by Wolters Kluwer Health Reflecting research-driven changes in clinical practice, a revised set of evidence-based recommendations for the medical and surgical treatment of left-sided colonic diverticulitis has been published in Diseases of the Colon & Rectum (DC&R), the official journal of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS). The journal is published by...
Tag: <span>antibiotics</span>
SMART researchers uncover new anti-phage defence mechanisms in bacteria
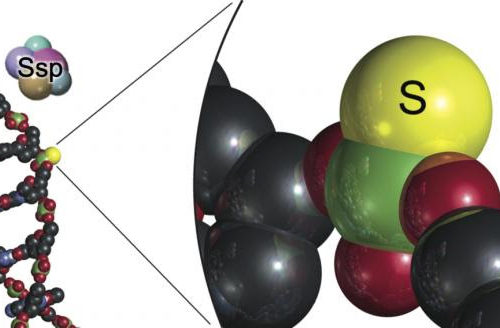
Groundbreaking discovery explains why some bacteria have been able to defend against phage therapy, and opens new ways for the medical community to overcome existing challenges Singapore, 6 May 2020 – Researchers from Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART), MIT’s research enterprise in Singapore, have discovered a new anti-phage defence mechanism found in some...
Peptide weakens superbugs to make old antibiotics effective again
By Michael Irving Viruses may be hogging all the headlines at the moment, but it’s important to remember that bacteria are also a looming threat to public health, as they continue to develop resistance to antibiotics. Now a new study has identified a peptide that can make existing antibiotics more effective at a much lower...
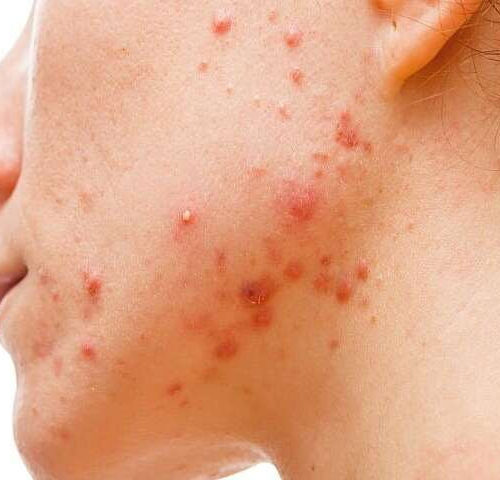
Clascoterone cream safe, effective for acne treatment
Adelaide Hebert, M.D., from the University of Texas Health Science Center in Houston, and colleagues assessed the safety and efficacy of clascoterone cream, 1 percent, a novel topical androgen receptor inhibitor, in two phase 3 clinical trials (including a total 1,440 patients) in which patients were randomly assigned to clascoterone cream, 1 percent, or a...
Study reveals raw-type dog foods as a major source of multidrug-resistant bacteria that could potentially colonize humans
New research due to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID)* reveals that raw-type dog foods contain high levels of multidrug-resistant bacteria, including those resistant to last-line antibiotics. The potential transfer of such bacteria between dogs and humans is an international public health risk, conclude the authors who...
Antibiotics can limit body’s ability to uptake analgesics
by Anne M Stark, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory LLNL biologists have found manipulating the gut microbiome with antibiotics alters the uptake and effectiveness of acetaminophen. The effectiveness of drug treatments can vary widely between individuals, which can lead to decreased efficacy or increased adverse reactions. Much of the variation can be contributed to genetics, but...
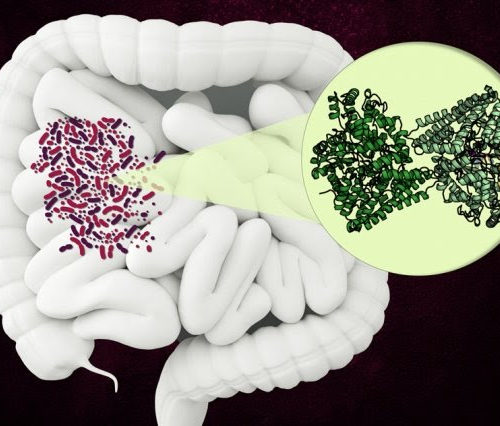
Bacterial enzyme could become a new target for antibiotics
Scientists discover the structure of an enzyme, found in the human gut, that breaks down a component of collagen. MIT and Harvard University chemists have discovered the structure of an unusual bacterial enzyme that can break down an amino acid found in collagen, which is the most abundant protein in the human body. The enzyme,...
Powerful antibiotics discovered using AI
Machine learning spots molecules that work even against ‘untreatable’ strains of bacteria. Jo Marchant A pioneering machine-learning approach has identified powerful new types of antibiotic from a pool of more than 100 million molecules — including one that works against a wide range of bacteria, including tuberculosis and strains considered untreatable. Antibiotic resistance has a...
Quality of life similar after surgery, antibiotics for uncomplicated appendicitis
For patients being treated for uncomplicated acute appendicitis, quality of life (QOL) is similar at seven years after appendectomy or antibiotic therapy, according to a study published online Feb. 19 in JAMA Surgery. Suvi Sippola, M.D., from Turku University Hospital in Finland, and colleagues assessed postintervention QOL and patient satisfaction and treatment preference during follow-up...
Lyme disease treatment: 2 herbal compounds may beat antibiotics
Lyme disease — transmitted via tick bite — affects thousands of people in the United States and around the world. Currently, doctors use antibiotics to treat it, but could plant-based remedies be more effective? Lyme disease is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi (B. burgdorferi). The disease spreads to humans through the...