by University of Alabama at Birmingham Precision medicine in cancer treatment uses genetic changes in the cancer cells to select the best therapies for individual patients. Now researchers led by James Bibb, Ph.D., professor of surgery at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, suggest using a broader lens of post-translational modification analysis to identify new...
Tag: <span>antibodies</span>
Rapid COVID-19 test detects neutralising antibodies with high specificity and sensitivity
by Duke-NUS Medical School As the current COVID-19 pandemic continues to adversely impact communities and economies across the world, efficiency in testing for the infection and antibodies is vital. A unique and rapid SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test (sVNT), developed in Singapore, may be the much-needed boost to current COVID-19 investigations to determine infection rate,...
Virus antibodies fade fast but not necessarily protection
by Marilynn Marchione In this Friday, June 12, 2020 file photo, a woman has blood drawn for COVID-19 antibody testing in Dearborn, Mich. Research published on Tuesday, July 21, 2020 suggests that antibodies the immune system makes to fight the new coronavirus may only last a few months in people with mild illness. (AP Photo/Paul...
Neutralizing antibodies isolated from COVID-19 patients may suppress virus
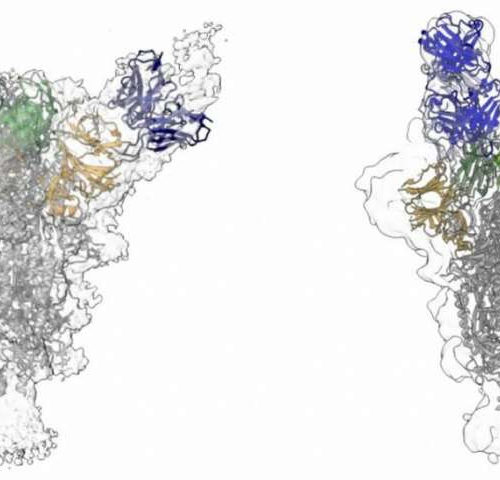
by Columbia University Irving Medical Center Cryo-EM reconstructions show how two different antibodies (blue) bind to the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Credit: David Ho / Columbia University Irving Medical Center Researchers at Columbia University Irving Medical Center have isolated antibodies from several COVID-19 patients that, to date, are among the most potent in...
Surrogate coronavirus may help researchers discover therapies and vaccines
by Albert Einstein College of Medicine To study the potentially lethal coronavirus, Albert Einstein College of Medicine scientists have turned a relatively harmless virus into a coronavirus “surrogate” that is much safer to work with. The research was described this month in Cell Host & Microbe. “Research on the ‘real’ coronavirus is limited by the...
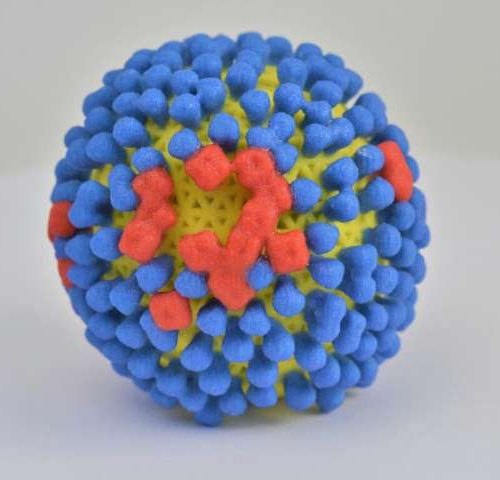
Fast-spreading mutation helps common flu subtype escape immune response
by Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health Strains of a common subtype of influenza virus, H3N2, have almost universally acquired a mutation that effectively blocks antibodies from binding to a key viral protein, according to a study from researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. The results have implications for flu...
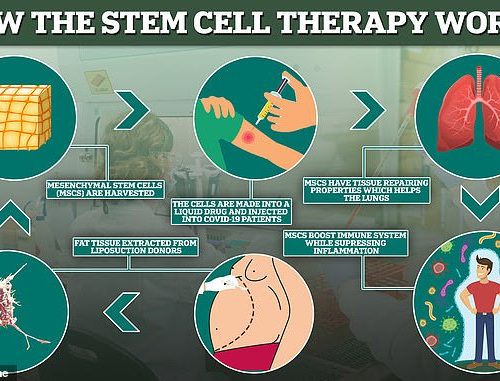
Liposuction treatment hope for coronavirus: Stem cells taken from fat-reduction donors boosts survival rates FIVE-fold for critically-ill patients hooked up to ventilators
Of a small number of patients, 15% died compared with the 85% expected Overall 70% of patients who were on the brink of death saw improvements The researchers admitted they did not expect such positive results The treatment works by injecting patients with cells taken from fat tissue The stem cells are known to bolster...
Antibodies against phosphorylcholine give protection against rheumatic systemic disease
by Karolinska Institutet A novel study from the Institute of Environmental Medicine at Karolinska Institutet indicates that antibodies against a small lipid entity, phosphorylcholine (PC), can be associated with protection in inflammatory systemic diseases, including SLE and Sjögren’s syndrome. The results support evidence for a potential treatment by providing antibodies (anti-PC) to patients with these...
How a mutation on the novel coronavirus has come to dominate the globe
by La Jolla Institute for Immunology Flashback to mid-March: the novel coronavirus had reached San Diego, California. Few people could get tested, and even less was known about how the virus mutated as it spread from person to person. Scientists now know that two variants of the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) were circulating at that time....
Smart structures: Structural cells of the body control immune function
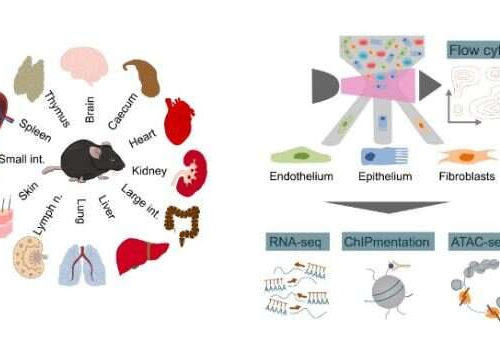
by Austrian Academy of Sciences Schematic outline of the study, which used genomic assays (RNA-seq, ATAC-seq, ChIPmentation, flow cytometry) to investigate epigenetic and transcription regulation in structural cells (endothelium, epithelium and fibroblast) from twelve mouse organs. Credit: Thomas Krausgruber / CeMM In a Nature paper, CeMM researchers report on the epigenetic and transcriptional regulation in...