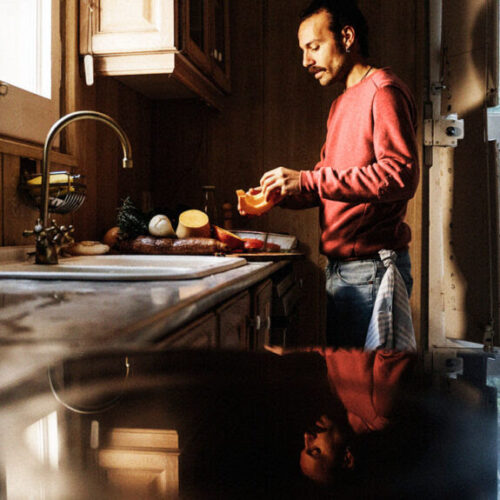
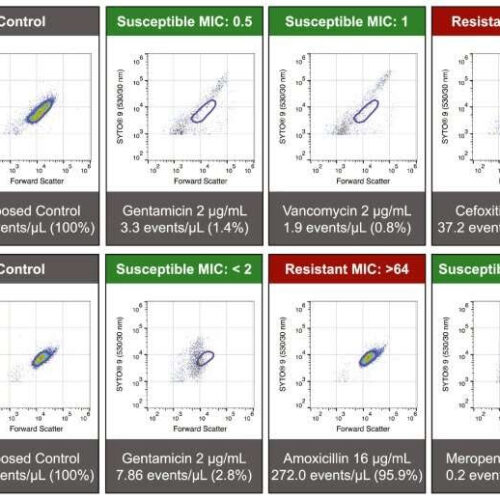
by Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research Susceptibility-associated signatures are associated with antimicrobial effect. When assayed using our FAST protocol, population-level changes in multiparametric distribution can be observed as reproducible patterns of deviation from the antimicrobial unexposed population (bounded in purple). Absence of these patterns can be used to determine a lack of susceptibility (i.e., resistance)...
Tag: <span>antibiotic resistance</span>
Can fiber help gut bacteria fight against antibiotic resistance?
Eating more fiber could be key to having fewer antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the gut. Alba Vitta/Stocksy Fiber is an essential component of a healthy diet, and researchers are still discovering more about its importance. Antibiotic resistance has become a growing issue in recent years, increasing people’s risks for severe illness and limiting treatment options. A...
Diets high in fiber associated with less antibiotic resistance in gut bacteria
by United States Department of Agriculture Credit: CC0 Public Domain Healthy adults who eat a diverse diet with at least 8-10 grams of soluble fiber a day have fewer antibiotic-resistant microbes in their guts, according to a study published by Agricultural Research Service scientists and their colleagues in mBio. Microbes that have resistance to various commonly...
Tiny jumping genes fingered as culprit in rise of antibiotic resistance
DUKE UNIVERSITY DURHAM, N.C. — Biomedical engineers at Duke University believe they have discovered the physical mechanism that causes high doses of antibiotics to promote the spread of antibiotic resistance between bacteria. The culprit, they say, is an overabundance of “jumping genes,” called transposons, that carry the genetic instructions for resistance from the cell’s source...
Study connects shorter course of antibiotics to fewer antibiotic resistance genes
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR MICROBIOLOGY Washington, DC – March 24, 2022 – Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem worldwide that threatens the efficacy of available treatments and can lead to extended hospital stays and increased mortality. Researchers have long sought ways to address the problem. Given that antibiotic use fuels resistance, reducing antibiotic use offers an appealing...
Antibiotic-prescribing algorithm cuts the risk of antibiotic resistance by half
by American Technion Society Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Antibiotics are a double-edged sword: on the one hand, antibiotics are essential to curing bacterial infections. On the other, their use promotes the appearance and proliferation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Using genomic sequencing techniques and machine learning analysis of patient records, the researchers have developed an antibiotic prescribing...
Halting antibiotic resistance is a little less futile
A new experimental platform developed at Rice University promises to speed up the discovery of how infectious bacteria become resistant to antibiotics. The microfluidic application by Rice bioscientist Yousif Shamoo and his team quickly encapsulates bacteria with varying concentrations of antibiotics to analyze how they evolve to become resistant. The details appear in the American Chemical Society journal ACS...
Concerning rates of clarithromycin prescribing for H. pylori, despite increasing antibiotic resistance, uncovered in new Digestive Diseases & Sciences publication
REDHILL BIOPHARMA IMAGE: REDHILL BIOPHARMA CREDIT: REDHILL BIOPHARMA RALEIGH, N.C. and TEL-AVIV, Israel, December 9, 2021, RedHill Biopharma Ltd.(Nasdaq: RDHL) (“RedHill” or the “Company”), a specialty biopharmaceutical company, today announced the publication in the journal Digestive Diseases and Sciences of a new study entitled “Pitfalls of Physician-Directed Treatment of Helicobacter pylori: Results from Two Phase...
With antibiotic resistance, ‘we are running out of options’
UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT ARLINGTON IMAGE: HANNAH BOVERMANN, LEFT, AND JOSEPH BOLL. CREDIT: UTA/RANDY GENTRY Experts predict that without intervention, the problem of multidrug-resistant bacterial infections could be catastrophic by 2050, killing nearly 10 million people each year. To seek solutions, the National Institutes of Health awarded a five-year, $1.8 million grant to Joseph Boll,...
Antibiotic resistance outwitted by supercomputers
by University of Portsmouth Escherichia coli, one of the top three pathogens on World Health Organisation’s target list. Credit: University of Portsmouth Scientists may have made a giant leap in fighting the biggest threat to human health by using supercomputing to keep pace with the impressive ability of diseases to evolve. A new study by...