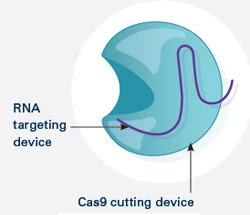
BY ALISA ZAPP MACHALEK You’ve probably heard news stories and other talk about CRISPR. If you’re not a scientist—well, even if you are—it can seem a bit complex. Here’s a brief recap of what it’s all about. In 1987, scientists noticed weird, repeating sequences of DNA in bacteria. In 2002, the abbreviation CRISPR was coined...
Tag: <span>bacterial infections</span>
Bacteria’s secret weapon revealed
Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute (BDI) scientists have discovered a previously unknown method used by bacteria to evade immune responses. The study, published in Nature Microbiology, points to potential new ways of countering bacterial infections, which are becoming increasingly resistant to antibiotics. First author Dr Pankaj Deo said researchers in Dr Thomas Naderer’s laboratory took a...
Antibiotics linked to higher heart disease risk in individuals with type 1 diabetes
Results from a study published in the Journal of Internal Medicine suggest that bacterial infections may elevate the risk of coronary heart disease in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Among 3,781 individuals with type 1 diabetes, 370 developed coronary heart disease over an average follow-up of 13.7 years. Antibiotic purchases, reflecting bacterial infections in outpatient...
‘Good’ virus for common infection
Antibiotic-resistant diabetic foot ulcer application FLINDERS UNIVERSITY Australian researchers have shown how viruses can be used to save lives, developing the potential use of bacteriophages in bandages to treat life-threatening golden staph infections which may not respond to traditional antibiotics. Targeting multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (‘golden staph’) in diabetic foot ulcers, Flinders University microbiology researchers have...
Compounds show promise in search for tuberculosis antibiotics
by John Innes Centre Compounds tested for their potential as antibiotics have demonstrated promising activity against one of the deadliest infectious diseases—tuberculosis (TB). Researchers from the John Innes Centre evaluated two compounds with antibacterial properties, which had been produced by the company Redx Pharma as antibiotic candidates, particularly against TB. TB, which is caused by...
Battle royale: How bacteria fight antibiotics and up the ante in chemical warfare
by Delthia Ricks , Medical Xpress Inadequate development of new antibiotics and rising rates of resistance by bacteria to existing antimicrobials are dual forces pushing the world ever closer to a post-antibiotic era. It has been an 80-year war, the battle pitched by bacteria against the chemical warfare designed to knock out infections—and on multiple...
Phage therapy shows potential for treating prosthetic joint infections
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Bacteriophages, or phages, may play a significant role in treating complex bacterial infections in prosthetic joints, according to new Mayo Clinic research. The findings suggest phage therapy could provide a potential treatment for managing such infections, including those involving antibiotic-resistant microbes. The research is published in the July issue of Clinical Infectious...
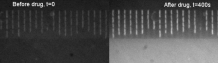
New technique in which drugs make bacteria glow could help fight antibiotic resistance
A new technique could help reduce antibiotic prescribing by predicting which drugs could be effective in fighting bacteria within minutes. Scientists at the University of Exeter have developed the method, which allows users to see whether a bacterium is likely to respond to antibiotics. The research is currently in early stages of development, and the...
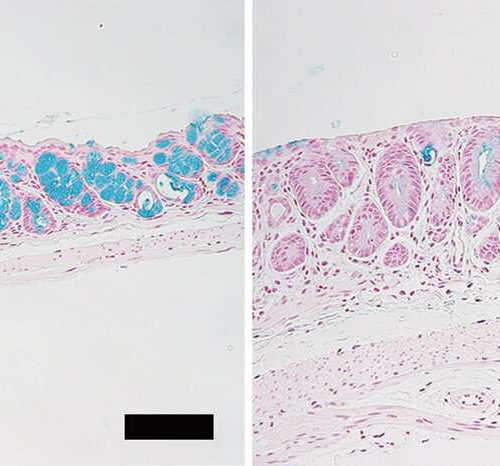
Loss of intestinal goblet cells causes fatal disease after stem cell transplantation
by Hokkaido University In mice large intestine, the goblet cells (blue) are significantly reduced in number after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (right), comparing to a control syngeneic recipients (left). Allogeneic stem cell transplantation can cause a loss of protective goblet cells from the colon’s inner lining, which can be fatal. But boosting those cells beforehand...
New vaccination strategy targets toxic molecules released by all Staphylococcal bacteria
Experiments in mice have shown early success in vaccinating them against potentially deadly bacterial infections, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcal aureus, or MRSA, the strain resistant to most drug treatments. The new vaccination strategy, developed by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, targets toxic molecules released by all Staphylococcal bacteria, called leukocidins, rather than directly...