by Treasure McGuire, The Conversation Credit: Shutterstock In the depths of winter we are more at risk of succumbing to viral respiratory infections—from annoying sore throat, common cold and sinusitis, to the current resurgence of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza and COVID. Symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection range in severity. They can include fever, chills, muscle...
Tag: <span>antidepressant</span>
Antidepressant Medications Might Help Block COVID-19
Jay Croft June 23, 2023 Can common anti-depressants prevent COVID-19 infection? That’s the suggestion of research in BMC Medicine, based on infection trends among more than 5,600 mental health care patients in the United Kingdom from April to December 2020. The report says that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) were particularly effective in blocking COVID-19 transmission....
B-Vitamin May Help Boost Antidepressant Efficacy
Batya Swift Yasgur, MA, LSW June 02, 2023 The B vitamin, L-methylfolate (LMT) can be an effective adjunctive treatment for patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) with an inadequate response to antidepressants, new research suggests. Investigators analyzed six studies and found support for adjunctive use of LMF with patients with MDD not responding to antidepressant monotherapy. Treatment...
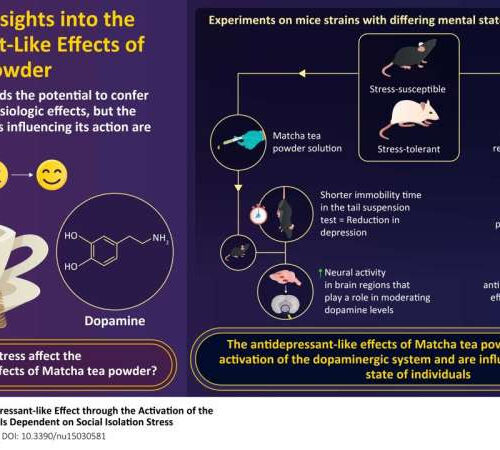
A closer look at Matcha tea powder’s antidepressant-like effects
by Kumamoto University Credit: Kumamoto University Matcha, a traditional Japanese tea, has been touted for its health benefits—it can boost mood and mental performance in humans and mice alike—but more mechanistic research is required. Hence, researchers from Japan evaluated the anti-depressive effects of Matcha tea powder in mice. The powder activates dopaminergic neural circuits and...
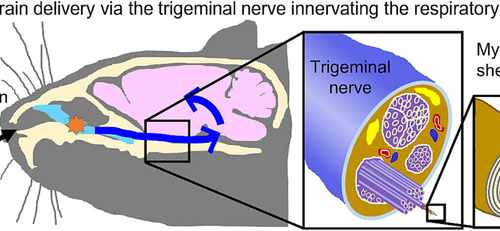
The nose-brain pathway: exploring the role of trigeminal nerves in delivering intranasally administered antidepressant
TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE IMAGE: INTRANASAL ADMINISTRATION OF PAS-CPP-GLP-2 RESULTS IN ITS DELIVERY TO THE BRAIN VIA TRIGEMINAL AXONS OF THE TRIGEMINAL NERVES. THEREFORE, IT IS THOUGHT TO CONSTITUTE A NERVE-ASSOCIATED TRANSCELLULAR PATHWAY FOR DRUG DELIVERY. CREDIT: PROF. CHIKAMASA YAMASHITA FROM TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE Intranasal (in.) administration has been garnering increasing popularity as a...
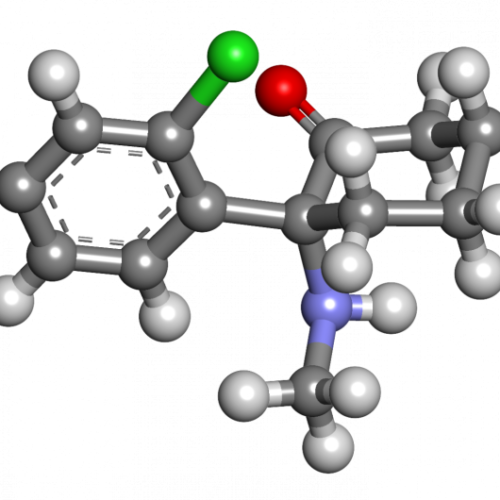
Why ketamine is a speedster antidepressant
by Northwestern University 3-D model of Ketamine. Credit: Wikipedia Ketamine is the speedster of antidepressants, working within hours compared to more common antidepressants that can take several weeks. But ketamine can only be given for a limited amount of time because of its many side effects. Now, a new Northwestern Medicine study identifies for the...
Study sheds new light on a promising antidepressant
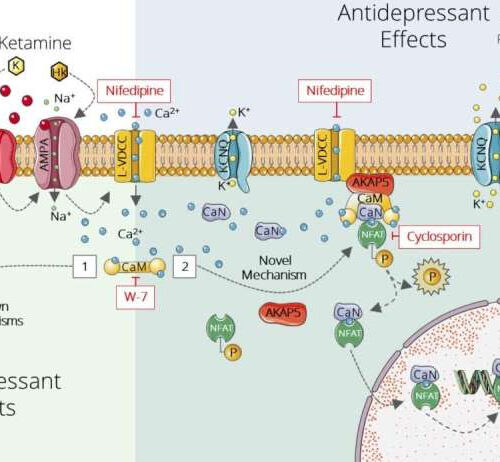
by Weizmann Institute of Science How ketamine works: A schematic representation of ketamine’s newly discovered and previously known mechanisms of action. Ketamine molecules directly inhibit a receptor for the neurotransmitter glutamate (top left), generating a cascade of biochemical reactions that increases the expression of potassium channels (KCNQ) in neurons belonging to the glutamate network in...
How natural remedies can help with antidepressant withdrawal
Antidepressant withdrawal may have associations with antidepressant discontinuation syndrome. Therefore, under the advice of a doctor, a person should reduce or taper their medication gradually. Symptoms of antidepressant withdrawal can include flu-like symptoms and occur within 2–4 days after drug stoppage. Ceasing antidepressant medications without slowly reducingTrusted Source them can lead to a number of symptoms, most of which...
New study helps those with depression pick antidepressant based on health history
by George Mason University Credit: CC0 Public Domain Although antidepressants are one of the most frequently taken medications in the United States (11% of the population takes antidepressants) 60% of depressed patients do not benefit from their first antidepressant. The sales of antidepressants exceed several billion dollars annually. According to a new study published today from...
TOGETHER Trial finds common antidepressant reduced the need for hospitalizations in early treated COVID-19 patients
Vancouver, Canada (26 August 2021) In June 2020, The TOGETHER Trial was established as an adaptive platform randomised clinical trial to test a range of potential treatments for COVID-19 that might be suitable for clinical use in a community setting in Brazil and other low- and middle-income countries. The trial specifically tested each treatment’s potential to prevent clinical worsening of COVID-19 requiring...