MAYO CLINIC ROCHESTER, Minn. — In a retrospective case study, Mayo Clinic researchers have found that antibiotics administered to children younger than 2 are associated with several ongoing illnesses or conditions, ranging from allergies to obesity. The findings appear in Mayo Clinic Proceedings. Using health record data from the Rochester Epidemiology Project, a population-based research collaboration...
Tag: <span>antibiotics</span>
Algorithm reduces unnecessary use of antibiotics for UTIs
One paradox about antibiotics is that broadly speaking, the more we use them, the less they continue to work. The Darwinian process of bacteria growing resistant to antibiotics means that, when the drugs don’t work, we can no longer treat infections, leading to groups like the World Health Organization warning about our ability to control major public...
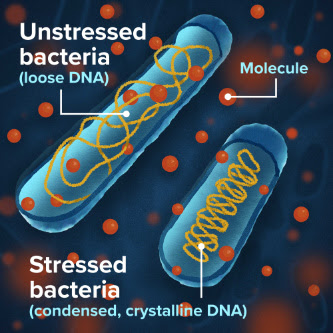
A route to better antibiotics: understanding ‘stressed bacteria’
Doctors often treat ear infections, strep throat, and urinary tract infections with antibiotics that kill the bacteria causing these infections. Sometimes, however, bacteria mount strong responses to stressors such as antibiotics, allowing these “stressed” bacteria to survive. This is especially the case when a person takes multiple antibiotics. Understanding the mechanisms behind bacteria’s responses is...
Making tuberculosis more susceptible to antibiotics
Every living cell is coated with a distinctive array of carbohydrates, which serves as a unique cellular “ID” and helps to manage the cell’s interactions with other cells. MIT chemists have now discovered that changing the length of these carbohydrates can dramatically affect their function. In a study of mycobacteria, the type of bacteria that...
Antibiotics for Flu: Here’s Why Antibiotics Don’t Work
Megan N. Brown, PharmD, RPhMegan N. Brown, PharmD, RPh, is a public health pharmacist with fellowship training in drug information and health communications. Antibiotics are one of the most popular types of infection-fighting drugs out there. But it turns out that we use them more often than needed. According to the Centers for Disease Control...
How antibiotics interact with each other
by University of Cologne It is usually difficult to predict how well drugs will work when they are combined. Sometimes, two antibiotics increase their effect and inhibit the growth of bacteria more efficiently than expected. In other cases, the combined effect is weaker. Since there are many different ways of combining drugs—such as antibiotics—it is...
Are antivitamins the new antibiotics?
Research team from University of Göttingen develops drug approach against bacterial infections UNIVERSITY OF GÖTTINGEN FIRST AUTHOR DR. RABE VON PAPPENHEIM EXAMINES PROTEIN CRYSTALS OF A BACTERIAL ENZYME THAT WAS “POISONED ” WITH AN ANTIVITAMIN. view more CREDIT: LISA-MARIE FUNK Antibiotics are among the most important discoveries of modern medicine and have saved millions of...
Nanoparticles show promise in defeating antibiotic-resistant bacteria, U of T researchers find
A new therapy developed by researchers at the University of Toronto may bring us one step closer to effectively killing deadly drug-resistant superbugs. “The threat posed by pathogens that are increasingly becoming resistant to all known antibiotics is an alarming and pressing health care problem,” says Ruby Sullan, assistant professor in the department of physical...
Breakthrough in using stem cells to treat enteric nervous system disorders
by University of Sheffield Scientists have made a breakthrough in understanding how the enteric nervous system forms, which could pave the way for new treatments for neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s. The findings, published in the journal Stem Cell Reports, pave the way for using stem cells to understand and treat a range of diseases...
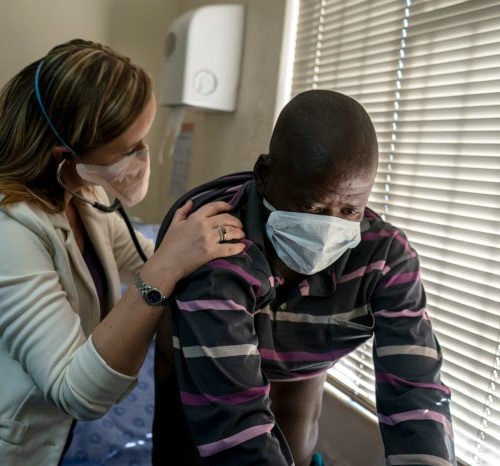
The antibiotic paradox: why companies can’t afford to create life-saving drugs
Paratek Pharmaceuticals successfully brought a new antibiotic to the market. So why is the company’s long-term survival in question? A patient in South Africa battles a strain of tuberculosis that is resistant to multiple antibiotics. Drug resistance is a growing problem with many diseases. Credit: Joao Silva/NYT/Redux/eyevine PDF version As the COVID-19 pandemic caught hold...