CREDIT: PHOTO BY JOHAN WINGBORG Certain patients who receive hospital care for coronavirus infection (COVID-19) exhibit clinical and neurochemical signs of brain injury, a University of Gothenburg study shows. In even moderate COVID-19 cases, finding and measuring a blood-based biomarker for brain damage proved to be possible. Some people infected with the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 get...
Tag: <span>biomarkers</span>
GLP-1-based treatment of diabetes does not cause pancreatitis
UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN THE FACULTY OF HEALTH AND MEDICAL SCIENCES About 50,000 Danish diabetic patients are treated with GLP-1-based medicine. GLP-1 is a hormone that reduces the blood sugar and inhibits the appetite, and it is a frequent treatment for type 2 diabetes and obesity. A known side effect of this particular treatment is that...
Blood sample can be used to assess the severity and prognosis of frontotemporal lobar degeneration in the future
by University of Eastern Finland Biomarkers to support the diagnosis of frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and to assess the severity and expected prognosis of the disease are needed. Neurofilament light chain (NfL) measured from a blood sample strongly correlates with the duration of the disease in FTLD patients and the rate of brain atrophy, according...
Simple blood test could one day diagnose motor neurone disease
by University of Sussex Scientists at the University of Sussex have identified a potential pattern within blood which signals the presence of motor neuron disease; a discovery which could significantly improve diagnosis. Currently, it can take up to a year for a patient to be diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis(ALS), more commonly known as motor...
Heralding a new era in protein analytics
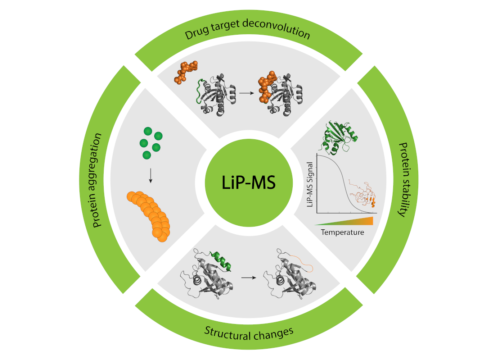
Systems biologist Paola Picotti receives this year’s Rössler Prize for her groundbreaking work in the field of proteomics. She has developed a method of measuring structural changes in thousands of proteins at the same time, paving the way for personalised therapy. The announcement in March 2003 that a human genome had been completely sequenced for...
New evidence for a blood-based biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease
by Massachusetts General Hospital A potential blood-based biomarker for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases seems even more promising thanks to new research from a Massachusetts General Hospital-led study. According to this team’s work, neurofilament light chain (NfL) has great potential as a biomarker for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease and could be also useful for...
Blood test as a potential new weapon in the fight to eliminate malaria
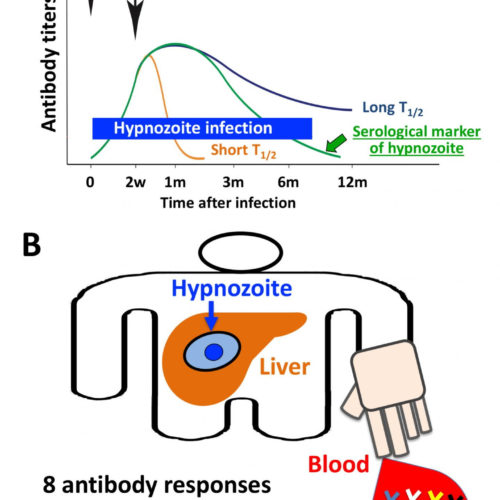
Development and validation of serological markers for detecting recent Plasmodium vivax infection Plasmodium vivax is the most widespread malaria parasite worldwide, with up to two billion people at risk of infection. As well as causing illness and death in its ‘active’ stage of infection, the parasite can hide as hypnozoites, a dormant stage, in the...
New biomarker could flag tumors that are sensitive to common diabetes drug
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (May 19, 2020) — A newly identified biomarker could help scientists pinpoint which cancers are vulnerable to treatment with biguanides, a common class of medications used to control blood sugar in Type 2 diabetes. Biguanides, particularly a medication called metformin, have long been of interest to cancer researchers because of their ability...
Game-changing blood test accurately detects Alzheimer’s disease
A simple blood test that can detect Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has been discovered and validated in a joint effort by a McGill team and researchers in Sweden. Their results are published in the May issue of The Lancet Neurology. An accompanying commentary calls the discovery “transformative.” The blood test accurately measures one of the proteins...
A new biomarker for the aging brain
by RIKEN Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research (BDR) in Japan have identified changes in the aging brain related to blood circulation. Published in the scientific journal Brain, the study found that natural age-related enlargement of the ventricles—a condition called ventriculomegaly—was associated with a lag in blood drainage from a specific deep...