by Josep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute
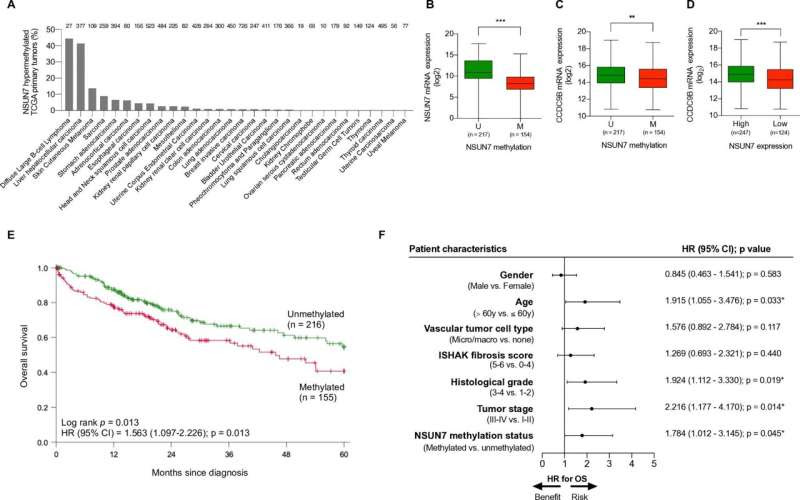
NSUN7 epigenetic loss occurs in human primary HCC tumors in association with worse clinical outcome. (A) Percentage of NSUN7 methylation in the TCGA data set of primary tumors according to cancer type. (B) NSUN7 methylation is inversely correlated with NSUN7 transcript expression in TCGA HCC tumors. (C) NSUN7 methylation is associated with decreased CCDC9B transcript levels in primary TCGA HCC tumors. (D) Low expression of the NSUN7 mRNA is associated with decreased CCDC9B transcript levels in primary TCGA HCC tumors. (E) Kaplan–Meier analysis of overall survival (OS) in the TCGA liver cancer cohort with respect to NSUN7 methylation status. Significance of the log-rank test is shown. Results of the univariate Cox regression analysis are represented by the hazards ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI). (F) Forest plot of the multivariable Cox regression analysis for clinical outcome in the TCGA liver cohort studied for NSUN7 methylation status taking into account different prognostic factors. P-values correspond to hazard ratios (HR), with a 95% CI, associated with OS. Co-variables with associated p-value under 0.05 were considered as independent prognostic factor (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). Credit: Molecular Cancer (2023). DOI: 10.1186/s12943-023-01785-z
Researchers at the Josep Carreras Leukemia Research Institute, led by Dr. Manel Esteller, have discovered a key epigenetic alteration that anticipates the clinical course of liver cancer. This is the deactivation of the NSUN7 gene, which is an epigenetic editor of RNA. Tumors with this alteration tend to have a poor clinical prognosis, although the research indicates that they are more vulnerable to bromodomain inhibitors, a family of anticancer drugs.
Liver cancer is a very frequent type of tumor, in fact in many countries it is among the three most commonly detected. In addition to its high incidence, with around one million cases diagnosed each year worldwide, it is a type of tumor that is highly aggressive, with a mortality rate of about 80% of patients.
The group of Dr. Manel Esteller, Director of the Josep Carreras Leukemia Research Institute, ICREA research professor and professor of genetics at the University of Barcelona, has experience in the study of liver cancer, as they were the first to determine the epigenome of this tumor and thus identify the main chemical alterations in the DNA that change its genetic expression.
In the research, written by Vanessa Ortiz-Barahona and Marta Soler as lead authors and published in Molecular Cancer, the scientific team has focused on the study of chemical modifications on RNA, the intermediary molecule between genetic information and proteins, the real tools of the cell. In this sense, Esteller emphasizes that “in the last five years, we have contributed to demonstrate that not only the chemical regulation of DNA is altered in cancer but also the ‘marks’ that control the activity of ribonucleic acid (RNA).”
During the study about what controls these chemical modifications of RNA (the so-called epitranscriptome), the researchers found that the NSUN7 gene was clearly altered in liver cancer. “We observed that the NSUN7 gene suffered a loss of functionality in liver tumors and this led to a degradation of its RNA targets, ultimately leading to a superactivation of the MYC oncogene,” says Dr. Esteller.
Oncogene activation is usually associated with worse survival, as the results of the study showed. However, Esteller comments that “at the same time we found that the aforementioned tumors were more sensitive to drugs that block MYC, such as the so-called bromodomain inhibitors,” opening up a new therapeutic avenue worth exploring in clinical trials of liver cancer depending on the activation status of NSUN7.
An unforeseen consequence that emerges from the research is that those liver tumors with intact NSUN7 might be more receptive to immunotherapy. Thus, determining the epigenetic status of NSUN7 in liver cancer patients could be of high clinical value and help to design a more precise and personalized therapy for the patient.

Leave a Reply