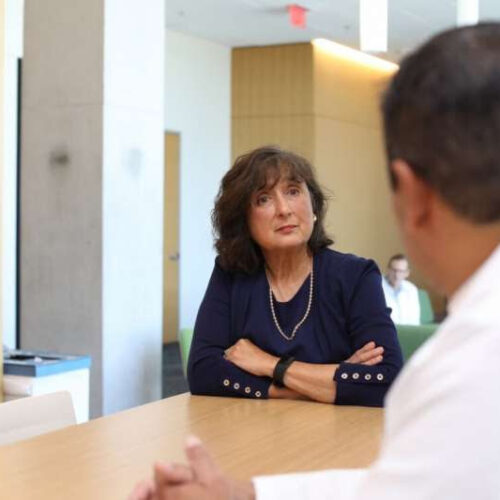
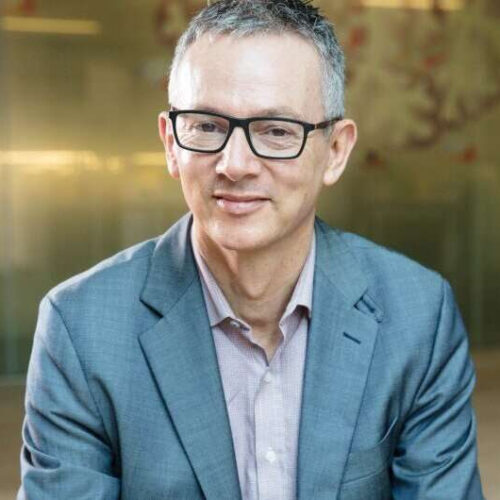
by Paul Tumarkin, University of Arizona Roberta Diaz Brinton. Credit: Photo courtesy of Tech Launch Arizona and NeuTherapeutics University of Arizona researchers have developed a new therapy for Alzheimer’s disease designed to restore cognitive function in early-stage patients. The therapy is now proceeding through a Phase 2b clinical trial. Phase 2b trials involve rigorous testing for efficacy in...
Tag: <span>Alzheimer’s disease</span>
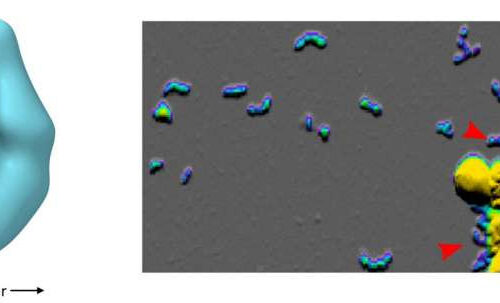
New insights into the formation of toxic protein clumps in Alzheimer’s disease
by Forschungszentrum Juelich Small Aβ oligomers (left: cryo-electron microscopy) are clumps consisting of just a few Aβ molecules. They cluster together to form short, worm-like structures known as protofibrils (right: atomic force microscopy). In an acidic environment, the Aβ oligomers form very quickly and cluster to form large particles from which protofibrils are separated following neutralization...
Spinal Fluid Biomarkers Detect Neurodegeneration, Alzheimer’s Disease in Living Patients
Alzheimer’s disease and related diseases can still only be confirmed in deceased patients’ brains via autopsy. Even so, the development of biomarkers can give patients and their families answers during life: Alzheimer’s disease can be accurately detected via peptides and proteins in a patient’s cerebrospinal fluids (CSF), which can be collected through a lumbar puncture...
Arterial stiffening linked to Alzheimer’s disease
by Paul Govern, Vanderbilt University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A research team from Vanderbilt University Medical Center reports in Neurology that greater stiffening of the aorta, the main artery in the human body, is associated in older adults with increased Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathology as reflected in a range of neurochemical indicators measured in cerebrospinal fluid. “These results have major...
Researchers identify signaling molecule that may help prevent Alzheimer’s disease
MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL BOSTON – New research in humans and mice identifies a particular signaling molecule that can help modify inflammation and the immune system to protect against Alzheimer’s disease. The work, which was led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), is published in Nature. Cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s disease develops when neurons begin to die....
Potential noninvasive treatment for Alzheimer’s disease
by University of Queensland Credit: University of Queensland Ultrasound can overcome some of the detrimental effects of aging and dementia without the need to cross the blood-brain barrier, researchers at The University of Queensland have found. Professor Jürgen Götz from UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute (QBI) led a multidisciplinary team who showed low-intensity ultrasound effectively restored cognition without opening the barrier...
Subconscious changes in movement may predict Alzheimer’s disease
by Brigham and Women’s Hospital Credit: CC0 Public Domain As people go about their daily activities, complex fluctuations in their movement occur without conscious thought. These fluctuations—known as fractal motor activity regulation (FMAR)—and their changes are not readily detectable to the naked eye, but FMAR patterns can be recorded using a wristwatch-like device known as an...
Potential noninvasive treatment for Alzheimer’s disease
by University of Queensland Credit: University of Queensland Ultrasound can overcome some of the detrimental effects of aging and dementia without the need to cross the blood-brain barrier, researchers at The University of Queensland have found. Professor Jürgen Götz from UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute (QBI) led a multidisciplinary team who showed low-intensity ultrasound effectively restored cognition without opening the barrier...
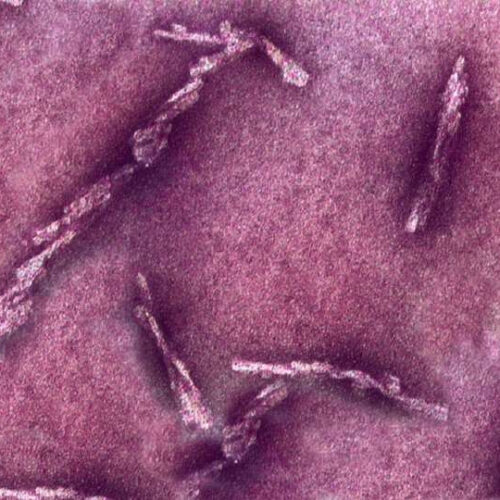
Researchers find new hints that could explain how Alzheimer’s disease spreads in human brains
by Case Western Reserve University Prions. Credit: Case Western Reserve University Case Western Reserve University researchers studying prions—misfolded proteins that cause lethal incurable diseases—have identified for the first time surface features of human prions responsible for their replication in the brain. The ultimate goal of the research is to help design a strategy to stop prion disease in humans—and, ultimately, to translate...
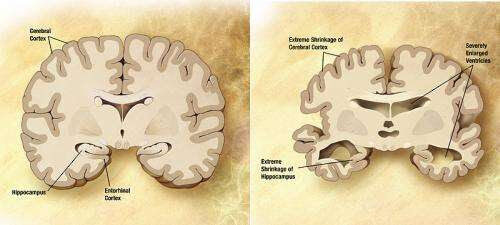
New treatment stops progression of Alzheimer’s disease in monkey brains
by NYU Langone Health Diagram of the brain of a person with Alzheimer’s Disease. Credit: Wikipedia/public domain. A new therapy prompts immune defense cells to swallow misshapen proteins, amyloid-beta plaques, and tau tangles, whose buildup is known to kill nearby brain cells as part of Alzheimer’s disease, a new study shows. Led by researchers at NYU...