CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES HEADQUARTERS Epidemiological studies have shown that women are twice as likely as men to develop Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but the cause of this phenomenon has been unclear. Now, however, a study led by Prof. Keqiang Ye from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences provides...
Tag: <span>Alzheimer’s disease</span>
The role of lipids in the development of Alzheimer’s disease
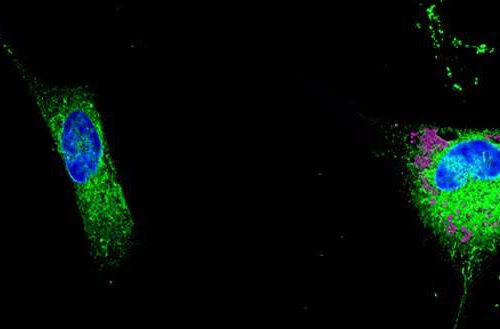
by University of Geneva Left: normal astrocyte able to destroy toxic lipids produced by neurons. Right: an astrocyte that stores lipids in droplets (pink) and starts secreting toxic lipids in the surrounding tissue. Credit: UNIGE / A.-C. Gavin Neurons in the brain coexist with and rely on many other cell types to function properly. Astrocytes, which take their name from their star shape, ensure the survival...
Endocrinologist takes Alzheimer’s disease research in new directions
For decades, the thinking about Alzheimer’s disease has been dominated by the so-called amyloid hypothesis which proposes that an abnormal accumulation of amyloid-beta plaques in various parts of the brain is the main driver of a cascade of events, leading to the loss of synapses and the death of neurons causing deficits in cognition and...
Physical fitness linked to lower risk of Alzheimer’s disease
by American Academy of Neurology Credit: Pixabay/Pete Linforth. People who are more physically fit are less likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease than people who are less physically fit, according to a preliminary study released today, February 27, 2022, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 74th Annual Meeting being held in person...
Identification of new risk factors or early signs of Alzheimer’s disease
INSTITUT DU CERVEAU (PARIS BRAIN INSTITUTE) What risk factors are associated with Alzheimer’s up to 15 years before the onset of the first symptoms? This is a vital question for specialists of this neurodegenerative disease – which develops over many years before becoming clinically visible – who aim to improve early prevention for at-risk patients....
Bacteria in the nose may increase risk of Alzheimer’s disease
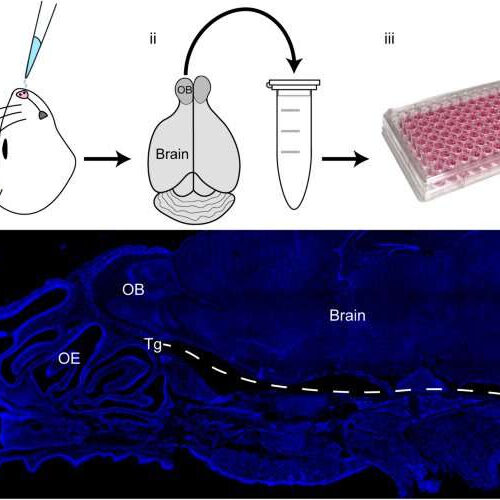
by Griffith University Schematics illustrating the process for quantifying the amount of viable infectious C. pneumoniae present in various mouse tissues. (A) Mice were first intranasally inoculated with C. pneumoniae (i), some with epithelial injury and some without. Following either 24 h, 3 days or 7 days or 28 days post inoculation, selected tissues were collected and homogenized in...
Human olfactory mucosa cell model opens a new perspective on Alzheimer’s disease
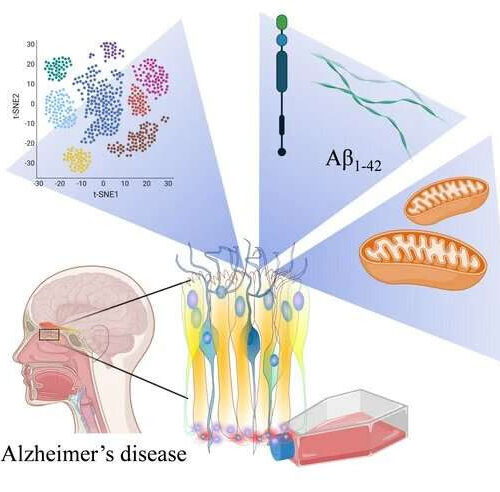
by University of Eastern Finland Graphical abstract. Credit: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/11/4/676 Researchers at the University of Eastern Finland have developed and characterized a new cell model for Alzheimer’s disease that has wide utility for research and could prove useful in early diagnosis and testing of new therapies. In collaboration with clinicians at Kuopio University Hospital, the researchers collected...
The Cell That Might Trigger Alzheimer’s Disease
Bret Stetka, MD January 31, 2022 It all started with genetic data. A gene here, a gene there. Eventually the story became clearer: If scientists are to one day find a cure for Alzheimer’s disease, they should look to the immune system. Over the past couple decades, researchers have identified numerous genes involved in various immune...
Researchers introduce into human cells a genetic mutation that protects against Alzheimer’s disease
by Laval University Credit: Pixabay/Pete Linforth. Researchers from the Université Laval Faculty of Medicine and CHU de Québec–Université Laval Research Center have successfully edited the genome of human cells grown in vitro to introduce a mutation providing protection against Alzheimer’s disease. The details of this breakthrough were recently published in The CRISPR Journal. “Some genetic mutations increase the...
Ally and enemy? Scientists explore immune cell suspect in Alzheimer’s disease
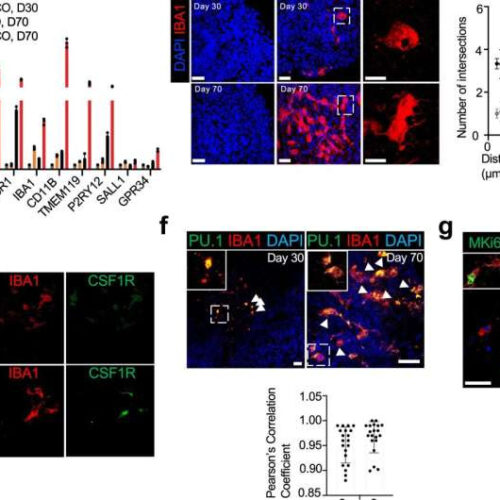
by Bill Hathaway, Yale University Fig. 1: Characterization of microglia-like cells in mhCOs. a Schematic for generating mhCOs. 10% of PU.1-infected hESCs were mixed with 90% parental HES3 hESCs, and PU.1 priming and full induction were performed on day 2 and 18, respectively. b Expression of microglia-related genes from control hCOs and mhCOs (30-day and...