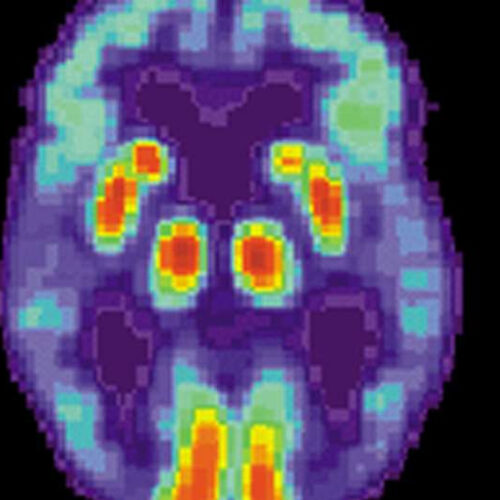
by University of Cincinnati PET scan of a human brain with Alzheimer’s disease. Credit: public domain New research from the University of Cincinnati bolsters a hypothesis that Alzheimer’s disease is caused by a decline in levels of a specific protein, contrary to a prevailing theory that has been recently called into question. UC researchers led...
Tag: <span>Alzheimer’s disease</span>
New therapeutic target could check the progress of Alzheimer’s disease
UNIVERSITY OF MALAGA IMAGE: INES MORENO, SCIENTIST OF THE UMA, PROPOSES THE REMOVAL OF TOXIC PROTEINS IN THE BRAIN, THE MAIN CAUSE OF NEURONAL DEATH, AT A CIRCULATORY LEVEL CREDIT: UNIVERSITY OF MALAGA A new study conducted by the scientist of the UMA Inés Moreno, in collaboration with the University of Texas, has identified a...
Risk factor for developing Alzheimer’s disease increases by 50-80% in older adults who have had COVID-19
by Case Western Reserve University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Older people who were infected with COVID-19 show a substantially higher risk—as much as 50% to 80% higher than a control group—of developing Alzheimer’s disease within a year, according to a study of more than 6 million patients 65 and older. In a study published today...
New antibody shows therapeutic effects in mice with Alzheimer’s disease
by University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A newly developed agonistic antibody reduced the amyloid pathology in mice with Alzheimer’s disease, signaling its promise as a potential treatment for the disease, according to a team of researchers at UTHealth Houston. Research led by senior author Zhiqiang An, Ph.D., professor...
Scientists diagnose Alzheimer’s disease by blood test
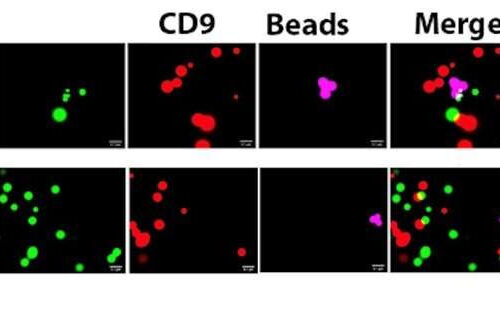
by Zhejang University Figure1: The novel peripheral blood nerve-derived extracellular vesicle-related marker. Credit: NMDAR2A Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by a decline in cognitive function, memory loss, and in severe cases, language impairment, and ultimately the loss of independent living ability. According to estimates by Chinese Center for disease Control and Prevention, there are about...
Altered brain connections in early Alzheimer’s disease
by University of Tsukuba Researchers from the University of Tsukuba identify a brain region that becomes overly important in the brain connections of people with pre-clinical Alzheimer’s disease. Credit: ART-ur/Shutterstock Although a lot is known about brain alterations in symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease (AD), less is known about changes in the brain network early in the...
