Onera Health, a company headquartered in Silicon Valley but with R&D offices in the Netherlands, has developed a bioimpedance patch, to be worn on the chest, that can detect sleep apnea. It has just been successfully trialed in 25 patients and the results show that it is about as accurate as automatic scoring using a traditional polysomnography respiration channel (sensitivity of 58.4%, specificity of 76.2%, and an accuracy of 72.8%).
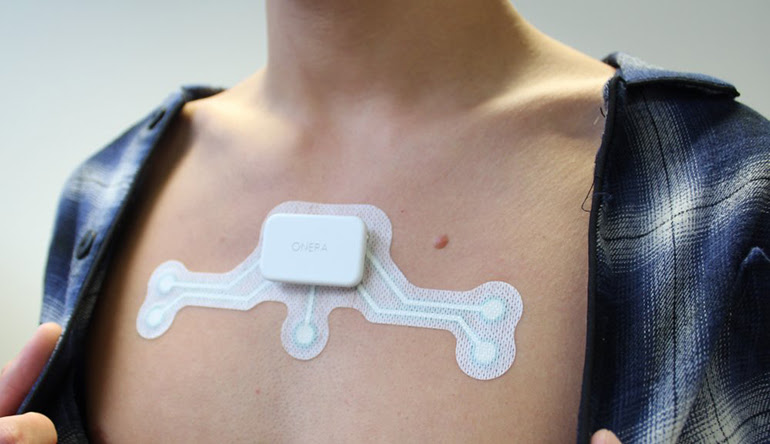
Because the device is fairly unobtrusive, and is worn on the chest, it has the potential to allow for sleep apnea diagnosis outside of sleep clinics. This may improve the quality of diagnoses, as patients will be able to perform testing under normal conditions in their own bed.
The Onera device originates from imec and Ghent University, two Belgian institutions that have done a great deal of work in the field of mobile and personal health. They partnered in developing a bioimpedance measuring device that sends an electric current at a given frequency into the body and assesses how the signal returns. Having identified that it can detect breathing, the researchers tested it for sleep apnea detection and have gone ahead and commercialized the technology via Onera Health.
Some more details, according to the study abstract in IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics:
In this study, the potential of using the bio-impedance (bioZ) of the chest as a respiratory surrogate is analyzed. A novel portable device is presented, combined with a two-phase Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) deep learning algorithm for automated event detection. The setup is benchmarked using simultaneous recordings of the device and the traditional polysomnography in 25 patients. The results demonstrate that using only the bioZ, an area under the precision-recall curve of 46.9% can be achieved, which is on par with automatic scoring using a polysomnography respiration channel. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy are 58.4%, 76.2% and 72.8%, respectively. This confirms the potential of using the bioZ device and deep learning algorithm for automatically detecting sleep respiration events during the night, in a portable and comfortable setup.
Study in IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics: Portable Detection of Apnea and Hypopnea Events using Bio-Impedance of the Chest and Deep Learning

Leave a Reply