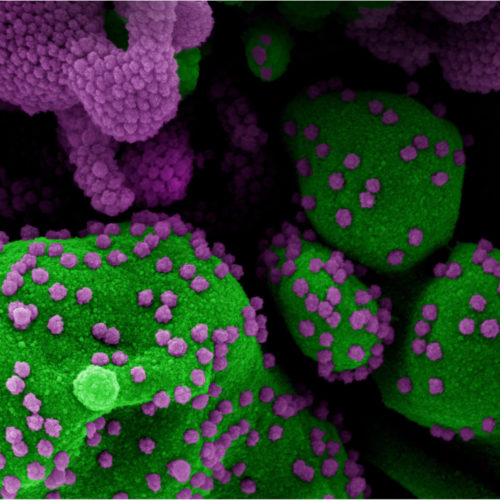
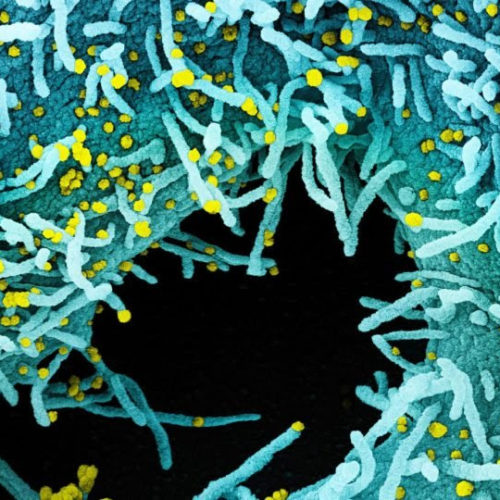
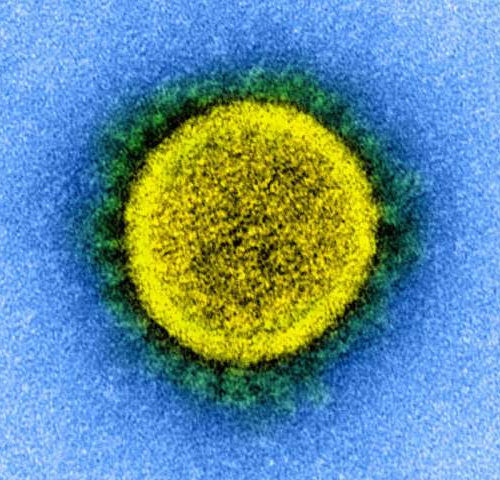
Reviewed by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Antibodies are formed to fight off an infection by neutralizing disease-causing microorganisms. Scientists across the globe are racing to study how antibodies can help suppress the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes the coronavirus disease (COVID-19). A team of researchers at Columbia University Irving Medical...
Tag: <span>Antibody</span>
How neurons reshape inside body fat to boost its calorie-burning capacity
By Dr. Tomislav Meštrović, MD, Ph.D. A new study published on the preprint server medRxiv* by a research group from the U.S. and Germany indicates that a novel BNT162b1 RNA-based vaccine against coronavirus disease (COVID-19) induces functional and proinflammatory T cell responses in almost all participants – marking another landmark achievement for this promising vaccine...
The explosion of new coronavirus tests that could help to end the pandemic
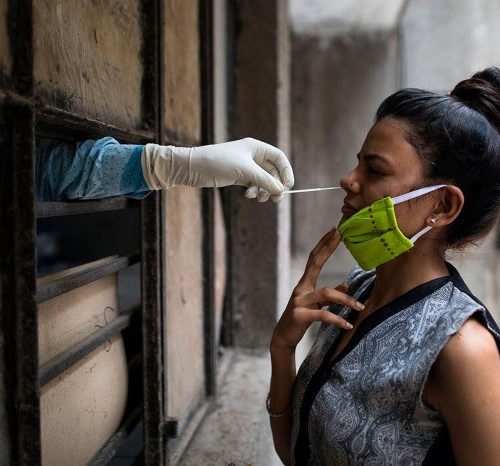
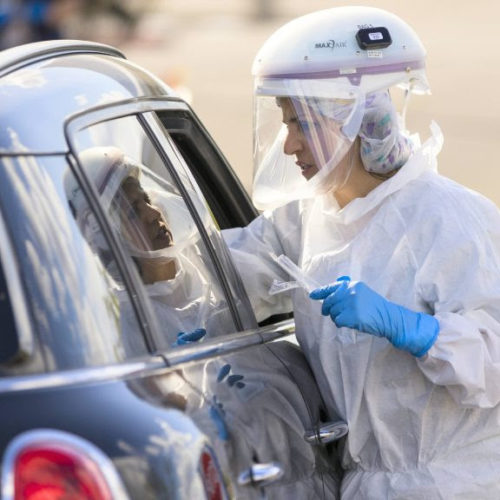
Researchers are scrambling to find other ways to diagnose the coronavirus and churn out millions of tests a week — a key step in returning to normality. The timing couldn’t have been worse. In March, just as Thailand’s coronavirus outbreak began to ramp up, three hospitals in Bangkok announced that they had suspended testing for...
