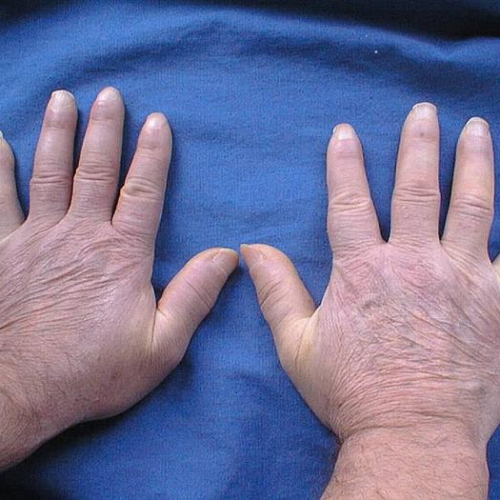
NEWS RELEASE 17-MAY-2024 Study finds the supplement effective in inhibiting fibrosis and suppressing disease activity and progression of systemic sclerosis, an intractable disease Peer-Reviewed PublicationLOUIS PASTEUR CENTER FOR MEDICAL RESEARCH OXIDATIVE STRESS IS KNOWN TO EXACERBATE FIBROSIS AND AUTOIMMUNITY. IN A NEW STUDY, RESEARCHERS FROM JAPAN HAVE INVESTIGATED THE EFFECTS OF A DIETARY ANTIOXIDANT SUPPLEMENT...
Tag: <span>Antioxidant</span>
Study: Antioxidant flavonols linked to slower memory decline
by American Academy of Neurology Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain People who eat or drink more foods with antioxidant flavonols, which are found in several fruits and vegetables as well as tea and wine, may have a slower rate of memory decline, according to a study published in Neurology. “It’s exciting that our study shows making specific diet...
Researchers discover molecule that may be linked to athletic performance
by University of Bergen Carnosine and its precursor beta-alanine increase muscle strength, and have recently become extremely popular as dietary supplements in competitive sports. Researchers at University of Bergen, Norway, have recently discovered an enzyme that forms beta-alanine from the common amino acid aspartic acid. “This contrasts conventional wisdom that most beta-alanine is generated by...
Antioxidant-rich foods like black tea, chocolate, and berries may increase risk for certain cancers, new study finds
by Hebrew University of Jerusalem It is a fact that has long baffled doctors: Cancer in the small intestine is quite rare, whereas colorectal cancer, a neighboring though much smaller organ, is one of the leading causes of cancer death for men and women. What is it about the colon that seems to attract cancer?...
The Aging Gut Microbiome Produces More Trimethylamine, Harming Arterial Function
In recent years academic interest has grown in the study of the gut microbiome. Researchers are making inroads into understanding the considerable influence of these microbial populations over the progression of health and aging. The gut microbiome may be as influential as physical activity in these matters. The balance of microbial populations shifts unfavorably over...
In mouse study, black raspberries show promise for reducing skin inflammation
by Laura Arenschield, The Ohio State University Eating black raspberries might reduce inflammation associated with skin allergies, a new study indicates. In a study done with mice and published earlier this month in the journal Nutrients, researchers found that a diet high in black raspberries reduced inflammation from contact hypersensitivity—a condition that causes redness and...
Fruit fly study reveals link between the gut and death by sleep deprivation
by Harvard Medical School The first signs of insufficient sleep are universally familiar. There’s tiredness and fatigue, difficulty concentrating, perhaps irritability or even tired giggles. Far fewer people have experienced the effects of prolonged sleep deprivation, including disorientation, paranoia and hallucinations. Total, prolonged sleep deprivation, however, can be fatal. While it has been reported in...
Antioxidant nanofiber mats help prevent food spoilage and heal wounds
By Michael Irving Antioxidants are important for fighting the process of oxidation, which can spoil food and alcohol and harm cells in the body. Now, researchers at Texas A&M University have woven antioxidants into nanofiber mats, which release the vital compounds slowly and could be useful for food coverings or bandages. Oxidation is a chemical...
COVID-19: Exercise may protect against deadly complication
by University of Virginia A review by Zhen Yan, Ph.D., of the University of Virginia School of Medicine, showed that medical research findings “strongly support” the possibility that exercise can prevent or at least reduce the severity of ARDS, which affects between 3% and 17% of all patients with COVID-19. Based on available information, the...
IKBFU researchers have discovered another natural antioxidant — alder bark
An alder bark may become a great source of anti-aging and anti-disease natural antioxidants IMMANUEL KANT BALTIC FEDERAL UNIVERSITY An alder bark may become a great source of anti-aging and anti-disease natural antioxidants. That’s the results discovered by the IKBFU’s Institute of Living Systems researchers. For the past 10 years, the workers of the IKBFU’s...
- 1
- 2