Researchers at the University of Alberta have uncovered new information about a cellular mechanism in the immune system that provides a critical step toward better understanding how antibodies evolve and improve in the human body. The antibodies our immune system produces need fine-tuning to reach maximum effectiveness. When a vaccine or pathogen is first introduced into our...
Tag: <span>antibodies</span>
Additional antibodies may protect against COVID
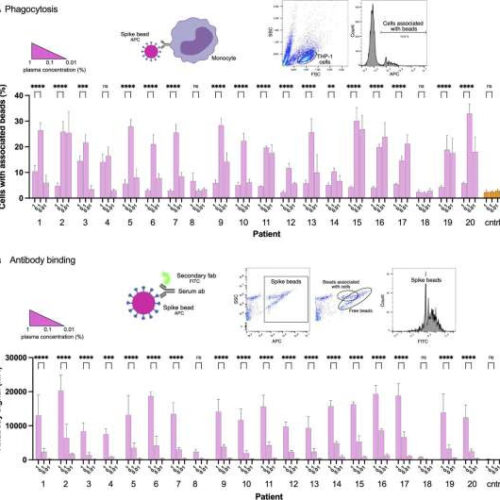
JANUARY 17, 2022 by Lund University Figure 1. Convalescent patient plasma reduces Spike-monocyte interaction. (A) Biotinylated Spike protein was conjugated to fluorescent (APC) streptavidin microspheres and was opsonized with three convalescent patient plasma concentrations (1%, 0.1%, and 0.01%). The beads were then mixed with THP-1 cells at a ratio of 2:1, and the association was measured using...
Scientists identify antibodies that can neutralize omicron
An international team of scientists have identified antibodies that neutralize omicron and other SARS-CoV-2 variants. These antibodies target areas of the virus spike protein that remain essentially unchanged as the viruses mutate. By identifying the targets of these “broadly neutralizing” antibodies on the spike protein, it might be possible to design vaccines and antibody treatments that will...
Unsung gene is key to how antibodies develop
Researchers at the University of Toronto have discovered that an overlooked gene plays a major role in the development of antibodies, which help the immune system recognize and fight viruses including SARS-CoV-2, bacteria, and other causes of infectious disease. The gene – FAM72A – facilitates production of high-quality antibodies by enabling the effect of an enzyme called...
Antibodies mimicking the virus may explain long haul COVID-19, rare vaccine side effects
by Nadine A Yehya, UC Davis Creative rendition of SARS-CoV-2 particles (not to scale). Credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, NIH With around 256 million cases and more than 5 million deaths worldwide, the COVID-19 pandemic has challenged scientists and those in the medical field. Researchers are working to find effective vaccines and therapies,...
COVID-19: The older you are, the more antibodies you have
by University of Montreal A colorized scanning electron micrograph of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Credit: NIAID With the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants worldwide, the pandemic’s spread is accelerating. A research team led by Joelle Pelletier and Jean-François Masson, both professors in Université de Montréal’s Department of Chemistry, wanted to find out whether natural infection or vaccination...
Scientists discover antibodies that may neutralize a range of SARS-CoV-2 variants
Share on Pinterest An antibody called S2E12 could inhibit several respiratory viruses. Sebastian Condrea/Getty Images Researchers have studied a dozen anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies isolated from people who had previously contracted the infection. They looked for antibodies that would not lose their effectiveness to new variants and that would work against a variety of respiratory viruses. They identified...
Rapid and sensitive on-site measurement of antibodies against the COVID-19 virus
IMAGE: THE RESEARCHERS DEVELOPED A CHIP UPON WHICH KEY SARS-COV-2 ARE FIXED. A SMALL DROP OF BLOOD FROM THE FINGERTIP IS NECESSARY, AND THE SENSITIVITY OF THE SYSTEM IS 500 TIMES HIGHER THAN THAT OF CONVENTIONAL METHOD. CREDIT: RIKEN A research team at the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS) in Japan has developed a diagnostic system...
Antibodies block specific viruses that cause arthritis, brain infections
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified two antibodies that protect animals from disease caused by alphaviruses. The antibodies worked for every alphavirus tested, meaning they potentially could form the basis of treatments or serve as a template for a universal vaccine. The findings are published Aug. 19 in the journal Cell....
Creating a female birth control option using antibodies that trap sperm
by Bob Yirka , Medical Xpress Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A team of researchers affiliated with a host of institutions in the U.S. has found that an antibody they created was 99.9% effective at trapping human sperm. In their paper published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, the group describes how they developed their birth control antibodies as...