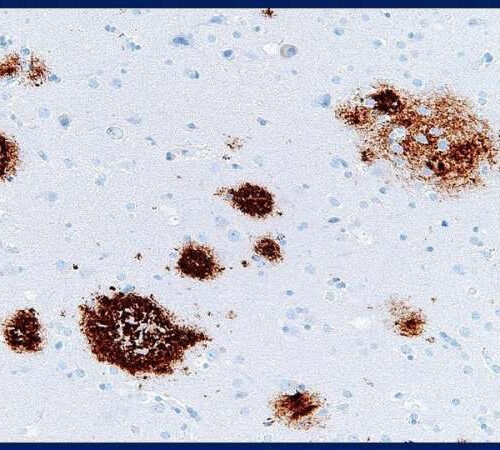
by Michael E. Newman, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Photomicrograph showing amyloid beta-protein (brown from staining) in tissue taken from a human brain. Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers have shown that the glymphatic system — the vascular network that removes waste from the central nervous system — helps clear amyloid beta from the brain and that...
Tag: <span>Alzheimer’s disease</span>
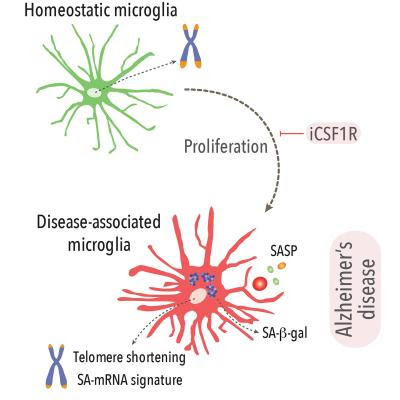
Scientists discover immune cell behavior that plays a key role in Alzheimer’s disease
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON IMAGE: GRAPHICAL DEPICTION. CREDIT: DIEGO GOMEZ-NICOLA / CELL REPORTS A new study has pinpointed a small group of cells in the brain which could be crucial to understanding how Alzheimer’s disease begins and how to slow its progression. This discovery could help research into treatment for the disease by focusing on this key group of...
Association between blood plasma lipids and risk of Alzheimer’s disease
by CHeBA Credit: CC0 Public Domain Latest research from UNSW Sydney’s Center for Healthy Brain Aging (CHeBA) has uncovered new insight into the underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease. The findings, published in Translational Psychiatry, examined differences between the plasma lipidome of people with Alzheimer’s disease and ‘healthy’ individuals of the same age from CHeBA’s Sydney Memory and Aging...
Secondary infections inflame the brain, worsening cognition in Alzheimer’s disease
TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN New research into Alzheimer’s disease (AD) suggests that secondary infections and new inflammatory events amplify the brain’s immune response and affect memory in mice and in humans – even when these secondary events occur outside the brain. Scientists believe that key brain cells (astrocytes and microglia) are already in an active state...
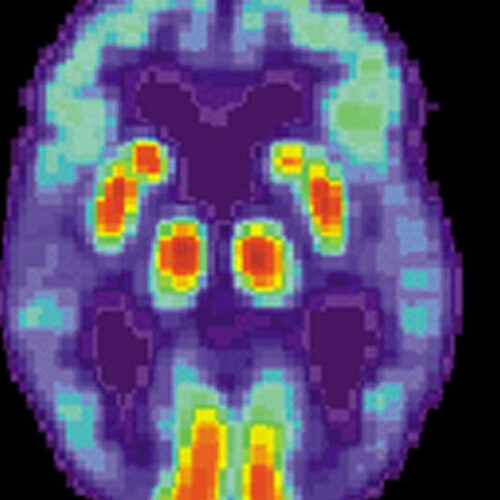
Role of sleep-related brain activity in clearing toxic proteins and preventing Alzheimer’s disease
by Public Library of Science PET scan of a human brain with Alzheimer’s disease. Credit: public domain Evidence of sleep-dependent low-frequency (<0.1 Hz) global brain activity in the clearance of Alzheimer’s disease-related toxin buildup is presented in research published on 1st June 2021 in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Xiao Liu and colleagues at The Pennsylvania State University....
Researchers discover link between local oxygen depletion in the brain and Alzheimer’s disease
by University of Seville Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain The study, published in the journal Nature Aging and led by the laboratories of Dr. Alberto Pascual (CSIC), from the Neuronal Maintenance Mechanisms Group, and Prof. Javier Vitorica (University of Seville/CIBERNED) of the Physiopathology of Alzheimer’s Disease Group at IBiS, demonstrates for the first time that low oxygen levels in...
Treatment for Alzheimer’s disease found effective in preventing inflammation in orthopedic implants
Dental and orthopedic implants are widely used around the world. Common causes for implant failure are the immune response against oral bacteria and titanium particles shed by the implant. These and other phenomena can generate an inflammatory response, activating the osteoclasts (bone resorbing cells), and ultimately leading to osteolysis (destruction of bone tissue) around the...