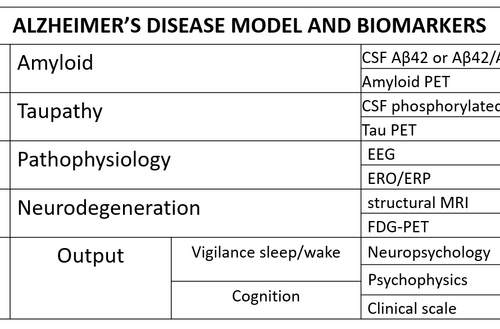
Researchers explore the “dark side” of Alzheimer’s Disease revealing new biomarkers
IOS PRESS IMAGE: THE MODEL DIMENSIONS INCLUDE AMYLOIDOSIS (A), TAUOPATHY (T), PATHOPHYSIOLOGY (P), AND NEURODEGENERATION (N). THE DISEASE PROCESSES WITHIN THOSE DIMENSIONS PRODUCE A CLINICAL OUTPUT (O) INVOLVING VIGILANCE, SLEEP-WAKE CYCLE, COGNITIVE FUNCTIONS, AND ABILITIES IN THE ACTIVITIES OF DAILY LIVING. KEY: CSF, CEREBROSPINAL FLUID; PET, POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY; EEG, ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY; ERO, EVENT-RELATED EEG OSCILLATIONS;...
LSU Health New Orleans discovers major contributor to Alzheimer’s disease
LOUISIANA STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER New Orleans, LA – Research led by Drs. Yuhai Zhao and Walter J Lukiw at the LSU Health New Orleans Neuroscience Center and the Departments of Cell Biology and Anatomy, Neurology and Ophthalmology, reports for the first time a pathway that begins in the gut and ends with a potent...
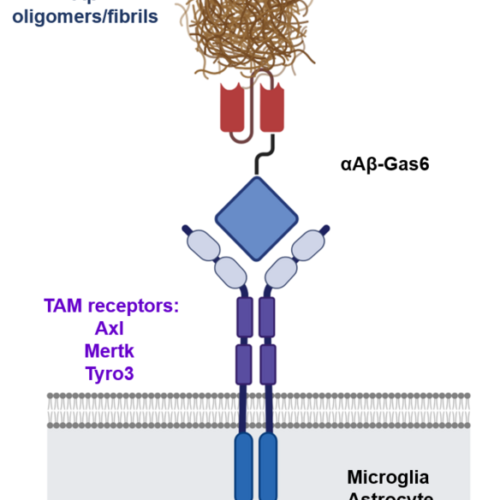
A new therapeutic drug for Alzheimer’s disease without inflammatory side effects
THE KOREA ADVANCED INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (KAIST) IMAGE: SCHEMATIC OF A CHIMERIC GAS6 FUSION PROTEIN. A SINGLE CHAIN VARIABLE FRAGMENT (SCFV) OF AN AMYLOID Β (AΒ)-TARGETING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY IS FUSED WITH A TRUNCATED RECEPTOR BINDING DOMAIN OF GAS6, A BRIDGING MOLECULE FOR THE CLEARANCE OF DEAD CELLS VIA TAM (TYRO3, AXL, AND MERTK)...
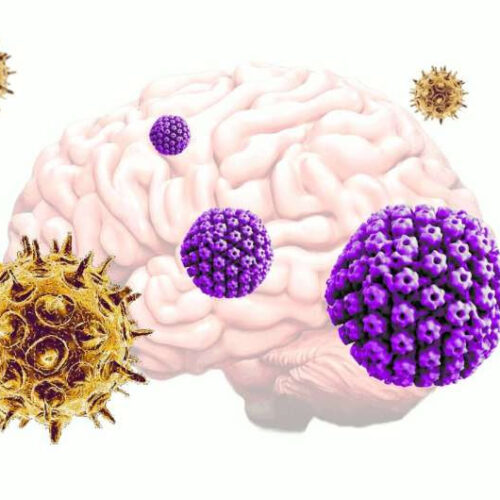
Common viruses may be triggering the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
by Tufts University Varicella zoster virus (VZV), which commonly causes chickenpox and shingles, activates herpes simplex virus (HSV) from dormancy in neural tissue grown in vitro, which then leads to an increase in plaque deposits and decrease in neural signaling – hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. Credit: Tufts University Alzheimer’s disease can begin almost imperceptibly, often masquerading...