Written by Dan Wagener, MA | Reviewed by Angela Dunn, MD, MPH
Key takeaways:
- The common cold often follows a timeline, and it can last up to 3 weeks.
- Symptoms often take 1 to 3 days to develop and then peak at 1 to 3 days. Symptoms can last up to 10 days.
- Colds usually go away on their own, so you don’t need to see a healthcare provider. But over-the-counter products can help with your symptoms.

LightFieldStudios/iStock via Getty Images
Even though catching a cold can come as a surprise, common colds typically show up in specific stages. Knowing the stages of a cold can help you act quickly. This way, you can prevent spreading it and take steps to treat it and get feeling better fast.
What is a cold?
A cold is a virus that infects the upper respiratory tract (nose, sinuses, voice box, and throat). More than 200 viruses can cause a cold, but the rhinovirus is the most common culprit.
Colds can spread when you:
- Breathe in air after someone with an infection coughs or sneezes
- Have close personal contact with someone who is infected
- Shake hands with someone who is infected or touch an infected surface and then put that hand to your eyes, nose, or mouth
Colds are more common in the fall and winter. But you can get them any time of year. Each year, adults have an average of two to three colds. And children have even more.
Flu and COVID-19 infections can feel very similar to a cold, and they’re also more common in the fall and winter. But there are some differences:
- Colds tend to cause much milder illnesses than COVID or flu.
- Colds do not usually cause high fevers or shortness of breath.
- Cold symptoms typically come on more gradually than symptoms of the flu or COVID.
How long does a common cold last?
Once a cold virus enters one of your cells, it starts to create copies of itself. And these copies go on to infect other cells. This can start happening within 8 to 10 hours of the initial infection.
Symptoms can begin right after that. But, for most people, symptoms show up within 1 to 3 days after exposure to the virus. This is different from the flu, where symptoms show up 1 to 7 days after the initial infection.
Cold symptoms usually last 7 to 10 days. But they can go on for as long as 3 weeks.
Infographic showing how long the symptoms of a cold last.
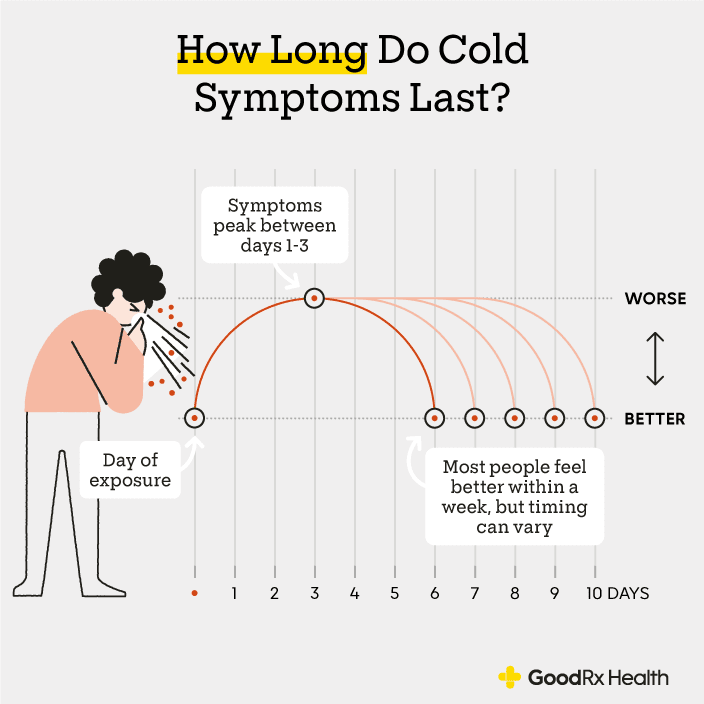
What are the common cold stages and symptoms?
Colds and cold symptoms tend to go through ordered stages. But you may experience the timing and stages a bit differently. Here are the general stages of a cold:
- Incubation: This is the time from when you were exposed to a virus to when you start to feel sick. After you’re exposed to a cold virus, it typically takes 1 to 3 days for you to develop symptoms. But it’s possible to develop symptoms as soon as 10 to 12 hours after exposure.
- Peak of symptoms: Cold symptoms peak at 1 to 3 days. This is when you’re most contagious. The main symptoms include sore throat, stuffy or runny nose, cough, discomfort, sneezing, headaches, clear mucus, and body aches. Fever is more common in children.
- Lessening symptoms: Cold symptoms usually last from 3 to 10 days. After 2 or 3 days of symptoms, the mucus from your nose may change to a white, yellow, or green color. This is normal and does not mean you need an antibiotic.
- 10 days and beyond: Symptoms can last up to 2 weeks in some people, especially runny nose, stuffy nose, and cough. But at this point, you should be feeling better, and the symptoms probably won’t be as bad.
How long are you contagious?
You’re generally contagious a few days before your symptoms start. You may also be contagious for as long as you have symptoms. In fact, you’re most likely to spread the virus in the first 2 to 3 days when the symptoms peak.
If you’re sick, stay home from work or school. If your child is sick, keep them out of day care or school. Try to avoid close contact with others. And wear a face mask if you must go out in crowded places.
Cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze. Also, make sure to wash your hands after coughing, sneezing, or blowing your nose. These can all help prevent the virus from spreading.
Do you need antibiotics?
No, an antibiotic will not get rid of a cold. Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), acne, and strep throat. But colds are caused by viruses, so antibiotics won’t work on them.
Taking antibiotics when you don’t need them can cause real harm. Antibiotics have side effects, including nausea, diarrhea, skin rashes, and yeast infection. And they can increase your risk for antibiotic-resistant infections in the future. This means you could have bacterial infections that don’t get better with conventional antibiotics.
So, you don’t need to take antibiotics for a cold.
When should you see a doctor?
There’s no cure for a cold. Usually it goes away on its own within 2 weeks without a visit to your healthcare provider. But there are times when you should see a provider:
- Your symptoms don’t get better in 10 days.
- Your symptoms are severe or unusual. For example, you have a fever that lasts longer than 4 days, dehydration, difficulty breathing, symptoms that go away and come back or get worse.
- Your child (younger than 2 months old) has a fever or is lethargic.
How do you treat a cold?
Here are some ways to ease the symptoms of a cold:
- Get plenty of rest.
- Drink lots of fluids.
- Use a humidifier or vaporizer.
- Use saline nasal spray (for adults) or drops (for children).
- Suck on cough drops and throat lozenges.
- Use honey to relieve coughs in adults and children at least 1 year of age or older.
Over-the-counter products that can help with symptoms include:
- Antihistamines
- Decongestants
- Expectorants
- Cough medications (antitussives)
- Fever reducers (antipyretics)
Talk with your provider about which medications are best for you. Some people may not be able to use these products because of other medications, health conditions, or symptoms, such as high fever or chest pain. Some of these medications also may not be appropriate for children.
The bottom line
Cold symptoms usually follow a predictable pattern. The most common symptoms are sore throat, runny nose, coughing, sneezing, and mucus. Symptoms can last up to 3 weeks.
A cold is a virus, so antibiotics won’t get rid of it. But most colds go away on their own. So you don’t need to see a healthcare provider unless your symptoms are severe and don’t begin to fade after 10 days. You can treat a cold with over-the-counter medications and by resting, drinking lots of fluids, and using a humidifier or nasal spray.
References
Allan, G. M., et al. (2014). Prevention and treatment of the common cold: Making sense of the evidence. Canadian Medical Association Journal.
American Lung Association. (2023). Facts about the common cold.

Leave a Reply