By Dr. Priyom Bose, Ph.D.
Reviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc.
Nucleic acids are building blocks of DNA or RNA of any cellular organisms or viruses.1, 2, 3A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene, which may occur due to errors in DNA replication during cell division, viral infection, and exposure to mutagens.4

Image Credit: Natali _ Mis/Shutterstock.comMutagens (e.g., chemicals and radiation) react with DNA and can alter the structures of individual nucleotides. An impaired DNA repair system that is responsible for correcting any errors during cell division is directly associated with gene mutation.5
Key types of mutations
Genetic disorders can occur due to mutations in one gene (monogenic), multiple genes (multifactorial inheritance), and mutation in one or more chromosomes. Point mutations are where one nucleotide in a genomic sequence is replaced or substituted with another.6 Chromosomes can fuse, translocate, and break, resulting in the loss of a large number of functional genes, whose consequences can be harmful.7
Different types of transposable elements are regarded as another source of mutation. These are small DNA entities that can move around within the entire genome. A transposon might disrupt existing gene functions when it gets inserted in the middle of another genetic region, trigger dormant gene functions, or produce new proteins by inserting different genetic materials into an existing genetic sequence.8
Genetic mutation may also occur through the insertion or deletion of a few nucleotides.6In the case of nonsynonymous mutation, an entire amino acid sequence is changed. This type of mutation results in the production of a different protein or premature termination of a protein. Synonymous mutations are linked with changes in amino acids that are encoded by multiple codons.9
Mutation patterns and diseases
Cell divisions are of two types: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells, whereas meiosis occurs in the gamete cells, i.e., egg and sperm cells. Mutations appearing in reproductive cells, called germline mutation, are heritable as they are passed on to offspring. This type of mutation is also known as an inherited mutation. Somatic mutations that occur in cells other than germ cells are not heritable.
Acquired mutations occur after a person is born due to “wear and tear” of genes over time. As stated above, this type of mutation occurs due to aging, exposure to toxins and chemicals, and certain viral infections.10
From an evolutionary perspective, somatic mutations have no significant impact, but they may lead to disease conditions if they are systematic and alter the cell survival capacity. For instance, cancers are potent somatic mutations that influence an organism’s survival.
Many genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, Down syndrome, and sickle cell disease, are inherited. Different genetic mutation patterns that are passed on from the parent to a child and lead to disease conditions are discussed below:11
X-linked dominant: Males have XY chromosomes, while females have XX chromosomes. In this case, only one mutation in the X chromosome must be passed from the parent to offspring for the child to inherit the disease. The X-linked dominant mutation is detected in Fragile X syndrome.
X-linked recessive: If the father carries the mutation, 100% of his female offspring will carry the mutation, and no male offspring will be affected. However, if the mother carries a similar mutation, there will be a 50% chance that both female and male offspring will express the condition. If both parents have the mutation, 50% of male offspring will have the condition, and 100% of female offspring will inherit the condition. This mutation pattern is responsible for color blindness.
Autosomal dominant: Only one parent needs to pass the mutation to the offspring for disease manifestation. This mutation pattern has been detected in Marfan syndrome.
Autosomal recessive: For disease expression, both parents need to pass the same genetic mutations to the child. This mutation pattern is observed in sickle cell disease.
X-linked: Both male and female offspring can inherit mutations on the X chromosomes in dominant or recessive patterns. Thrombocytopenia, a condition associated with low platelet counts, is an example of this mutation pattern.
Y-linked: Male babies having Y chromosomes can inherit this mutation. This mutation type is linked with webbed toes.
Mitochondrial: Mitochondrial inherence is also known as maternal inheritance because mitochondria from the egg survive fertilization. This mutation pattern is seen in sudden vision loss, also known as Leber hereditary optic neuropathy.
