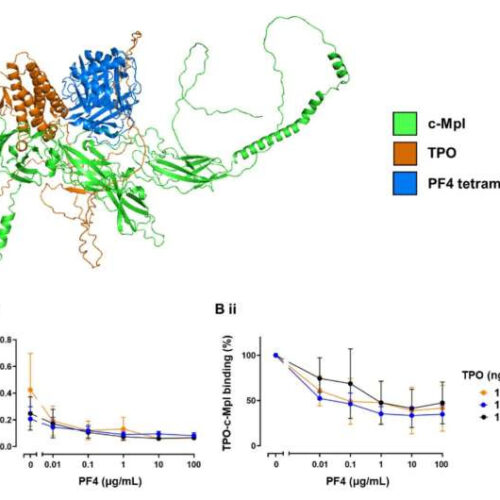
Protein interaction causing rare but deadly vaccine-related clotting found
by University of Birmingham PF4 binding to c-Mpl disrupts TPO binding. (A) AlphaFold prediction of the binding of PF4 and TPO to c-Mpl. Overlayed cartoon structures of c-Mpl (green) complexed with either PF4 (blue) or TPO (orange) as modeled using Colabfold. Structure predictions were ranked by pLDDT, a per-residue measure of the confidence of the predicted...
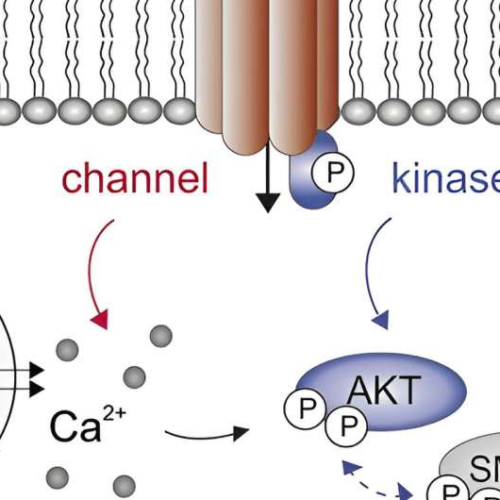
Key signaling protein identified as possible target for new therapies in hard-to-treat cancers
by American Physiological Society Credit: Function (2023). DOI: 10.1093/function/zqad053The unique signaling protein known as TRPM7 can stimulate and interact with an important cellular signaling hub called the AKT machinery, which is a well-known component of multiple cellular functions that drive growth and proliferation. This interaction causes a significant increase in the gene expression of COX-2, an...
Unexpected link found between 2 schizophrenia risk proteins
by Emily Caldwell, The Ohio State University Behavioral alterations in MAP6−/− and Kv3.1−/− mice. Adult (3–6 months old) WT B6 (black bars), MAP6−/− (red bars), and Kv3.1−/− (green bars) mice were used in a series of behavioral assays. Each group contained approximately half male and half female mice. a Example traces in the elevated plus maze...
Scientists identify cancer kill ‘switch’ that destroys tumours from the inside out
US researchers spotted a ‘switch’ that causes cancer cells to self-destructThe team now hopes to develop a treatment that targets this part of the cellBy EMILY CRAIG DEPUTY HEALTH EDITOR FOR MAILONLINE PUBLISHED: 05:45 EDT, 25 October 2023 | UPDATED: 05:45 EDT, 25 October 2023 A kill ‘switch’ which triggers the death of cancer cells...
Scientists discover a previously unknown way cells break down proteins
HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL At a glance: Scientists have discovered a previously unknown mechanism by which cells break down proteins that are no longer needed.These proteins are short-lived and modulate genes that support important neural, immune, and developmental processes.The mechanism could inform the design of therapies to treat conditions that arise when cells make too much...