Megan Brooks November 02, 2023 An investigational natural killer cell (NK) therapy has shown promise in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), in a small phase 1 proof-of-concept clinical trial. SNK01, being developed by NKGen Biotech, is an autologous, nongenetically modified NK cell product that has enhanced cytotoxicity and activating receptor expression. “When we give these enhanced...
Tag: <span>Alzheimer</span>
Experimental Alzheimer’s drug shows promise in injected-at-home form
by Robert Langreth and Gerry Smith, Bloomberg News Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public DomainAn experimental version of Eisai Co’s Alzheimer’s drug that might be given in patients’ homes exceeded the power of Leqembi, its approved infused formulation, in an early study that could pave the way to bolstering uptake. After six months of treatment, an injected form...
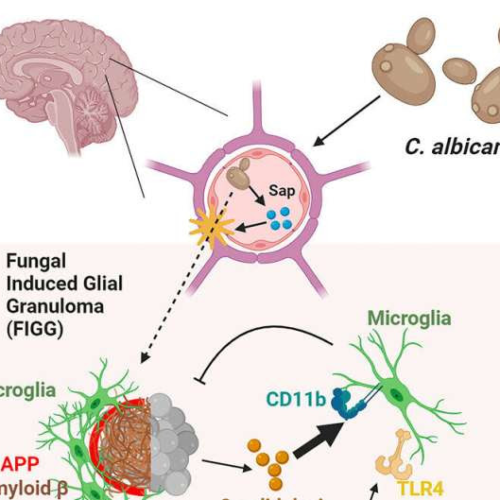
Brain fungal infection produces Alzheimer’s disease-like changes, says new study
by Homa Warren, Baylor College of Medicine Graphical abstract. Credit: Cell Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113240Previous research has implicated fungi in chronic neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, but there is limited understanding of how these common microbes could be involved in the development of these conditions. Working with animal models, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine...
Reprogramming the brain’s cleaning crew to mop up Alzheimer’s disease
by University of California, San Francisco Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain The discovery of how to shift damaged brain cells from a diseased state into a healthy one presents a potential new path to treating Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia, according to a new study from researchers at UC San Francisco. The research focuses on microglia, cells...
What allegations of Alzheimer’s research fraud mean for patients
by John Mamo, The Conversation News of the alleged research fraud is a blow for people living with Alzheimer’s. Credit: Shutterstock Alzheimer’s disease is the most prevalent form of dementia and, with a rapidly aging global population, it is fueling unprecedented demand for costly patient care. There have been an estimated 400 clinical studies since the first Alzheimer’s drug...
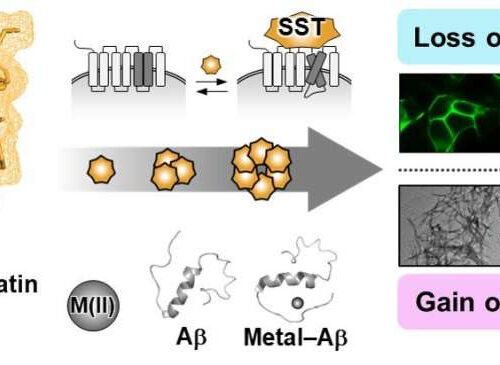
Research team proves how neurotransmitter may be key in controlling Alzheimer’s toxicity
by KAIST Functional shift of somatostatin (SST) by factors in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Credit: KAIST With nearly 50 million dementia patients worldwide, Alzheimers’s disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Its main symptom is the impairment of general cognitive abilities, including the ability to speak or to remember. The importance of finding a...
Rapid loss of smell predicts dementia and smaller brain areas linked to Alzheimer’s
by University of Chicago Medical Center Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Though we often undervalue our ability to smell compared to our abilities to see and hear, our olfactory sense provides our brain with critical information, from detecting potential dangers like smoke to recognizing the sweet smell of baking cookies. Researchers at the University of Chicago Medicine...
Combining genetics and brain MRI can aid in predicting chances of Alzheimer’s disease
by Simon Fraser University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Simon Fraser University researchers are studying how a combination of genetics and brain MRIs may be used to predict the chances of developing Alzheimer’s disease in the future. In a newly published study, researchers from SFU’s Functional and Anatomical Imaging & Shape Analysis Lab (FAISAL) identified distinct properties...
Treponema denticola found to induce Alzheimer-like tau hyperphosphorylation in mice
by International & American Associations for Dental Research A study investigating the role of Treponema denticola (T. denticola) in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis will be presented by Zhiqun Tang of the West China Hospital of Stomatology at Sichuan University, China at the 100th General Session and Exhibition of the IADR, to be held in conjunction...
Blood vessel breakthrough major step towards Alzheimer’s treatment
by University of Manchester Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A breakthrough in our understanding of Alzheimer’s disease has revealed changes to blood vessels in the brain, potentially presenting a path for developing new drugs to help fight the disease, according to University of Manchester research published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). Alzheimer’s Disease is...