Experimental COVID-19 vaccine safe, generates immune response
An investigational vaccine, mRNA-1273, designed to protect against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), was generally well tolerated and prompted neutralizing antibody activity in healthy adults, according to interim results published online in The New England Journal of Medicine. The ongoing Phase 1 trial is supported by the National Institute of Allergy...
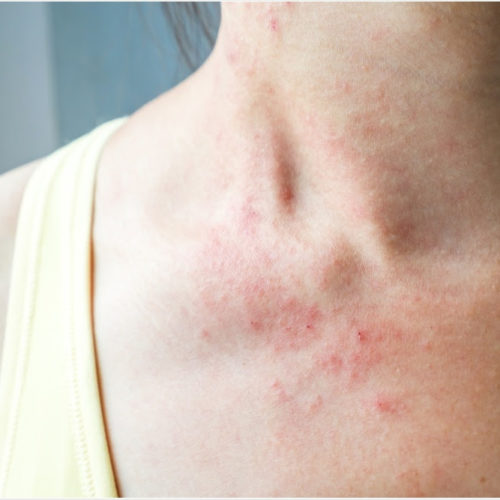
Skin rash may be a symptom of COVID-19
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc. Researchers at King’s College London and Zoe Global Ltd have conducted a study suggesting that skin rashes could be valuable predictors of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). In a large community-based study, 8.8% of people who had tested positive for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) also reported having a skin...
Coronavirus research updates: Antiviral antibodies peter out within weeks after infection
Nature wades through the literature on the new coronavirus — and summarizes key papers as they appear. People who have recovered from COVID-19 are discharged from a hospital in Kolkata, India.Credit: Samir Jana/Hindustan Times via Getty 16 July — Antiviral antibodies peter out within weeks after infection Key antibodies that neutralize the effects of the...
How do COVID-19 antibody tests differ from diagnostic tests?
I’ve heard about new antibody testing for COVID-19. What is antibody testing? Is it the same as testing to diagnose COVID-19? Answer: With all the talk about coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) testing in the news, it’s not surprising that there’s confusion about tests and how they differ. Antibody testing determines whether you had COVID-19 in...
COVID-19 could directly affect the heart
A recent stem cell study has shown that SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus, can infect heart cells via the same receptor present in the lungs. This may be responsible for the cardiac complications associated with COVID-19. New evidence shows how SARS-CoV-2 may affect the heart. Experts initially thought that COVID-19 was a respiratory disease, with symptoms...
Review finds major weaknesses in evidence base for COVID-19 antibody tests
by British Medical Journal Major weaknesses exist in the evidence base for COVID-19 antibody tests, finds a review of the latest research published by The BMJ today. The evidence is particularly weak for point-of-care tests (performed directly with a patient, outside of a laboratory) and does not support their continued use, say the researchers. Serological...
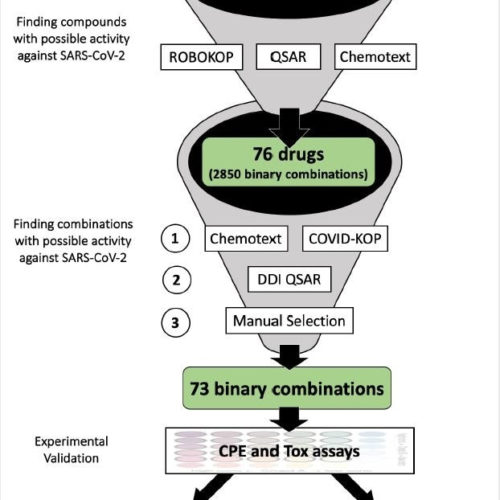
New platform prioritizes synergistic drug combinations against SARS-CoV-2
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc. Researchers in the U.S. have used a new web-based platform to help identify synergistic and antagonistic drug combinations and their underlying mechanisms of action in the context of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The tool, called COVID-KOP, prioritized 73 combinations of 32 drugs as potential treatments for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus...