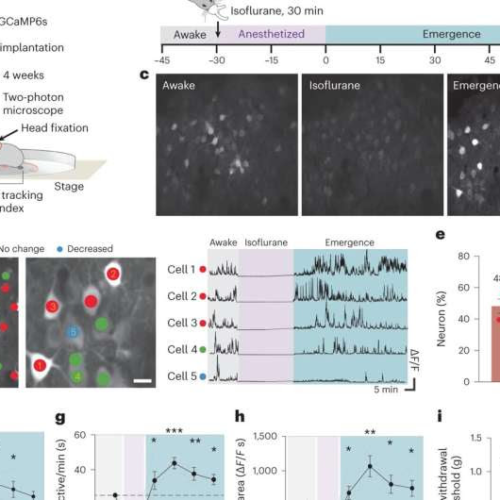
by Alison Satake, Mayo Clinic Neuronal hyperactivity occurs during emergence from general anesthesia. Credit: Nature Neuroscience (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01537-8According to a Mayo Clinic study published in Nature Neuroscience, the cells that act as the central nervous system’s first line of defense against harm also play a role in helping the brain awaken from anesthesia. This discovery...
Tag: <span>anesthesia</span>
Anesthesia blocks sensation by cutting off communication within the cortex
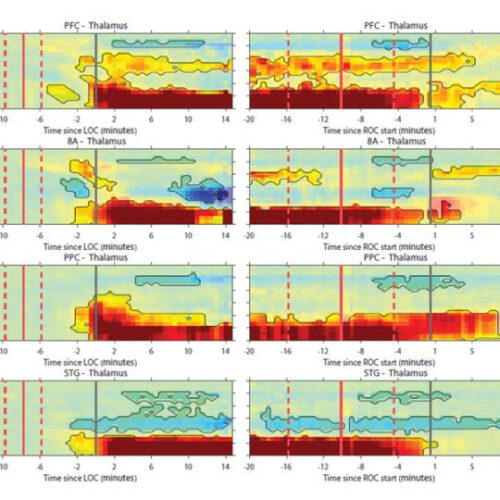
Under propofol general anesthesia, sensory input still reaches the brain, but signals do not spread. Results suggest consciousness requires cortical regions to all be “on the same page”Peer-Reviewed Publication EARL K. MILLER AT THE PICOWER INSTITUTE IN 2022. CREDIT: DAVID ORENSTEIN/MIT PICOWER INSTITUTE General anesthesia evokes a dual mystery: How does it disrupt consciousness, including...
Anesthesia can cause disturbing sexual hallucinations, leading to lasting psychological trauma
by Melody White and C. Michael White, The Conversation Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Some patients can have vivid and detailed sexual hallucinations during anesthesia with sedative-hypnotic drugs like propofol, midazolam, diazepam and nitrous oxide. Some make suggestive or sexual comments or act out, such as grabbing or kissing medical professionals or touching themselves in a sexual way. Others awaken erroneously...
Instability of brain activity during sleep and anesthesia underlies the pathobiology of Alzheimer’s disease
TEL-AVIV UNIVERSITY IMAGE: (LEFT TO RIGHT): PROF. INNA SLUTSKY, DANIEL ZARHIN AND REFAELA ATSMON. CREDIT: DR TAL LAVIV The researchers believe that low-arousal states such as sleep and anesthesia expose failures in a mechanism that regulates stability of brain activity in the early, pre-symptomatic stage of Alzheimer’s disease. This discovery paves the way to early...
Mimicking nature to provide long-lasting local anesthesia
by Children’s Hospital Boston This schematic shows the peptides P1 and P2 with hydrophobic modifications that enable them to self-assemble into nanostructures that bind to tetrodotoxin (TTX). Credit: Tianjiao Ji, PhD, Kohane lab in Nature Biomedical Engineering, Sept. 13, 2021. Site 1 sodium channel blockers such as tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin are small-molecule drugs with powerful local...
Anesthesia doesn’t simply turn off the brain — it changes its rhythms
Simultaneous measurement of neural rhythms and spikes across five brain areas reveals how propofol induces unconsciousness. In a uniquely deep and detailed look at how the commonly used anesthetic propofol causes unconsciousness, a collaboration of labs at the Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT shows that as the drug takes hold in the...
Brain noise contains unique signature of dream sleep
by University of California – Berkeley When we dream, our brains are filled with noisy electrical activity that looks nearly identical to that of the awake brain. But University of California, Berkeley, researchers have pulled a signal out of the noise that uniquely defines dreaming, or REM sleep, potentially making it easier to monitor people...
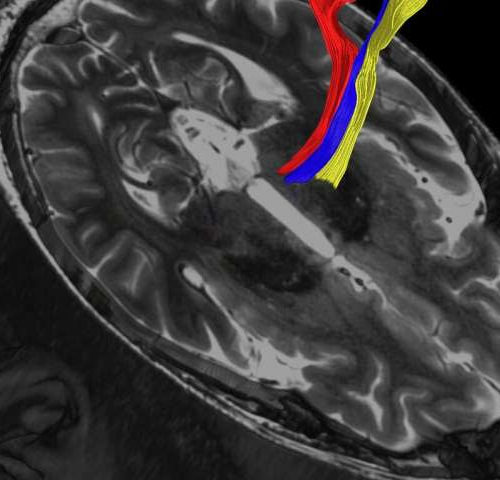
Advanced MRI scans may improve treatment of tremor, Parkinson’s disease
by UT Southwestern Medical Center Diffusion tractography uses the movement of water molecules to identify tracts that connect different parts of the brain. It can be used to pinpoint the part of the thalamus to treat with focused ultrasound. Credit: UT Southwestern Medical Center Recently developed MRI techniques used to more precisely target a small...
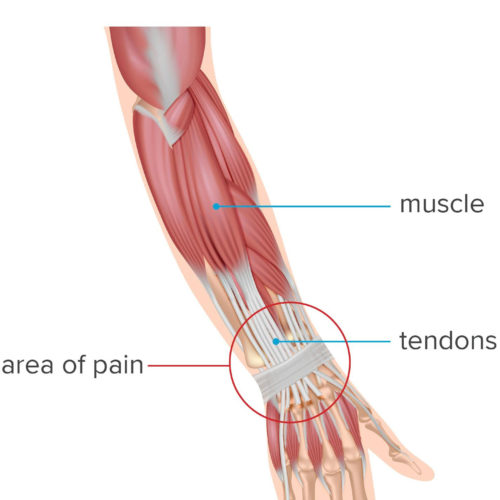
What to know about wrist tendonitis
Wrist tendonitis is the inflammation of a tendon in the wrist. Tendons are thick, fibrous cords that connect muscles to bones. Tendonitis can occur as a result of an injury or repetitive motion that causes the tendon to rub against other bodily tissues, such as bone. A person’s wrist contains many tendons. Together, they allow...
How do we disconnect from the environment during sleep and under anesthesia?
In normal sleep states, sounds fail to penetrate brain regions mediating consciousness and memory, and this natural disconnection is caused by low noradrenaline activity, say Tel Aviv University researchers During sleep and under anesthesia, we rarely respond to such external stimuli as sounds even though our brains remain highly active. Now, a series of new...
- 1
- 2