by Céline Gravot-Schüppel, Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres Characterization of proliferative white matter astrocytes. Credit: Nature Neuroscience (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-025-01878-6 A research team has identified different subtypes of white matter (WM) astrocytes, including a unique type with the ability to multiply and potentially aid in brain repair. Using single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics, the scientists mapped...
Tag: <span>Astrocytes</span>
Manipulating astrocytes affects long-term memory, researchers discover
by Tohoku University Selective suppression of long-term memory formation through ChR2 photoactivation of amygdala astrocytes. The experiments suggest the presence of parallel processes governing short-term and long-term memory formation, respectively. Credit: Hiroki Yamao, Ko Matsui One of the most powerful assets of the brain is that it can store information as memories, allowing us to learn...
New brain cell cleaner: astrocytes raise possibility of Alzheimer’s disease treatment
Autophagy plasticity in astrocytes enhances the removal of dementia-causing substances and the potential for brain function recovery. Astrocytes, non-neuronal cells, are a new target for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) treatment Peer-Reviewed PublicationNational Research Council of Science & Technology The mechanism of astrocytic autophagy plasticity plays a crucial role in AD. When the autophagy-regulating genes (LC3B and...
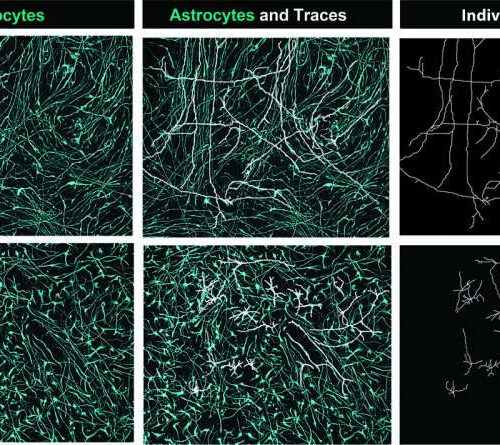
Study identifies ligand-receptor pairs driving the development of astrocytes
by Ingrid Fadelli , Medical Xpress The morphological consequences of the five-ligand cocktail added to cultured human astrocytes. Individual cell traces are highlighted in white and demonstrate the ability of the ligands to induce a more complex and branched astrocyte morphology. Credit: Nature Neuroscience (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01375-8 Astrocytes are a type of glial cell in the central...
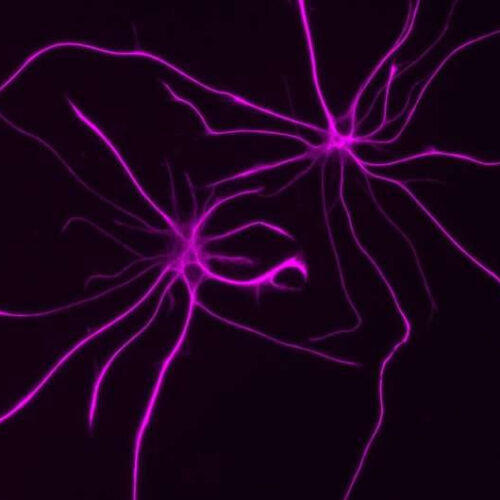
Neuronal activity shapes the development of astrocytes, shows study
by Baylor College of Medicine Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have unraveled the processes that give astrocytes, the most abundant glial cell in the brain, their special bushy shape, which is fundamental for brain function. They report in the journal Nature that neuronal activity is necessary and sufficient for astrocytes to develop their complex shape, and interrupting this...
Astrocytes in the brains of epileptic mice exhibit an acid response with intensified seizures
Reviewed by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Nov 25 2022 Researchers at Tohoku University have shown that astrocytes in the mouse brain exhibit an acid response with intensified epileptic seizures. The astrocytes’ acid response could lead to the amplification of excitatory neuronal signals and be the underlying drive for generating plasticity for epileptogenesis. The findings were detailed...
Beyond neurons: How cells called astrocytes contribute to brain disorders
by Salk Institute Salk researchers studied the molecules produced by astrocytes, like those pictured, to understand how the cells play a role in neurodevelopmental disorders. Credit: Salk Institute Neurons often get most of the credit for keeping our brains sharp and functioning—as well as most of the blame when it comes to brain diseases. But...
Some autism spectrum disorder symptoms linked to astrocytes
by Weill Cornell Medical College A humanized mouse model of autism. The image depicts sections of brain with astrocytes labeled in green. Top row: control astrocytes; Bottom row: astrocytes derived from patients with autism spectrum disorder. Credit: Megan Allen Abnormalities in a type of brain cell called astrocytes may play a pivotal role in causing...
Huntington’s disease: Astrocytes to the rescue !
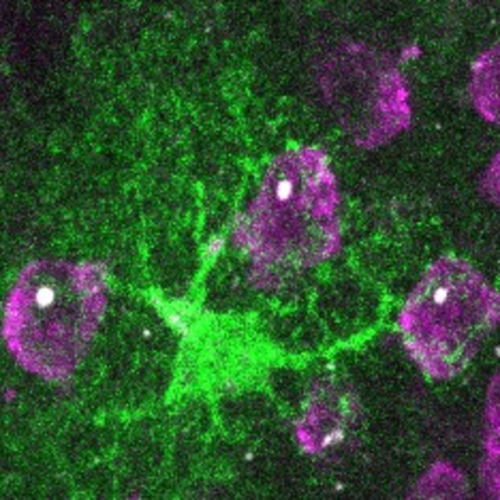
CNRS IMAGE: AN ASTROCYTE (GREEN) IS SURROUNDED BY NEURONS (MAGENTA) EACH CONTAINING AN AGGREGATE OF MUTATED HUNTINGTIN (WHITE). CREDIT: © LAURENE ABJEAN Huntington’s disease1 is caused by a mutation in the Huntingtin gene, a protein necessary for the proper functioning of several brain cells. Mutated, it is no longer able to perform properly: it can even...
In the quest for a TBI therapy, astrocytes may be the bull’s-eye
by Will Sansom, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Growing evidence suggests that traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an important risk factor for developing Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. But to date, effective therapies aren’t available for preventing or treating TBI-induced disease. Scientists may be on to something, though....