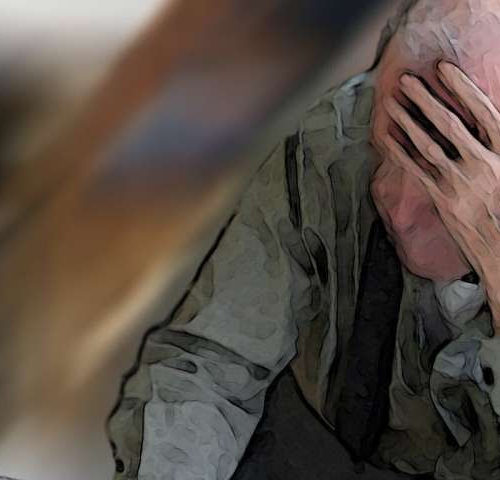
by University of Leeds The blood flow in the surface blood vessels of a mouse that was not treated with M-3. Drugs that were developed to treat Alzheimer’s Disease could be re-purposed to prevent—or even reverse—the damage done to the blood vessels in people who are obese or suffer from type 2 diabetes, according to...
Tag: <span>Alzheimer’s disease</span>
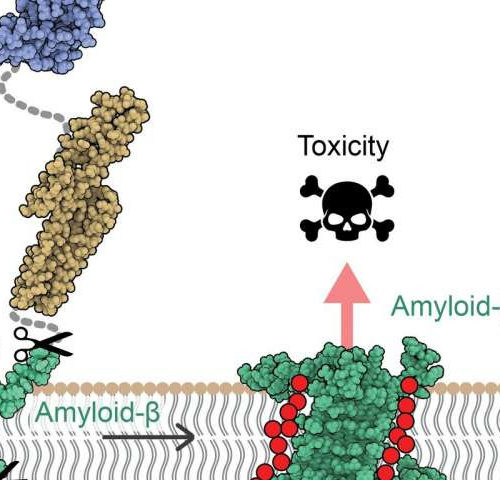
A new mechanism of toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease revealed by the 3-D structure of protein
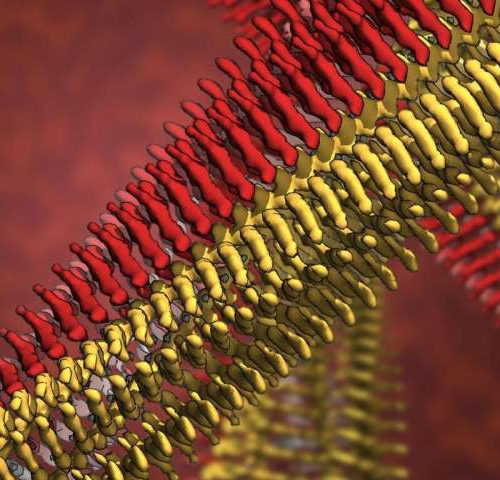
by Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) The amyloid precursor protein (APP) is inserted into the cell membrane of neurons. After sequential cleavage by β- and ?-secretases, the Aβ protein (in green) is released.The membrane oligomers are formed by 4 or 8 copies of the Aβ protein. The physicochemical properties of the edges of...
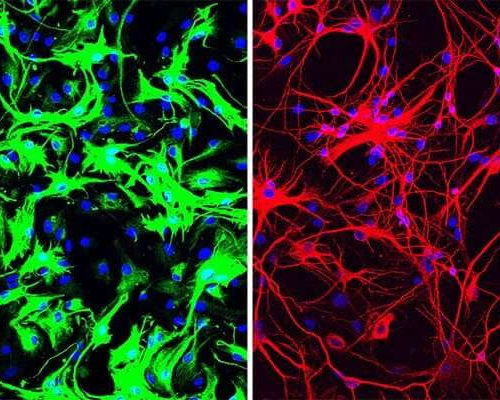
It’s not just Alzheimer’s disease: Research highlights form of dementia
by University of Kentucky The long-running study on aging and brain health at the University of Kentucky’s Sanders-Brown Center on Aging Alzheimer’s Disease Center has once again resulted in important new findings—highlighting a complex and under-recognized form of dementia. The work was recently published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA): Neurology. “One...
One-time treatment generates new neurons, eliminates Parkinson’s disease in mice
by University of California – San Diego Xiang-Dong Fu, Ph.D., has never been more excited about something in his entire career. He has long studied the basic biology of RNA, a genetic cousin of DNA, and the proteins that bind it. But a single discovery has launched Fu into a completely new field: neuroscience. For...
Repeated head impacts associated with later-life depression symptoms, worse cognitive function
by Boston University School of Medicine Scientists have long believed that a single traumatic brain injury (TBI) earlier in life may contribute to problems with memory, thinking and depression later in life. In most previous studies, however, research failed to examine the possible role of having a history of exposure to repetitive head impacts, including...
How ApoE4 endangers the brain
by Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is kind of like a delivery service for the human brain. It supplies neurons with important nutrients, including with polyunsaturated fatty acids—which are building blocks of the membranes surrounding the neurons. In addition, certain unsaturated fatty acids are converted into so-called endocannabinoids. These are endogenous...
Study finds protein in mitochondria appears to regulate health and longevity
by University of Southern California A new study led by researchers at the USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology is the first to demonstrate that a tiny protein has a big impact on health and longevity in both animals and humans. The researchers examined humanin, a peptide encoded in the small genome of mitochondria—the powerhouses...
Different ‘subtypes’ of Alzheimer’s may be linked to different modifications of the tau protein
by Massachusetts General Hospital A new study reveals a possible biological reason that Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) progresses at different rates in different patients. The study, which was led by Massachusetts General Hospital researchers, focused on tau, a protein found in the neurofibrillary tangles in the brain that are a well-known sign of AD. Tau can...
New indication of a link between Alzheimer’s and diabetes
by Forschungszentrum Juelich Pathological protein clumps are characteristic of a series of diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and type 2 diabetes. Scientists at Forschungszentrum Jülich, Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, and Maastricht University have now used cryo-electron microscopy to obtain a sharp image for the first time of how individual molecules are arranged in...
Memory impairment in mice reduced by soy derivate that can enter the brain intact
Ingestion of the protein fragment improved working and long-term memory in mice treated to simulate Alzheimer’s disease KYUSHU UNIVERSITY In a study that could help one day give a literal meaning to food for thought, researchers from Kyushu University in Japan have reported that a protein fragment that makes its way into the brain after...