Past studies have shown that intermittent fasting and living a physically active lifestyle may be able to slow age-related cognitive decline, which is a natural part of aging. New research has found that exercise, particularly short bursts of high intensity exercise can increase the amount of neuroprotective brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the body. The...
Tag: <span>Alzheimers</span>
Is Stem-Cell Therapy the Ultimate Treatment for Brain Diseases like Alzheimer’s and Autism?
Over the last decade, you have probably heard about stem cell research on the news or online. You are probably wondering what exactly stem cells are and why they are such a popular subject for debate. In recent years, scientists and medical institutions have been studying many ways stem cell therapy can treat various diseases. Notably, in the field...
Hormone replacement therapy could ward off Alzheimer’s among at-risk women
by University of East Anglia Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) could help prevent Alzheimer’s Dementia among women at risk of developing the disease—according to University of East Anglia research. The study shows that HRT use is associated with better memory, cognition and larger brain volumes in later life among women carrying the APOE4...
Some BP Meds Tied to Significantly Lower Risk for Dementia, Alzheimer’s
Pauline Anderson January 10, 2023 Antihypertensive medications that stimulate rather than inhibit type 2 and 4 angiotensin II receptors can lower the rate of dementia among new users of these medications, new research suggests. Results from a cohort study of more than 57,000 older Medicare beneficiaries showed that the initiation of antihypertensives that stimulate the receptors was...
Neuroscientists solve mysteries about leading biomarker for Alzheimer’s
by Josh Barney, University of Virginia The discovery of how tau tangles form in Alzheimer’s brains could lead to treatment breakthroughs. Credit: Emily Faith Morgan, University Communications University of Virginia neuroscientists have revealed how a toxic form of tau protein, notorious for forming tangles in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease and several other...
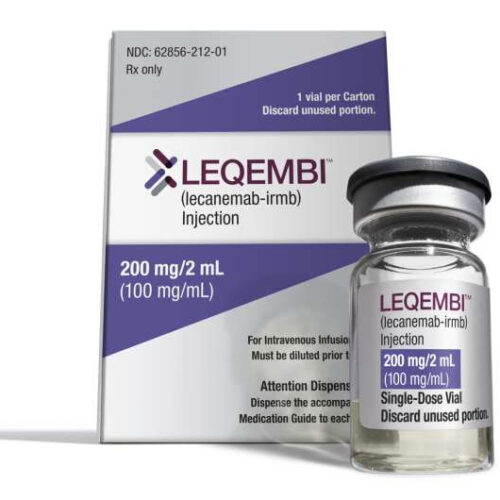
EXPLAINER: New drug slows Alzheimer’s but comes with caveats
by LAURAN NEERGAARD and MATTHEW PERRONE This Dec. 21, 2022 image provided by Eisai in January 2023, shows vials and packaging for their medication Leqembi. On Friday, Jan. 6, 2023, U.S. health officials approved Leqembi, a new Alzheimer’s drug that modestly slows the brain-robbing disease. The Food and Drug Administration granted the approval Friday for patients in the early...
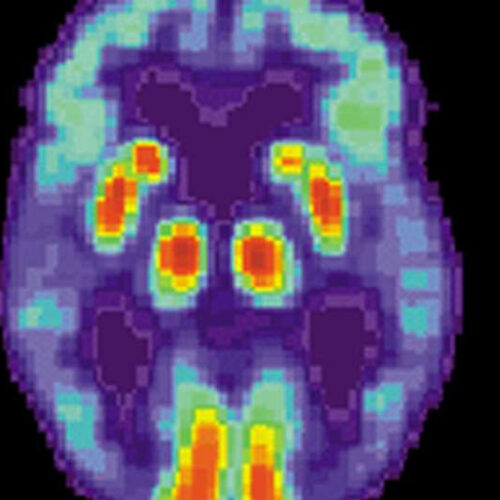
Inflammatory trigger a new clue in Alzheimer’s
by University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio PET scan of a human brain with Alzheimer’s disease. Credit: public domain Scientists from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) today reported that an inflammatory trigger like one present during viral infections is elevated in Alzheimer’s disease...
Why do some people get Alzheimer’s and others don’t? How a new tool checks your risk
by Michelle Marchante, Miami Herald Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Why do some people develop Alzheimer’s disease and others don’t? What makes one person’s brain healthier than another’s? And what can be done to improve, or at least slow, a brain’s deterioration? Researchers at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have developed a new...
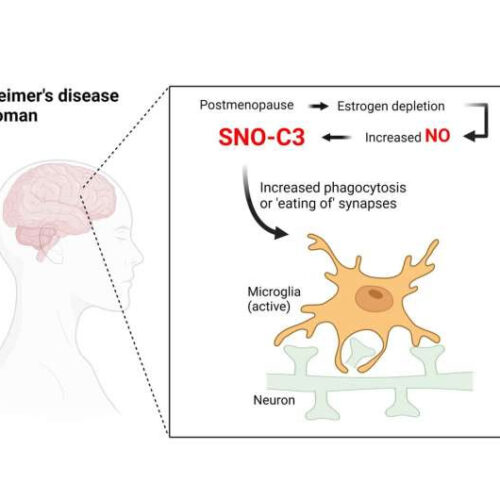
Discovery could explain why women are more likely to get Alzheimer’s
by The Scripps Research Institute In postmenopausal women, depletion of estrogen causes excessive elevation of nitric oxide (NO) in the brain and thus generates S-nitrosylated complement factor C3 (SNO-C3). SNO-C3 triggers activated microglial cells, the innate immune cells in the brain, to phagocytose (or ‘eat’) neuronal synapses—the connections that mediate signaling between nerve cells in...
New immune culprit discovered in Alzheimer’s disease Alzheimer’s
by Northwestern University Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain The reason your three-pound brain doesn’t feel heavy is because it floats in a reservoir of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which flows in and around your brain and spinal cord. This liquid barrier between your brain and skull protects it from a hit to your head and bathes your...