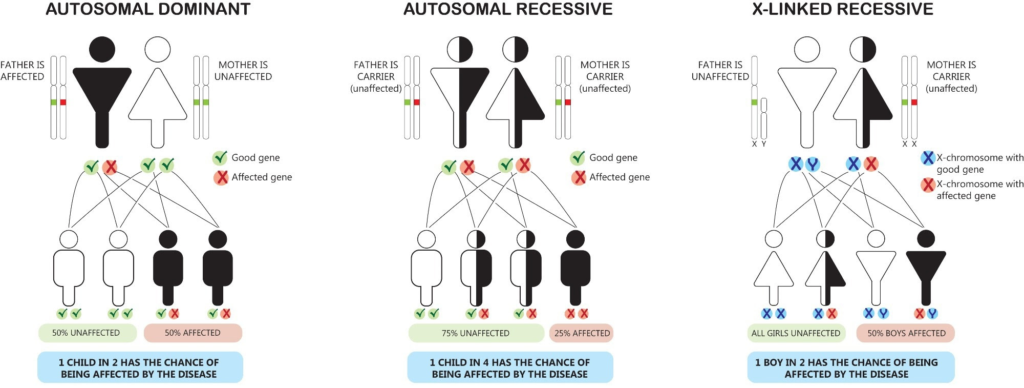
Image Credit: Katrien Francois/Shutterstock.com
Genetic testing and treatments
Genetic tests, such as cytogenetic, biochemical, and molecular tests, are performed for newborn screening, carrier testing, prenatal diagnosis, and disease diagnostics.12 In many countries, such as the USA, every newborn is screened for several genetic diseases. Early disease detection improves outcome rates.
Carrier testing helps a couple to understand if they are carriers of a recessive allele for genetic diseases, such as sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and Tay-Sachs disease. In prenatal diagnostic testing, a fetus’s genes or chromosomes are tested to identify the presence of specific mutations. Genetic tests are also used to confirm a diagnosis in symptomatic individuals and monitor disease prognosis.
Genetic counseling helps patients and their families to understand the implications of genetic testing and treatment strategies. At present, many advanced gene therapies are available that entail the correction or replacement of faulty genes with healthy ones to cure or prevent genetic disorders, such as hemophilia and cystic fibrosis.13
References
Zeiger E. Genetic Toxicology Testing. Comprehensive Toxicology (Second Edition). 2010; 139-158. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-046884-6.00316-X
Rosendahl Huber A, et al. The Mutagenic Impact of Environmental Exposures in Human Cells and Cancer: Imprints Through Time. Front Genet. 2021;12:760039. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.760039.
Minchin S, Lodge J. Understanding biochemistry: structure and function of nucleic acids. Essays Biochem. 2019;63(4):433-456. doi: 10.1042/EBC20180038.
Basu AK. DNA Damage, Mutagenesis and Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018;19(4):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19040970
Alhmoud JF, et al. DNA Damage/Repair Management in Cancers. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(4):1050. doi: 10.3390/cancers12041050.
Chial, H. Rare Genetic Disorders: Learning About Genetic Disease Through Gene Mapping, SNPs, and Microarray Data. Nature Education. 2008;1(1):192. https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/rare-genetic-disorders-learning-about-genetic-disease-979/
Canoy RJ, et al. Factors That Affect the Formation of Chromosomal Translocations in Cells. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(20):5110. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205110.
Wicker T, et al. DNA transposon activity is associated with increased mutation rates in genes of rice and other grasses. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12790. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12790.
Oelschlaeger P. Molecular Mechanisms and the Significance of Synonymous Mutations. Biomolecules. 2024;14(1):132. doi: 10.3390/biom14010132.
Vijg J. From DNA damage to mutations: All roads lead to aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2021l;68:101316. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101316.
Basta M, Pandya AM. Genetics, X-Linked Inheritance. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2024; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557383/
Genetic Alliance; Understanding Genetics: A District of Columbia Guide for Patients and Health Professionals. 2010; Chapter 2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK132142/
Saini D. Gene therapy. Advances in Animal Genomics. 2021;165-183. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820595-2.00011-4

Leave a Reply