U.S. ARMY RESEARCH LABORATORY IMAGE: ARMY-FUNDED RESEARCHERS FINDS THAT SOLDIERS’ INCREASED RISK OF DEVELOPING ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE IS LIKELY ROOTED IN THE ALTERATIONS TO THE TINY CONNECTIONS BETWEEN NEURONS IN THE HIPPOCAMPUS INSTIGATED BY BLAST EXPOSURES CREDIT: UNC PEMBROKE RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. — Research shows that Soldiers exposed to shockwaves from military explosives are at a higher risk for developing...
Tag: <span>Alzheimers</span>
Protein linked to Alzheimer’s, strokes cleared from brain blood vessels
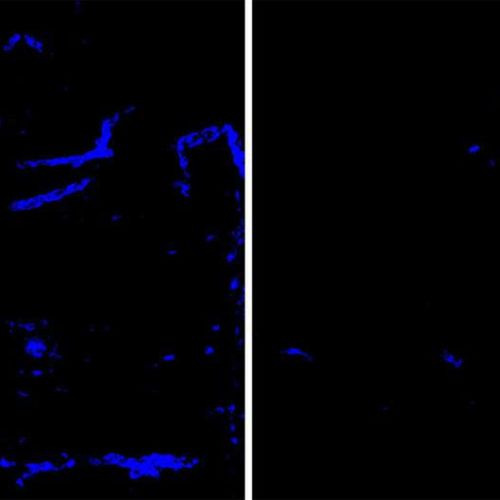
by Washington University School of Medicine Amyloid deposits (blue) in mouse brain tissue and blood vessels are reduced after treatment with an antibody that targets the protein APOE (right), a minor component of amyloid deposits, compared to a placebo antibody (left). Amyloid deposits in the brain increase the risk of dementia and strokes. Researchers at Washington University School...
Mount Sinai researchers identify and characterize 3 molecular subtypes of Alzheimer’s
THE MOUNT SINAI HOSPITAL / MOUNT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE (New York, NY – January 6, 2021) – Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have identified three major molecular subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) using data from RNA sequencing. The study advances our understanding of the mechanisms of AD and could pave the...
Loneliness can help grow parts of brain tied to imagination, study finds
By Ryan Prior, CNN Being lonely is linked to worse health outcomes, but isolation can also stimulate areas of the brain that control creativity, a new study has indicated. (CNN)As many people face the prospect of being alone for the holidays, new science is showing how loneliness might actually help build structures in the brain tied...
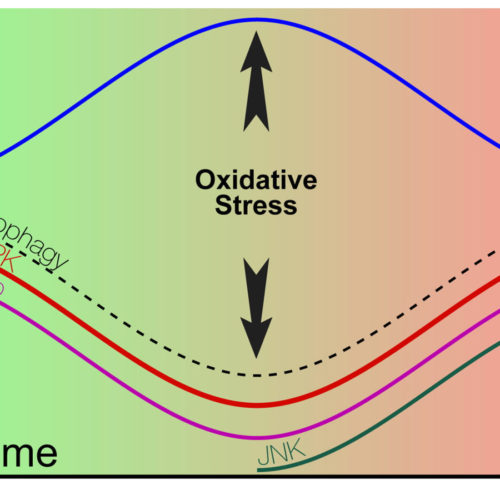
DISEASES LIKE ALZHEIMER’S HAPPEN IN 2 PHASES
The researchers conducted countless experiments over more than a decade, and they’ve summarized all they’ve learned in a simple diagram they hope may change how doctors perceive and treat degenerative diseases as varied as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and muscle atrophy. The study in Molecular Psychiatry proposes that very different activities of protein signaling pathways that regulate basic cell functions mark...
App predicts risk of developing Alzheimer’s
LUND UNIVERSITY A new study from Lund University in Sweden shows that validated biomarkers can reveal an individual’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Using a model that combines the levels of two specific proteins in the blood of those with mild memory impairment, the researchers are able to predict the risk of developing Alzheimer’s. The researchers have also developed...
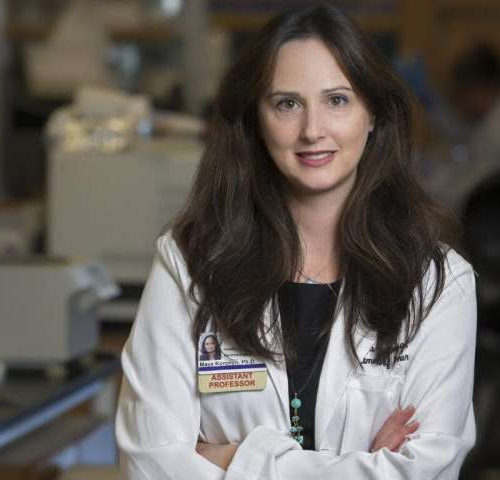
New potential clues in diagnosing, treating Alzheimer’s found in retinas
by Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Maya Koronyo-Hamaoui, PhD, is an associate professor of Neurosurgery and Biomedical Sciences at Cedar-Sinai. A study led by the Cedars-Sinai Department of Neurosurgery has identified certain regions in the retina—the lining found in the back of the eye—that are more affected by Alzheimer’s disease than other areas. The findings may help physicians...
Study offers “indisputable” link between Alzheimer’s and gut microbiome
By Nick Lavars, November 15, 2020 A new study has highlighted the role gut bacteria may play in Alzheimer’s disease, while inflammation may also have a part to play Research into the relationship between the brain and the bacteria in our bellies is uncovering links to an increasing number of neurological conditions, with Alzheimer’s among them....
Alzheimer’s Breakthrough
James Cook University researcher Dr Brandon Mahan worked with a team of French researchers at the Université de Paris, Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris (UP, IPGP; Paris, France) who compared brains with and without Alzheimer’s to discover what made them different. “Our study is the first time it has clearly been shown that healthy human...
USC study reveals one-two punch of symptoms that exacerbate Alzheimer’s
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA A new Alzheimer’s study found that impaired blood flow in the brain is correlated with the buildup of tau tangles, a hallmark indicator of cognitive decline. The work, published this week in the Journal of Neuroscience, suggests that treatments targeting vascular health in the brain — as well as amyloid plaques and tau...