Retinal scans tie blood vessel deterioration to genetic marker for Alzheimer’s disease
by Robin Marks, University of California, San Francisco Credit: CC0 Public Domain While it has been said that the eyes are a window to the soul, a new study shows they could be a means for understanding diseases of the brain. According to new research by scientists at the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, retinal scans can detect...
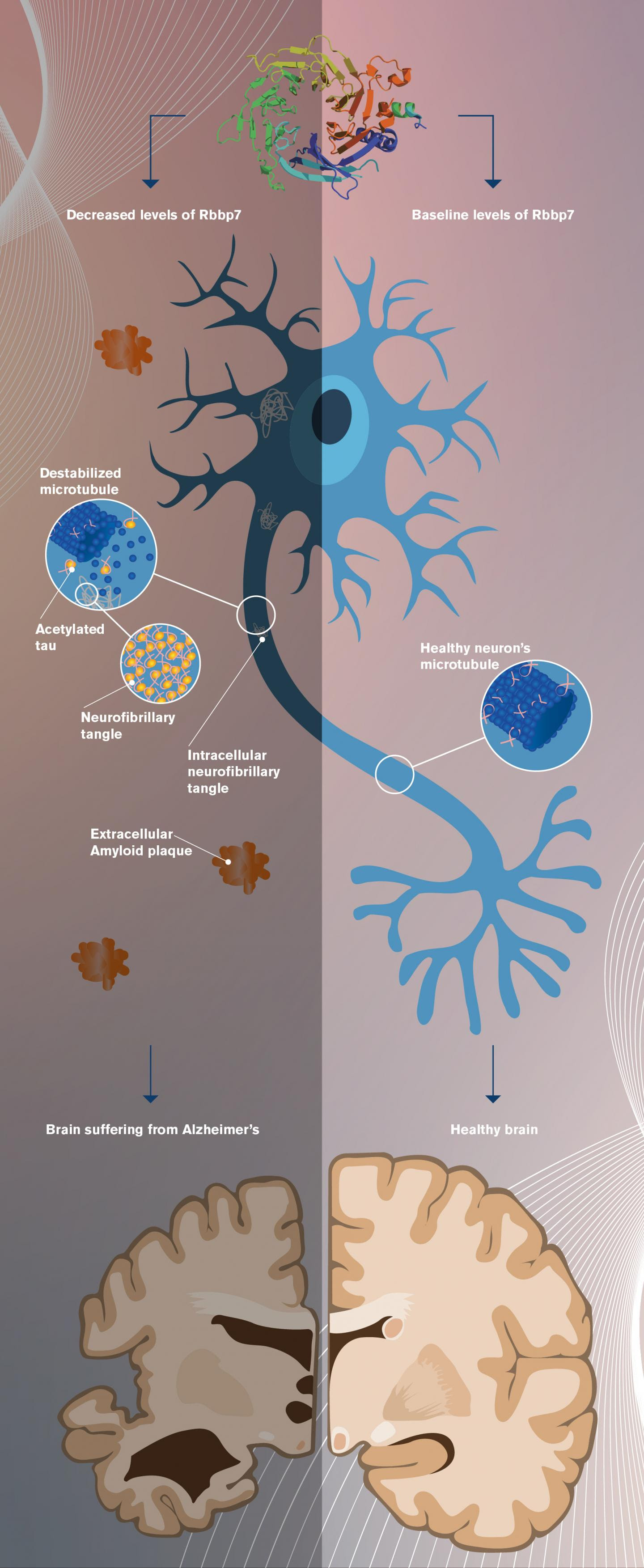
Untangling the brain: new research offers hope for Alzheimer’s disease
ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY IMAGE: The image shows the development of neurodegenerative pathology resulting from low levels of the protein Rbbp7 (on the left), compared with normal levels associated with a healthy brain (on the right). Graphic by Shireen Dooling for the Biodesign Institute. CREDIT: SHIREEN DOOLING FOR THE BIODESIGN INSTITUTE AT ASU Since the discovery...
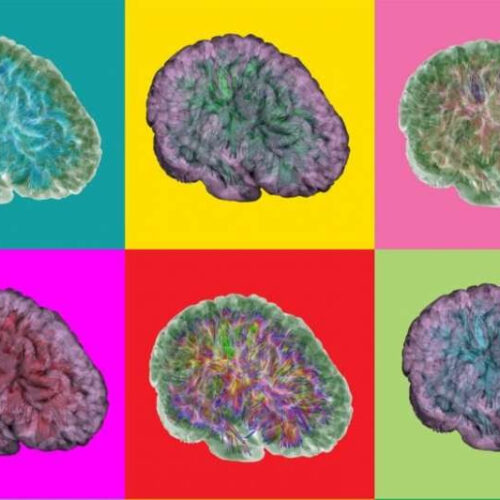
Brain changes following traumatic brain injury share similarities with Alzheimer’s disease
by Jenesse Miller, University of Southern California The image displays a TBI-affected brain’s white matter connectivity as inferred using diffusion tensor imaging and streamline tractography. The brain surface is rendered as a translucent layer to provide anatomical context for the streamline display. White matter connections and the brain surface are displayed using different colors across for...