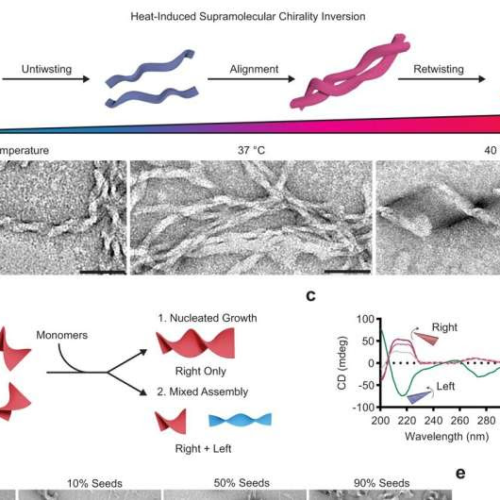
by University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Chirality inversion mechanisms. Scheme and TEM images (a) of Fmoc-FFFF-PEG2 prepared at RT, or heated to 37 and 40 °C to track the chirality inversion (50 nm scale bars). Schematic (b) of seeded growth via right-handed nucleation points. CD spectra (c) of nucleated assemblies grown with varying monomer:seed ratios. TEM...
Tag: <span>Alzheimers</span>
Drug repairs systems that remove Alzheimer’s-causing waste from the brain, study shows
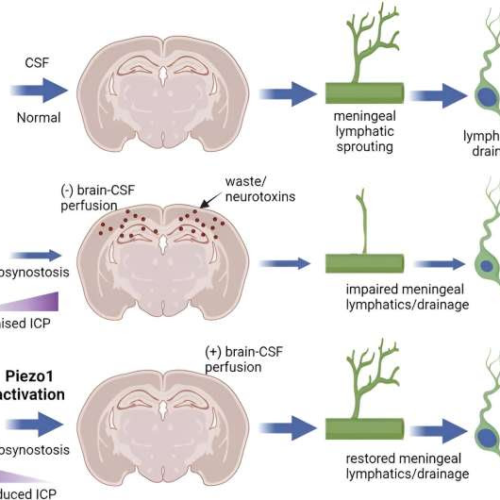
by Andrew Smith, Rutgers University Graphical abstract. Credit: Journal of Clinical Investigation (2023). DOI: 10.1172/JCI171468A team of Rutgers undergraduates has shown that an experimental drug known as Yoda1 may help drain cranial waste plus neurotoxins that cause Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. “The brain’s lymphatic system is one of the hottest research areas in...
Exposure to Agent Orange damages brain tissue in ways similar to Alzheimer’s disease, study reveals
by Brown University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainAgent Orange, an herbicide used during the Vietnam War, is a known toxin with wide-ranging health effects. Even though Agent Orange has not been used for decades, there is increasing interest in its effects on the brain health of aging veterans. A new study by scientists at Brown University reveals...
Alzheimer’s may have once spread from person to person, but the risk of that happening today is incredibly low
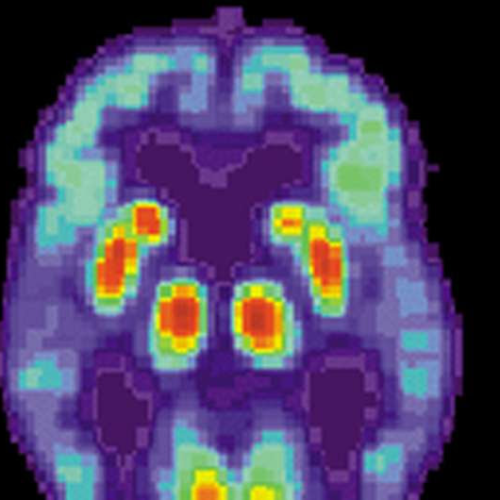
by Steve Macfarlane, The Conversation PET scan of a human brain with Alzheimer’s disease. Credit: public domainAn article published this week in the journal Nature Medicine documents what is believed to be the first evidence that Alzheimer’s disease can be transmitted from person to person. The finding arose from long-term follow up of patients who received...
Tiny particles offer big clues toward predicting Alzheimer’s decades in advance
by Translational Genomics Research Institute Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainIn a study published in the journal, Cells, a team of scientists describe using machine learning models to identify changes in RNA molecules of plasma extracellular vesicles (EVs) that may hold potential for identifying Alzheimer’s disease (AD) at its earliest stages. EVs are tiny particles released by the...
Scientists discover a potential way to repair synapses damaged in Alzheimer’s disease
by Buck Institute for Research on Aging The art depicts the recovery of the functional plasticity at synapses on neurons despite tau-induced toxicity in the brain. Credit: Larissa BrownWhile newly approved drugs for Alzheimer’s show some promise for slowing the memory-robbing disease, the current treatments fall far short of being effective at regaining memory. What...
Re-energizing mitochondria to treat Alzheimer’s disease
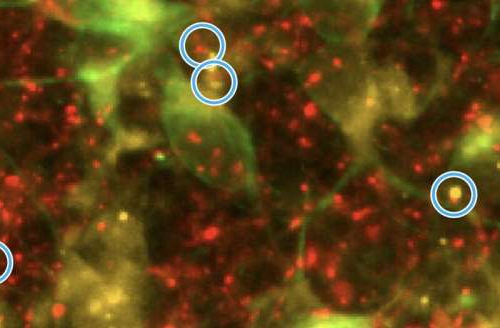
by The Scripps Research Institute Alzheimer’s nerve cells manifest a decrease in the connections between nerve cells, called synapses, shown here within the blue circles. Half the synapse is marked with a red fluorescent stain and the other half with a yellow stain. Credit: Scripps ResearchNerve cells in the brain demand an enormous amount of energy...
Could bizarre visual symptoms be a telltale sign of Alzheimer’s?
by University of California, San Francisco Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public DomainA team of international researchers, led by UC San Francisco, has completed the first large-scale study of posterior cortical atrophy, a baffling constellation of visuospatial symptoms that present as the first symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. These symptoms occur in up to 10% of cases of Alzheimer’s disease....
APOE genetic variants linked to Alzheimer’s disease also associated with the development of subclinical atherosclerosis
by Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III (F.S.P.) Individuals who carry the APOE4 gene variant have an elevated riskof developing subclinical atherosclerosis in middle age, whereas carriers of the variant APOE2 are protected. Credit: CNICScientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) in Madrid have found that one of the most potent genetic...
New blood test that screens for Alzheimer’s may be a step closer to reality, study suggests
CNN Testing a person’s blood for a type of protein called phosphorylated tau, or p-tau, could be used to screen for Alzheimer’s disease with “high accuracy,” even before symptoms begin to show, a new study suggests. The study involved testing blood for a key biomarker of Alzheimer’s called p-tau217, which increases at the same time...